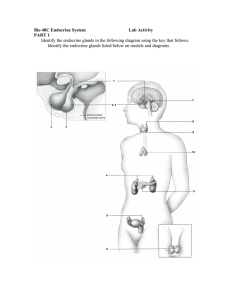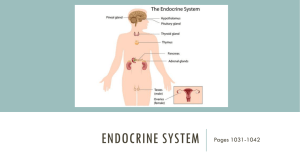
Endocrine System
... Oxytocin - Oxytocin causes milk letdown in nursing mothers and contractions during childbirth. Antidiuretic hormone or ADH - ADH, also called vasopressin, is stored in the back part of the pituitary gland and regulates water balance. If this hormone is not secreted properly, this can lead to probl ...
... Oxytocin - Oxytocin causes milk letdown in nursing mothers and contractions during childbirth. Antidiuretic hormone or ADH - ADH, also called vasopressin, is stored in the back part of the pituitary gland and regulates water balance. If this hormone is not secreted properly, this can lead to probl ...
Hypothyroid patient undergoing Coronary bypass surgery
... period, with bradycardia being most common, but other more severe abnormalities have also been documented with some frequency, including the ventricular tachyarrhythmia, as in our case as well, we had an episode of ventricular fibrillation, which could be influenced by other factors as well.9 ...
... period, with bradycardia being most common, but other more severe abnormalities have also been documented with some frequency, including the ventricular tachyarrhythmia, as in our case as well, we had an episode of ventricular fibrillation, which could be influenced by other factors as well.9 ...
11-12 (Bell)
... a. Hyperthyroidism is a hypermetabolic state caused by elevated levels of circulating free T3 and T4. b. Causes include: i. Diffuse hyperplasia of thyroid gland (Graves’ Disease). ii. Exogenous thyroid hormone in someone who is taking replacement thyroid hormone, but takes too much iii. Hyperfunctio ...
... a. Hyperthyroidism is a hypermetabolic state caused by elevated levels of circulating free T3 and T4. b. Causes include: i. Diffuse hyperplasia of thyroid gland (Graves’ Disease). ii. Exogenous thyroid hormone in someone who is taking replacement thyroid hormone, but takes too much iii. Hyperfunctio ...
1 - Lone Star College
... Affects the height of an individual Pituitary dwarfism- too little GH during childhood Gigantism- too much GH produced during childhood Acromegaly- too much GH is secreted in adulthood ...
... Affects the height of an individual Pituitary dwarfism- too little GH during childhood Gigantism- too much GH produced during childhood Acromegaly- too much GH is secreted in adulthood ...
An Introduction to Endocrinology
... • Primarily promotes growth indirectly by stimulating liver’s production of somatomedins – Primary somatomedin is insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1 -2) • Acts directly on bone and soft tissues to bring about most growthpromoting actions ...
... • Primarily promotes growth indirectly by stimulating liver’s production of somatomedins – Primary somatomedin is insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1 -2) • Acts directly on bone and soft tissues to bring about most growthpromoting actions ...
File - Endocrine System
... _____ heart (Specialized muscle cells in the heart produce a hormone that regulates blood pressure and blood volume.) _____ thymus gland (THĪ-mus) (The thymus produces several hormones which play a role in developing and maintaining normal immunological defenses.) ...
... _____ heart (Specialized muscle cells in the heart produce a hormone that regulates blood pressure and blood volume.) _____ thymus gland (THĪ-mus) (The thymus produces several hormones which play a role in developing and maintaining normal immunological defenses.) ...
Role of Post operative Serum TSH
... low risk patients who are clinically free of residual tumor w/ undetectable serum Tg and has negative neck ultrasound NOT necessary if the Tg is elevated and ultrasound of the neck is positive, since therapeutic options (surgery or RAI ...
... low risk patients who are clinically free of residual tumor w/ undetectable serum Tg and has negative neck ultrasound NOT necessary if the Tg is elevated and ultrasound of the neck is positive, since therapeutic options (surgery or RAI ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... secondary sexual characteristics Secretes adrenaline at times of emotional or ...
... secondary sexual characteristics Secretes adrenaline at times of emotional or ...
Sensory –approx 15 to 16 questions
... Eye structure and function, Distinguish b/w rods and cones, Distinguish b/w blind spot and fovea centralis, Accessory structures for the eye, visual pathway, tunics and functions Humors and associated cavities of eye Ear structure (inner, middle and outer ear) and function(s), hearing pathway Utricl ...
... Eye structure and function, Distinguish b/w rods and cones, Distinguish b/w blind spot and fovea centralis, Accessory structures for the eye, visual pathway, tunics and functions Humors and associated cavities of eye Ear structure (inner, middle and outer ear) and function(s), hearing pathway Utricl ...
Hormones
... of ductless glands that secrete chemical messenger substances, called hormones, into the bloodstream. • Hormones are responsible for the longterm regulation of many bodily functions. • The endocrine system includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus and adrenal glands, and the pancreas and ...
... of ductless glands that secrete chemical messenger substances, called hormones, into the bloodstream. • Hormones are responsible for the longterm regulation of many bodily functions. • The endocrine system includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus and adrenal glands, and the pancreas and ...
Thyroiditis
... Treatment T4 is the treatment of choice and is administered in dosages varying from 50 to 200 μg per day, depending on the patient’s size and condition. Starting doses of 100 μg of T4 daily are well tolerated; however, elderly patients and those with coexisting heart disease and profound hypothyroid ...
... Treatment T4 is the treatment of choice and is administered in dosages varying from 50 to 200 μg per day, depending on the patient’s size and condition. Starting doses of 100 μg of T4 daily are well tolerated; however, elderly patients and those with coexisting heart disease and profound hypothyroid ...
variation in thyroid hormones level among people of different age
... affect the requirement of iodine.3 The Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) also known as thyrotropin is an anterior pituitary hormone. The thyroid function is controlled by TSH, whose secretion is controlled by hypothalamus.4 In normal individuals the range of thyroid hormones and TSH in the blood is ...
... affect the requirement of iodine.3 The Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) also known as thyrotropin is an anterior pituitary hormone. The thyroid function is controlled by TSH, whose secretion is controlled by hypothalamus.4 In normal individuals the range of thyroid hormones and TSH in the blood is ...
Endocrinology
... Crine = secretion. Those glands are ductless gland (excretory duct) which empty their production into the blood stream or lymph, Their production called hormones which they have either stimulating or inhibitor effects upon the development or function of the body organs. There is no anatomical contin ...
... Crine = secretion. Those glands are ductless gland (excretory duct) which empty their production into the blood stream or lymph, Their production called hormones which they have either stimulating or inhibitor effects upon the development or function of the body organs. There is no anatomical contin ...
2. GOITER
... SIMPLE (NON-TOXIC) GOITER • Enlargement of the thyroid without toxic manifestations. ...
... SIMPLE (NON-TOXIC) GOITER • Enlargement of the thyroid without toxic manifestations. ...
Thyroid Function
... thyroid hormone overproduction or insufficiency, but it can occur also in conditions with normal thyroid hormone production. Goitres may be diffuse, involving the entire gland without evidence of nodularity, or they may contain nodules. Worldwide, over 90% cases (more than one billion) of goitre are ...
... thyroid hormone overproduction or insufficiency, but it can occur also in conditions with normal thyroid hormone production. Goitres may be diffuse, involving the entire gland without evidence of nodularity, or they may contain nodules. Worldwide, over 90% cases (more than one billion) of goitre are ...
Endocrine system
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target ...
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target ...
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA)
... thyroid or pituitary disorders. For in vitro diagnostic use only. ...
... thyroid or pituitary disorders. For in vitro diagnostic use only. ...
correct - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 7 : The pituitary is located beneath the thalamus in the brain. a. True b. False 8 : The hypothalamus regulates ___________. a. heart rate b. body temperature c. water balance d. glandular secretions e. all of the above 9 : The pituitary gland is divided into two portions: the posterior pituitary an ...
... 7 : The pituitary is located beneath the thalamus in the brain. a. True b. False 8 : The hypothalamus regulates ___________. a. heart rate b. body temperature c. water balance d. glandular secretions e. all of the above 9 : The pituitary gland is divided into two portions: the posterior pituitary an ...
Production, Regulation, and Action of Thyroid Hormones
... When not bound to hormone, the thyroid hormone receptor binds to target DNA (TRE on 5’ flanking region). It is associated with corepressor proteins that cause DNA to be tightly wound and inhibit transcription. Binding of hormone causes a conformational change, resulting in loss of corepressor bind ...
... When not bound to hormone, the thyroid hormone receptor binds to target DNA (TRE on 5’ flanking region). It is associated with corepressor proteins that cause DNA to be tightly wound and inhibit transcription. Binding of hormone causes a conformational change, resulting in loss of corepressor bind ...
Endocrine part 2
... e. Hypersecretion: (1) Graves disease (autoimmune dissorder) in which persons body makes antobodies which mimic TSH. (2) Symptoms include increased metabolic rate, sweating, rapid irregular heart beat, weight loss, nervousness, exophthalmous (protruding of the eyes due to mucoprotein deposits behind ...
... e. Hypersecretion: (1) Graves disease (autoimmune dissorder) in which persons body makes antobodies which mimic TSH. (2) Symptoms include increased metabolic rate, sweating, rapid irregular heart beat, weight loss, nervousness, exophthalmous (protruding of the eyes due to mucoprotein deposits behind ...
Pituitary Gland - inetTeacher.com
... What are the symptoms of this disease? What is glycosuria? If the glucose is in the blood and not available for the cells, what happens? List 7 symptoms of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar): ...
... What are the symptoms of this disease? What is glycosuria? If the glucose is in the blood and not available for the cells, what happens? List 7 symptoms of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar): ...
Hormones and Biological Rhythms
... 1. The bilobed thyroid gland is located in the neck just below the larynx. Four small parathyroid glands are embedded in its posterior surface. 2. The thyroid is the largest of the endocrine glands, weighing between 20 and 25g in humans. 3. On a microscopic level, the thyroid gland consists of many ...
... 1. The bilobed thyroid gland is located in the neck just below the larynx. Four small parathyroid glands are embedded in its posterior surface. 2. The thyroid is the largest of the endocrine glands, weighing between 20 and 25g in humans. 3. On a microscopic level, the thyroid gland consists of many ...
Hypothyroidism following hemithyroidectomy for benign nontoxic
... less definitive for subclinical hypothyroidism. The latter has been reported to occur spontaneously in 10% of women older than 60 years.10 Although patients with subclinical hypothyroidism are clinically asymptomatic, they have an increased risk of developing a major depressive disorder or mood diso ...
... less definitive for subclinical hypothyroidism. The latter has been reported to occur spontaneously in 10% of women older than 60 years.10 Although patients with subclinical hypothyroidism are clinically asymptomatic, they have an increased risk of developing a major depressive disorder or mood diso ...
Thyroid disorders. Part II: hypothyroidism and thyroiditis
... Part II of the series on thyroid disorders discusses hypothyroidism and thyroiditis that may be found in dental patients. An overview of the conditions is presented. Presenting signs and symptoms, laboratory tests used to diagnose hypothyroidism and thyroiditis, and their medical management is discu ...
... Part II of the series on thyroid disorders discusses hypothyroidism and thyroiditis that may be found in dental patients. An overview of the conditions is presented. Presenting signs and symptoms, laboratory tests used to diagnose hypothyroidism and thyroiditis, and their medical management is discu ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.