Abnormalities in saccade dynamics in first-episode treatment
... Abstract: Objective: To explore the potential difference of eye saccade dynamics between first-episode treatmentnaïve hyperthyreosis patients without pre-existing eye damage and healthy controls by using basic visually guided saccade (VGS). Methods: 15 hyperthyroidism outpatients and 15 healthy cont ...
... Abstract: Objective: To explore the potential difference of eye saccade dynamics between first-episode treatmentnaïve hyperthyreosis patients without pre-existing eye damage and healthy controls by using basic visually guided saccade (VGS). Methods: 15 hyperthyroidism outpatients and 15 healthy cont ...
Chapter 26- Chemical Regulation
... • ACTH- stimulates cortex to secrete steroid hormonescorticosteroids (2 types) • Mineralcorticoids- mainly affect salt and water balance- makes kidneys reabsorb = increase blood volume = increase BP • Glucocorticoids- mobilize cellular fuel, reinforce glucagon effectpromote synthesis of glucose from ...
... • ACTH- stimulates cortex to secrete steroid hormonescorticosteroids (2 types) • Mineralcorticoids- mainly affect salt and water balance- makes kidneys reabsorb = increase blood volume = increase BP • Glucocorticoids- mobilize cellular fuel, reinforce glucagon effectpromote synthesis of glucose from ...
The Endocrine System - Immaculateheartacademy.org
... Diabetes Mellitus Two Types Type I - secretion of too little insulin from the pancreas - onset childhood, very thin , require insulin Type 2 - insufficient numbers of insulin receptors on target cells or defective recepetors - adult onset, usually overweight, can take medications that help increase ...
... Diabetes Mellitus Two Types Type I - secretion of too little insulin from the pancreas - onset childhood, very thin , require insulin Type 2 - insufficient numbers of insulin receptors on target cells or defective recepetors - adult onset, usually overweight, can take medications that help increase ...
Thyroid Hormones
... a single “outer-ring” iodine atom. • D3 “inactivates” thyroid hormone by removing a single “inner-ring”iodine atom. • All family members contain the novel amino acid selenocysteine (Se-Cys) in their catalytic center. ...
... a single “outer-ring” iodine atom. • D3 “inactivates” thyroid hormone by removing a single “inner-ring”iodine atom. • All family members contain the novel amino acid selenocysteine (Se-Cys) in their catalytic center. ...
Hormone Handout
... Heat production - Increased oxidation of glucose and fatty acids; increased heart output; increased breathing; increased red blood cells. Promotes growth and nervous system development- increased protein synthesis; stimulates GH secretion. ( excess- high heart rate , low weight , fatigue; defic.-cr ...
... Heat production - Increased oxidation of glucose and fatty acids; increased heart output; increased breathing; increased red blood cells. Promotes growth and nervous system development- increased protein synthesis; stimulates GH secretion. ( excess- high heart rate , low weight , fatigue; defic.-cr ...
The Endocrine System
... Identify the principal functions of each major endocrine hormone and describe the conditions that may result from hypersecretion of hyposecretion. Refer to pages 345-347 in text. ...
... Identify the principal functions of each major endocrine hormone and describe the conditions that may result from hypersecretion of hyposecretion. Refer to pages 345-347 in text. ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Signals Maintain Homeostasis
... • Located at the base of the neck in front of the trachea • Makes 2 important hormones: thyroxine (T4) and ...
... • Located at the base of the neck in front of the trachea • Makes 2 important hormones: thyroxine (T4) and ...
the endocrine system
... reaches puberty, its tissue is replaced by fat Thyroid gland – located in the front of your neck, it releases hormones that control your metabolism and govern the way your body uses energy ...
... reaches puberty, its tissue is replaced by fat Thyroid gland – located in the front of your neck, it releases hormones that control your metabolism and govern the way your body uses energy ...
Endocrine organs - Ping Pong
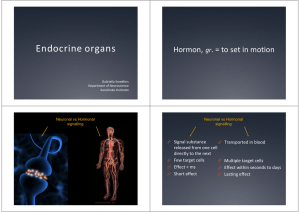
... released from one cell directly to the next Few target cells Multiple target cells Effect < ms Effect within seconds to days Short effect Lasting effect ...
... released from one cell directly to the next Few target cells Multiple target cells Effect < ms Effect within seconds to days Short effect Lasting effect ...
CLinical Manifestations
... or the hypothalamus. -If it results from thyroid gland malfunction, low TH (thyroxin hormone) levels are accompanied by high TSH( thyroid stimulating hormone) and high TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) because of the lack of negative feedback on the pituitary and hypothalamus by TH. -If hypothyroidism ...
... or the hypothalamus. -If it results from thyroid gland malfunction, low TH (thyroxin hormone) levels are accompanied by high TSH( thyroid stimulating hormone) and high TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) because of the lack of negative feedback on the pituitary and hypothalamus by TH. -If hypothyroidism ...
Treatment of Thyrotoxicosis - Society of Nuclear Medicine
... with the expectation for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement. The incidence of recurrence after subtotal thyroidectomy is high, and this almost always should be treated with 131I. Thus, the patient receives radioiodine treatment which, for one reason or another, was originally believed to be less d ...
... with the expectation for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement. The incidence of recurrence after subtotal thyroidectomy is high, and this almost always should be treated with 131I. Thus, the patient receives radioiodine treatment which, for one reason or another, was originally believed to be less d ...
Endocrine System
... development of breasts, increased risk for prostate cancer • For women—growth of facial hair, malepattern baldness, changes in or cessation of the menstrual cycle, enlargement of the clitoris, deepened voice • For adolescents—stunted growth due to premature skeletal maturation and accelerated pubert ...
... development of breasts, increased risk for prostate cancer • For women—growth of facial hair, malepattern baldness, changes in or cessation of the menstrual cycle, enlargement of the clitoris, deepened voice • For adolescents—stunted growth due to premature skeletal maturation and accelerated pubert ...
Tài liệu PDF
... number of endocrine glands release hormones when stimulated by hormones released by other endocrine glands. For example, the hypothalamus produces hormones that stimulate the anterior portion of the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary in turn releases hormones that regulate hormone production by ...
... number of endocrine glands release hormones when stimulated by hormones released by other endocrine glands. For example, the hypothalamus produces hormones that stimulate the anterior portion of the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary in turn releases hormones that regulate hormone production by ...
Chapter 18 Essays
... adenohypophysis, amplification, arachadonic acid, autocrine, bound fraction (of hormone), calmodulin, catecholamine, cholesterol, circulating hormone (endocrine), thyroid follicles and colloid, downregulation, eicosanoid, endocrine, exocrine, free fraction (of hormone), glucocorticoids, gonadocortic ...
... adenohypophysis, amplification, arachadonic acid, autocrine, bound fraction (of hormone), calmodulin, catecholamine, cholesterol, circulating hormone (endocrine), thyroid follicles and colloid, downregulation, eicosanoid, endocrine, exocrine, free fraction (of hormone), glucocorticoids, gonadocortic ...
Chapter 13
... chart of effects, sources, deficiency, etc. for each of the vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals (listed below). Have this chart next to you when you take the exam… YES, I am telling you that you should treat this part of the exam as open note. By the time you get your chart done, you’ll know most ...
... chart of effects, sources, deficiency, etc. for each of the vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals (listed below). Have this chart next to you when you take the exam… YES, I am telling you that you should treat this part of the exam as open note. By the time you get your chart done, you’ll know most ...
Book`s PowerPoint on Chapter 37
... Feedback Control of the Gonads Loop to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland from the ovaries ...
... Feedback Control of the Gonads Loop to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland from the ovaries ...
Vaughn Lawrence - Spirit of Health
... Classic symptoms of low thyroid (hypothyroidism) include sluggishness, weight gain, cold body temperature, poor quality hair, skin and nails, hair loss, and dry skin. However it can also include brain fog (short-term memory deficits), attention-deficit disorders, hypoglycemia, depression, dementia, ...
... Classic symptoms of low thyroid (hypothyroidism) include sluggishness, weight gain, cold body temperature, poor quality hair, skin and nails, hair loss, and dry skin. However it can also include brain fog (short-term memory deficits), attention-deficit disorders, hypoglycemia, depression, dementia, ...
Eating to support your thyroid — simple ways to naturally preserve
... Iodine (I). Your thyroid simply can’t function without this crucial trace element, and if you are iodine-deficient, higher iodine intake could make all the difference for your thyroid. The essential thyroid hormones that circulate in our bodies, known as T4 (also called thyroxine) and the more activ ...
... Iodine (I). Your thyroid simply can’t function without this crucial trace element, and if you are iodine-deficient, higher iodine intake could make all the difference for your thyroid. The essential thyroid hormones that circulate in our bodies, known as T4 (also called thyroxine) and the more activ ...
The Endocrine System
... uptake and lipid metabolism; is regulated by TSH Calcitonin • reduces Ca and P levels in blood; ...
... uptake and lipid metabolism; is regulated by TSH Calcitonin • reduces Ca and P levels in blood; ...
endocrinology notes
... meal. It is usually increased during sleep or during starvation. It causes both retention of sodium and potassium which are required for growth metabolism. Elevated GH levels increase IGF-1 blood levels. Because IGF-1 levels are much more stable over the course of the day, they are often a more prac ...
... meal. It is usually increased during sleep or during starvation. It causes both retention of sodium and potassium which are required for growth metabolism. Elevated GH levels increase IGF-1 blood levels. Because IGF-1 levels are much more stable over the course of the day, they are often a more prac ...
SYNTHROID PM
... your dose of SYNTHROID® will likely have to be increased; you have any heart problem, whether or not you have received treatment for them (especially history of heart attack, heart disease, hardening of the arteries); you have other medical problems, whether or not you have received treatment for th ...
... your dose of SYNTHROID® will likely have to be increased; you have any heart problem, whether or not you have received treatment for them (especially history of heart attack, heart disease, hardening of the arteries); you have other medical problems, whether or not you have received treatment for th ...
endocrine system
... Diseases and Abnormal Conditions • Addison’s Disease – Caused by a decreased secretion of aldosterone on the part of the adrenal cortex – This interferes with the reabsorption of sodium and water and causes an increased level of potassium in the blood – Signs and Symptoms: ...
... Diseases and Abnormal Conditions • Addison’s Disease – Caused by a decreased secretion of aldosterone on the part of the adrenal cortex – This interferes with the reabsorption of sodium and water and causes an increased level of potassium in the blood – Signs and Symptoms: ...
goiter - The Filipino Doctor
... is preferred rather than liothyronine, thyroglobulin or desiccated thyroid, because of its longer half-life and more modulated absorption. X. Diffuse non-toxic goiter is the most common thyroid disease usually seen among adolescents, young women (especially when they become pregnant), residents in ...
... is preferred rather than liothyronine, thyroglobulin or desiccated thyroid, because of its longer half-life and more modulated absorption. X. Diffuse non-toxic goiter is the most common thyroid disease usually seen among adolescents, young women (especially when they become pregnant), residents in ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.