* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
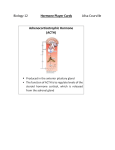
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Gland: Anterior Pituitary Target: Thyroid Gland Function: Stimulates the release of Thyroxin. Gland: Anterior Pituitary Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Human Growth Hormone (hGH) Target: Adrenal Cortex Function: Stimulates the release of stress mitigating hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone. Gland: Anterior Pituitary Target: Body Cells Function: Causes body cells to grow at certain times of life and at others it helps in daily repair. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Gland: Anterior Pituitary Target: Testes and the Ovaries Function: In women it stimulates the release of an egg in the follicle of the ovaries. In men it stimulates the production of sperm. Gland: Anterior Pituitary Lutenizing Hormone (LH) Target: Ovaries and the Testes Function: In women: It promotes ovulation and stimulates the production of estrogen. In men: it stimulates the production of testosterone. Gland: Anterior Pituitary Prolactin Target: Mammary Glands Function: Stimulates the production of milk. Gland: Posterior Pituitary Target: Uterus and Mammary Glands Oxytocin Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Function: In the uterus: causes string contractions or labour cramps In the mammary glands: causes the release of milk from the breasts. Gland: Posterior Pituitary Target: Kidneys Function: Stimulates the reabsorbtion of water from the nephrons back into the blood stream. Gland: Thyroid Thyroxin Target: Body Cells Function: Ups the metabolic rate of body cells. Gland: Thyroid Calcitonin Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Target: Blood Function: Takes excess blood calcium and deposits it in the bones for storage. Gland: parathyroid Target: Bones Function: When blood calcium levels are low it takes stores out of the bones and puts it in the blood. Gland: Beta Cells of the Pancreas Target: Liver, Muscles and Body Cells Insulin Function: Takes excess blood sugar out of the blood stores it in the liver and muscles as glycogen. Also increases cell permeability to glucose. Gland: Alpha Cells of the Pancreas Target: Liver, Muscles and Body Cells Glucagon Function: When blood sugar levels are low, it breaks down glycogen in the liver and muscles and releases it into the blood as glucose. Also decreases cell permeability to glucose. Gland: Delta Cells of the Pancreas Target: Blood Somatostatin Function: Cancels out all insulin and glucagon circulating in the blood to make sure they’re not working antagonistically. Gland: Adrenal Cortex Target: Body Cells Cortisol Function: Increases breakdown of fats and proteins into glucose to have available for increased cellular respiration. Or if the body’s damaged, the energy goes to the repair site. Gland: Adrenal Cortex Target: Kidneys Aldosterone Adrenaline Function: Stimulates the reabsorbtion of Na+ back into the blood which in turn pulls water with it. This keeps up blood volumes in times of bleeding. Gland: Adrenal Medulla Target: Body Cells Function: Increases the body’s sympathetic response to short term stress. Example: Increased heart rate, high blood pressure, pupil dilation ex. In times of fear Gland: Adrenal Medulla Noradrenaline Target: Body Cells Function: Constricts the arteries causing high blood pressure. Also focuses the memory and fixes attention. In times of anger