Anatomy and Physiology Unit 9 Review Sheet
... The rate at which energy is expended (heat produced) by the body per unit of time under controlled (basal) conditions 12 hours after a meal, at rest. Thyroid hormone (TH) 11. What is goiter? A benign enlargement of the thyroid gland that is caused by deficiency of iodine. 12. Explain the differences ...
... The rate at which energy is expended (heat produced) by the body per unit of time under controlled (basal) conditions 12 hours after a meal, at rest. Thyroid hormone (TH) 11. What is goiter? A benign enlargement of the thyroid gland that is caused by deficiency of iodine. 12. Explain the differences ...
Clinical and epidemiological studies on thyroid function Roos
... TSH concentration higher than 1.53 mIU/L (approximately defining the lower level of the top quartile) predicted thyroid dysfunction; 21 out of 406 euthyroid subjects developed a serum TSH above the normal reference range. No development of overt thyroid dysfunction was found in 293 patients with bas ...
... TSH concentration higher than 1.53 mIU/L (approximately defining the lower level of the top quartile) predicted thyroid dysfunction; 21 out of 406 euthyroid subjects developed a serum TSH above the normal reference range. No development of overt thyroid dysfunction was found in 293 patients with bas ...
Testing overview for canine thyroid disorder
... The only way that true progress can be made in the diagnosis of canine thyroid disorder is when the veterinary community realizes that serum T4 alone is not a reliable method of initial screening, as there are many circumstances in which it can provide misleading results. T4 can over diagnose hypoth ...
... The only way that true progress can be made in the diagnosis of canine thyroid disorder is when the veterinary community realizes that serum T4 alone is not a reliable method of initial screening, as there are many circumstances in which it can provide misleading results. T4 can over diagnose hypoth ...
chapt11_lecture
... 1. Found atop the kidneys 2. Consist of an outer adrenal cortex and an inner adrenal medulla that function as separate glands a. The adrenal medulla is neural tissue and secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine in response to sympathetic neural stimulation. b. The adrenal cortex is glandular epitheli ...
... 1. Found atop the kidneys 2. Consist of an outer adrenal cortex and an inner adrenal medulla that function as separate glands a. The adrenal medulla is neural tissue and secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine in response to sympathetic neural stimulation. b. The adrenal cortex is glandular epitheli ...
Introduction to Endocrinology Body communicating system 1
... 1-Nural: act locally to central cell function, in which chemical "neurotransmitters" are released at the synaptic junction. 2-Endocrine: in which glands or specialized cells release into blood circulating chemicals "hormones" that influence the function of cells at other location in the body. 3-Neur ...
... 1-Nural: act locally to central cell function, in which chemical "neurotransmitters" are released at the synaptic junction. 2-Endocrine: in which glands or specialized cells release into blood circulating chemicals "hormones" that influence the function of cells at other location in the body. 3-Neur ...
Chapter 9 Outline
... processes, and blood chemistry. Through the use of hormones, the endocrine system maintains balance within the body in a relatively leisurely and profound way. Hormones circulate in the blood until reaching the target organs upon which they are designed to act, bind with the awaiting cells, and imme ...
... processes, and blood chemistry. Through the use of hormones, the endocrine system maintains balance within the body in a relatively leisurely and profound way. Hormones circulate in the blood until reaching the target organs upon which they are designed to act, bind with the awaiting cells, and imme ...
HumanEndocrineSystem
... The posterior pituitary gland stores and then releases two hormones that are produced in the hypothalamus of the brain. The first hormone is antidiuretic hormone (ADH). This hormone stimulates water reabsorption in the kidneys. It is also called vasopressin. The second hormone is oxytocin, which sti ...
... The posterior pituitary gland stores and then releases two hormones that are produced in the hypothalamus of the brain. The first hormone is antidiuretic hormone (ADH). This hormone stimulates water reabsorption in the kidneys. It is also called vasopressin. The second hormone is oxytocin, which sti ...
Pathology Ch24 - Endocrine System - pp1073-1137
... Most commonly due to hyperthyroidism Also can be due to thyroiditis or extrathyroidal source of T3/T4 o Primary hyperthyroidism = Diffuse hyperplasia (Graves), hyperfunctioning multinodular goiter or adenoma, iodineinduced hyperthyroidism, neonatal thyrotoxicosis associated w/ maternal Graves di ...
... Most commonly due to hyperthyroidism Also can be due to thyroiditis or extrathyroidal source of T3/T4 o Primary hyperthyroidism = Diffuse hyperplasia (Graves), hyperfunctioning multinodular goiter or adenoma, iodineinduced hyperthyroidism, neonatal thyrotoxicosis associated w/ maternal Graves di ...
The Endocrine System
... Thyroid- The thyroid is located in the front of the lower neck, and is often compared to a butterfly given its unique shape. This gland produces hormones that stimulate the metabolism, which controls how fast the body breaks down food and used this fuel to create energy. The more of this chemical is ...
... Thyroid- The thyroid is located in the front of the lower neck, and is often compared to a butterfly given its unique shape. This gland produces hormones that stimulate the metabolism, which controls how fast the body breaks down food and used this fuel to create energy. The more of this chemical is ...
The Endocrine System
... converted to heat / energy Needed for normal tissue growth and development, especially reproductive and nervous ...
... converted to heat / energy Needed for normal tissue growth and development, especially reproductive and nervous ...
Title The effect of thyroid hormone on bone metabolism and
... range has been showed to be associated with a small decrement in vertebral and femoral bone density in both pre- and postmenopausal women.23 Bone loss in the hip and wrists was also observed in premenopausal women on physiologic dosage of T4 replacement therapy, with the degree of bone loss at the f ...
... range has been showed to be associated with a small decrement in vertebral and femoral bone density in both pre- and postmenopausal women.23 Bone loss in the hip and wrists was also observed in premenopausal women on physiologic dosage of T4 replacement therapy, with the degree of bone loss at the f ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... study, and the skin lesions have been recorded after a detailed history and clinical examination. Out of 100 patients, 63 patients had skin manifestations. Xerosis (acquired ichthyosis) and diffuse hair loss were the common skin manifestations which were seen in 38.09% and 34.8% of patients respecti ...
... study, and the skin lesions have been recorded after a detailed history and clinical examination. Out of 100 patients, 63 patients had skin manifestations. Xerosis (acquired ichthyosis) and diffuse hair loss were the common skin manifestations which were seen in 38.09% and 34.8% of patients respecti ...
Thyroid Gland
... Iodine is required for synthesis of thyroid hormone Iodine deficiency: thyroid cannot make sufficient hormone and the thyroid gland increases in size in an attempt to produce more thyroid hormone. ...
... Iodine is required for synthesis of thyroid hormone Iodine deficiency: thyroid cannot make sufficient hormone and the thyroid gland increases in size in an attempt to produce more thyroid hormone. ...
Endocrine System Notes
... Amino acid based (except thyroid hormone): Work via plasma membrane receptors and second messengers. The membrane receptors are usually coupled to G proteins which activate when the hormone binds to the rector. (“G-protein coupled receptors”). Know general principles of G protein coupling & 2nd mess ...
... Amino acid based (except thyroid hormone): Work via plasma membrane receptors and second messengers. The membrane receptors are usually coupled to G proteins which activate when the hormone binds to the rector. (“G-protein coupled receptors”). Know general principles of G protein coupling & 2nd mess ...
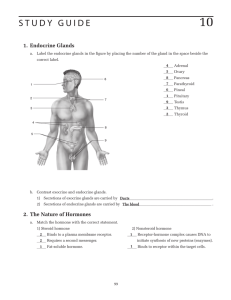
S T U D Y G U I D E
... Acromegaly ____________________________________________ Diabetes mellitis ...
... Acromegaly ____________________________________________ Diabetes mellitis ...
laboratory tests of thyroid function: pitfalls in interpretation
... management of thyroid disorders. Because of the diverse clinical presentations of thyroid dysfunction (the majority of thyroid disease symptoms are often subtle and nonspecific in presentation), initial requests for assessing thyroid function are often made. When the clinical suspicion is strong (e. ...
... management of thyroid disorders. Because of the diverse clinical presentations of thyroid dysfunction (the majority of thyroid disease symptoms are often subtle and nonspecific in presentation), initial requests for assessing thyroid function are often made. When the clinical suspicion is strong (e. ...
The Thyroid Autism Connection
... underactive thyroid), with the other two out of ten (20%) being hyperthyroid conditions (high or overactive thyroid). Women constitute about 80% of Americans with thyroid disease, and women are five times more likely than men to develop hypothyroidism. Thyroid autoimmune disease (as distinct from th ...
... underactive thyroid), with the other two out of ten (20%) being hyperthyroid conditions (high or overactive thyroid). Women constitute about 80% of Americans with thyroid disease, and women are five times more likely than men to develop hypothyroidism. Thyroid autoimmune disease (as distinct from th ...
Hormone receptors
... The definition of a target includes any cell in which the hormone (ligand) binds to its receptor, whether or not a biochemical or physiologic response has yet been determined. The hormone can affect several different cell types; also more than one hormone can affect a given cell type; and that hormo ...
... The definition of a target includes any cell in which the hormone (ligand) binds to its receptor, whether or not a biochemical or physiologic response has yet been determined. The hormone can affect several different cell types; also more than one hormone can affect a given cell type; and that hormo ...
Endocrine System - Moon Valley High School
... The endocrine system produces hormones, chemicals that act on cells to produce a response. The word “hormone” comes from the Greek word hormaein, “to set in motion.” This is, in fact, exactly what hormones do—set things in motion. Sometimes, the effects of the hormone occur over a long period of tim ...
... The endocrine system produces hormones, chemicals that act on cells to produce a response. The word “hormone” comes from the Greek word hormaein, “to set in motion.” This is, in fact, exactly what hormones do—set things in motion. Sometimes, the effects of the hormone occur over a long period of tim ...
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Clinical Outcomes
... trial with specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. However, collectively, they enrolled a broad spectrum of patients with HF and reduced LVEF, including many elderly patients. Although the INH study did not have specific thyroid exclusion criteria, CORONA did (and likely SCD-HeFT did, although it w ...
... trial with specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. However, collectively, they enrolled a broad spectrum of patients with HF and reduced LVEF, including many elderly patients. Although the INH study did not have specific thyroid exclusion criteria, CORONA did (and likely SCD-HeFT did, although it w ...
Nodular Hyperplasia of Thyroid Glands Induced
... granulated acidophiles between 1920and 9260days of the experimental period. Thereafter, well granu lated acidophiles occurred in large numbers and granulated basophiles were more frequently seen than ...
... granulated acidophiles between 1920and 9260days of the experimental period. Thereafter, well granu lated acidophiles occurred in large numbers and granulated basophiles were more frequently seen than ...
Paracrine interactions of thyroid hormones and thyroid stimulation
... Thyroid hormones regulate through binding to their nuclear receptors (TRs), which have been identified in many tissues and organs of the human body (Yen, 2001). TH receptors (TRs) belong to the steroid/retinoid/TH nuclear receptor family all having a similar structure involving a, enhancing N-termina ...
... Thyroid hormones regulate through binding to their nuclear receptors (TRs), which have been identified in many tissues and organs of the human body (Yen, 2001). TH receptors (TRs) belong to the steroid/retinoid/TH nuclear receptor family all having a similar structure involving a, enhancing N-termina ...
Hormones
... rate of metabolic processes (how energy is used) in the body and influences physical development § People may not produce enough of this hormone and get a condition known as hypothyroidism. They can take thyroxine to treat this condition. ...
... rate of metabolic processes (how energy is used) in the body and influences physical development § People may not produce enough of this hormone and get a condition known as hypothyroidism. They can take thyroxine to treat this condition. ...
File
... • The process by which our body maintains an internal balance of all body systems. • Usually it is regulated by one of two major systems ...
... • The process by which our body maintains an internal balance of all body systems. • Usually it is regulated by one of two major systems ...
iodine deficiency disorder
... 13% of world's population is suffering from IDD. In India, also about 8-10% are said to be suffering from IDD. The IDD is more common in hilly region because the fresh water does not contain much iodine. Iodine deficiency disorders Some of the IDD are: ...
... 13% of world's population is suffering from IDD. In India, also about 8-10% are said to be suffering from IDD. The IDD is more common in hilly region because the fresh water does not contain much iodine. Iodine deficiency disorders Some of the IDD are: ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.