* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hormones - TeacherWeb
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
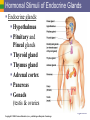
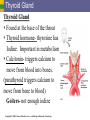
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint® Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Endocrine System Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction Growth and development Mobilization of body defenses Maintenance of much of homeostasis Regulation of metabolism Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Hormone Overview Cells secrete hormones into blood Blood transfers hormones to target sites The hormones regulate activity of other cells Types of hormones: Amino acid-based hormones (proteins) Steroids – made from cholesterol Prostaglandins – made from lipids Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Mechanisms of Hormone Action Hormones affect only certain tissues or organs (target cells or organs) Hormones can trigger cells to produce certain proteins, enzymes, reactions, cell divisions Hormone levels in the blood are maintained by negative feedback: A stimulus or low hormone levels in blood triggers the release of more hormone Hormone release stops once a certain level in the blood is reached Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Hormonal Stimuli of Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands: Hypothalmus Pituitary and Pineal glands Thyroid gland Thymus gland Adrenal cortex Pancreas Gonads (testis & ovaries Figure 9.2a Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Endocrine Pituitary Gland: near hypothalamus of brain Growth Hormone- general metabolism, growth of muscles and bones Prolactin (PRL)- milk production Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)regulates adrenal glands on-top of kidneys Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)- growth & activity of thyroid (Immune System) Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of Other Anterior Pituitary Hormones Pituitary Gland: Gonadotropic hormones Regulate hormonal activity of the gonads Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Stimulates ovaries and sperm development Luteinizing hormone (LH) Triggers ovulation and testosterone production Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Hormones of the Posterior Pituitary Pituitary Gland Oxytocin - stimulates contractions of the uterus during labor, milk ejection Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Triggers kidneys to retain water Can inhibit urine production In large amounts, causes raised blood pressure (vasopressin) Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Thyroid Gland Thyroid Gland Found at the base of the throat Thyroid hormone- thyroxine has Iodine. Important in metabolism. Calcitonin- triggers calcium to move from blood into bones. (parathyroid triggers calcium to move from bone to blood) Goiters- not enough iodine Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Adrenal Glands Adrenal Glands: sits on top of the kidneys Aldosterone- regulates mineral content in blood, water, and electrolyte balance Glucocorticoids (cortisone and cortisol)promote normal cell metabolism Sex hormones- androgens (male) and some estrogen (female) Epinephrine & Norepinephrine- prepare the body to deal with short-term stress Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Pancreatic Islets Pancreas: The islets of the pancreas produce hormones (formerly called islets of langerhans) Insulin – allows glucose to move from blood into cells Glucagon – allows glucose to move from cells into blood These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis Diabetes: issues with insulin hormone Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Pineal and Thymus Glands Pineal Gland: found in brain Melatonin- triggers the body’s wake and sleep cycles Thymus Gland: found under sternum Thymosin- white blood cells, important in developing the immune system Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Ovaries Ovaries Estrogens- stimulates development of secondary female characteristics, female reproductive organs, prepares uterus to receive a fertilized egg, maintains pregnancy, milk production Progesterone - produced by the corpus luteum acts with estrogen to bring about the menstrual cycle, helps in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Hormones of the Testes Testes Androgens- Testosterone is most important androgen. Responsible for male secondary sex characteristics, growth of male reproductive system, sperm production Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings