hormones - TeacherWeb
... Triggers kidneys to retain water Can inhibit urine production In large amounts, causes raised blood pressure (vasopressin) ...
... Triggers kidneys to retain water Can inhibit urine production In large amounts, causes raised blood pressure (vasopressin) ...
SChapter9
... -Precise changes in a cell following hormone binding are specific to the hormone and cell, but typically one or more of the following occur: ...
... -Precise changes in a cell following hormone binding are specific to the hormone and cell, but typically one or more of the following occur: ...
BSC597.02W/.CRW: CASE STUDIES IN ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY COURSE SYLLABUS: SPRING 2013 Instructor:
... At the end of this web-based course, the student should be able to sufficiently address each of the following objectives. I have made the list comprehensive since this is a web-based course, and I prefer to have all outcomes in a single document. The student understands the general principles of end ...
... At the end of this web-based course, the student should be able to sufficiently address each of the following objectives. I have made the list comprehensive since this is a web-based course, and I prefer to have all outcomes in a single document. The student understands the general principles of end ...
Question IN BOOK Answers of Oral Contraceptive Case 1. Account
... suggesting the ovaries as the most likely target of dysfunction. Usually, this hormonal pattern, coupled with amenorrhoea, hot flushes of the skin and anxiety, is only seen at the time of the menopause. Question 2: How may this condition arise? The patient is most likely suffering from a premature ...
... suggesting the ovaries as the most likely target of dysfunction. Usually, this hormonal pattern, coupled with amenorrhoea, hot flushes of the skin and anxiety, is only seen at the time of the menopause. Question 2: How may this condition arise? The patient is most likely suffering from a premature ...
presentation source
... hormones, and explain how the hypothalamus regulates their release. 3. list the hormones of the anterior pituitary and explain how their secretion is regulated by the hypothalamus. 4. describe the production and actions of the thyroid hormones and explain how thyroid secretion is regulated. 5. descr ...
... hormones, and explain how the hypothalamus regulates their release. 3. list the hormones of the anterior pituitary and explain how their secretion is regulated by the hypothalamus. 4. describe the production and actions of the thyroid hormones and explain how thyroid secretion is regulated. 5. descr ...
Provocative Tests of the Hypothalamic-Anterior Pituitary
... endogenous Ta and T, released by the hyperactive thyroid gland. This test has occasionally been helpful in subtle forms of hyperthyroidism where conventional studies may be negative, for example in the newly-recognised condition of tri-iodothyronine (Ta) thyrotoxicosis. Quite unexpectedly, HPrl has ...
... endogenous Ta and T, released by the hyperactive thyroid gland. This test has occasionally been helpful in subtle forms of hyperthyroidism where conventional studies may be negative, for example in the newly-recognised condition of tri-iodothyronine (Ta) thyrotoxicosis. Quite unexpectedly, HPrl has ...
Endocrine Emergencies - Department of Library Services
... Patient with Graves disease who has discontinued antithyroid medication OR is previously undiagnosed Hyperpyrexia ( >40 0C ) Sweating Tachycardia with or without AF Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea Tremulousness and delirium, occasionally apathetic ...
... Patient with Graves disease who has discontinued antithyroid medication OR is previously undiagnosed Hyperpyrexia ( >40 0C ) Sweating Tachycardia with or without AF Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea Tremulousness and delirium, occasionally apathetic ...
The Endocrine System
... Homeostasis (the internal salt water balance of body systems) Metabolism (body energy levels) Reproduction Response to stimuli (stress and/or injury) The Endocrine Network The endocrine system completes these tasks through its network of glands, which are small but highly important organs that produ ...
... Homeostasis (the internal salt water balance of body systems) Metabolism (body energy levels) Reproduction Response to stimuli (stress and/or injury) The Endocrine Network The endocrine system completes these tasks through its network of glands, which are small but highly important organs that produ ...
EndocrineSystem
... Heart rate and blood pressure regulation-for physical activity. Blood glucose control Immune system regulations Reproductive functions control ...
... Heart rate and blood pressure regulation-for physical activity. Blood glucose control Immune system regulations Reproductive functions control ...
Iodine_New_Member
... My TSH went up on Iodine – This is a common occurrence when a person starts to take iodine after being deficient. The body increases TSH to stimulate production of thyroglobulin which is used to bind to the iodine in thyroid hormone production. Individuals can have TSH levels as high as 75 for up to ...
... My TSH went up on Iodine – This is a common occurrence when a person starts to take iodine after being deficient. The body increases TSH to stimulate production of thyroglobulin which is used to bind to the iodine in thyroid hormone production. Individuals can have TSH levels as high as 75 for up to ...
These statements have not been evaluated by
... T4 is the primary hormone made by the thyroid gland but It is biologically inactive. In order to create energy & do its job, it needs one of it’s iodine atoms removed to become T3 T4 is a storage hormone it stays in the body for several weeks. T3 is only active for a few days Without enoug ...
... T4 is the primary hormone made by the thyroid gland but It is biologically inactive. In order to create energy & do its job, it needs one of it’s iodine atoms removed to become T3 T4 is a storage hormone it stays in the body for several weeks. T3 is only active for a few days Without enoug ...
Chapters 15, and 16
... The anterior pituitary produces at least six types of hormones. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid; ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex; the gonadotropic hormones FSH and LH stimulate the gonads; prolactin causes mammary glands to produce milk; and growth hormone promotes bone g ...
... The anterior pituitary produces at least six types of hormones. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid; ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex; the gonadotropic hormones FSH and LH stimulate the gonads; prolactin causes mammary glands to produce milk; and growth hormone promotes bone g ...
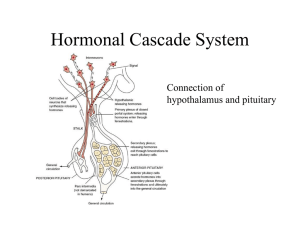
Hormonal Cascade System
... Hormones that Stimulate Synthesis of Steroid Hormones Steroid Hormone ...
... Hormones that Stimulate Synthesis of Steroid Hormones Steroid Hormone ...
Endocrine
... Normal thyroid levels are essential to regulate cellular metabolism, and for normal growth and development. Production of thyroid hormone is caused by release of TSH (stimulated ...
... Normal thyroid levels are essential to regulate cellular metabolism, and for normal growth and development. Production of thyroid hormone is caused by release of TSH (stimulated ...
Contribution of radioiodine uptake measurement and thyroid
... Overt thyrotoxicosis is usually obvious on clinical grounds, biochemical confirmation being based on suppressed serum levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), elevated serum levels of free thyroxine (fT4), and/or free triiodothyronine (fT3). Subclinical thyrotoxicosis is characterized by partial ...
... Overt thyrotoxicosis is usually obvious on clinical grounds, biochemical confirmation being based on suppressed serum levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), elevated serum levels of free thyroxine (fT4), and/or free triiodothyronine (fT3). Subclinical thyrotoxicosis is characterized by partial ...
Goiter and Hypothyroidism in Two Siblings due to Impaired Ca /NAD
... mental development were normal. During adolescence his goiter increased in size. At the time of surgery a large multinodular asymmetrical goiter with a fiber-elastic texture was noted. Thyroid autoantibodies (anti-TPO and anti-Tg) were negative. Two-hour thyroid radioiodine uptake was 63% (normal, 4 ...
... mental development were normal. During adolescence his goiter increased in size. At the time of surgery a large multinodular asymmetrical goiter with a fiber-elastic texture was noted. Thyroid autoantibodies (anti-TPO and anti-Tg) were negative. Two-hour thyroid radioiodine uptake was 63% (normal, 4 ...
Module Specifications Institution: King Abdul
... 1. Strategies for Obtaining Student Feedback on Effectiveness of Teaching Confidential completion of standard course evaluation questionnaire Confidential completion of course objectives’ evaluation questionnaire Frequent meetings of the module committee with 3rd year leaders 2. Other Strategies ...
... 1. Strategies for Obtaining Student Feedback on Effectiveness of Teaching Confidential completion of standard course evaluation questionnaire Confidential completion of course objectives’ evaluation questionnaire Frequent meetings of the module committee with 3rd year leaders 2. Other Strategies ...
Contribution of radioactive iodine uptake and scan to the diagnosis
... Overt thyrotoxicosis is usually obvious on clinical grounds, biochemical confirmation being based on suppressed serum levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), elevated serum levels of free thyroxine (fT4), and/or free triiodothyronine (fT3). Subclinical thyrotoxicosis is characterized by partial ...
... Overt thyrotoxicosis is usually obvious on clinical grounds, biochemical confirmation being based on suppressed serum levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), elevated serum levels of free thyroxine (fT4), and/or free triiodothyronine (fT3). Subclinical thyrotoxicosis is characterized by partial ...
Chapter 7
... luteum formation 3. the feedback control of FSH / LH secretion by ovarian hormones. ...
... luteum formation 3. the feedback control of FSH / LH secretion by ovarian hormones. ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.