Endocrine System
... Regulates or supports a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic, and homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.20 ...
... Regulates or supports a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic, and homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.20 ...
File
... • Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland that produced it through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. • When the hormone reaches its target cell, it locks onto the cell's specific receptors and these hormone-rece ...
... • Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland that produced it through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. • When the hormone reaches its target cell, it locks onto the cell's specific receptors and these hormone-rece ...
Complete resolution of autoimmune thyroiditis after R
... Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Dysfunction of suppressor T cells is thought to lead to overgrowth of Th1 cells, which leads to cytokine production. Cytokines activate cytotoxic T cells, which in turn cause apoptosis of epithelial thyroid cells. Cytokines also stimulate B cells in the thyroid to produce an ...
... Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Dysfunction of suppressor T cells is thought to lead to overgrowth of Th1 cells, which leads to cytokine production. Cytokines activate cytotoxic T cells, which in turn cause apoptosis of epithelial thyroid cells. Cytokines also stimulate B cells in the thyroid to produce an ...
Chapter 1 A Perspective on Human Genetics
... Thyroid Gland • Abnormalities – Hyperthyroidism • Most common cause is Graves’ disease – Autoimmune disease – Body erroneously produces thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI) – Characterized by exopthalmos ...
... Thyroid Gland • Abnormalities – Hyperthyroidism • Most common cause is Graves’ disease – Autoimmune disease – Body erroneously produces thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI) – Characterized by exopthalmos ...
Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS) Testing
... The equine thyroid panel consisting of Total T4, Total T3 and Free T4 by Equilibrium Dialysis is routinely used for assessment of overall health and for the initial evaluation of thyroid function in the horse. The T4 baseline is recommended for monitoring horses on thyroid supplementation. Thyroid h ...
... The equine thyroid panel consisting of Total T4, Total T3 and Free T4 by Equilibrium Dialysis is routinely used for assessment of overall health and for the initial evaluation of thyroid function in the horse. The T4 baseline is recommended for monitoring horses on thyroid supplementation. Thyroid h ...
Assessing endocrine function
... Hypofunction of an endocrine organ - stimulation tests Example of a pituitary function test The ACTH response to a bolus injection of CRH is measured The grey shaded area shows the range of responses measured in control subjects In hypopituitarism there is no response ...
... Hypofunction of an endocrine organ - stimulation tests Example of a pituitary function test The ACTH response to a bolus injection of CRH is measured The grey shaded area shows the range of responses measured in control subjects In hypopituitarism there is no response ...
Pathology Chapter 24 p1107-1130 [4-20
... o Probably caused by an acute increase in cathecholamine levels, like during an infection, surgery, or stopping antithyroid medicines, or any form of stress o They usually present with a fever, and can progress to tachycardia and death by cardiac arrhythmia Apathetic hyperthyroidism- thyrotoxicosis ...
... o Probably caused by an acute increase in cathecholamine levels, like during an infection, surgery, or stopping antithyroid medicines, or any form of stress o They usually present with a fever, and can progress to tachycardia and death by cardiac arrhythmia Apathetic hyperthyroidism- thyrotoxicosis ...
smarter approach - Integrative Health Matters
... to Thyroid Health According to the American Thyroid Association, more than 20 million Americans suffer from thyroid dysfunction and over half are unaware that their thyroid is affected. Even more alarming is the fact that more than half of these cases are due to autoimmunity (where the immune system ...
... to Thyroid Health According to the American Thyroid Association, more than 20 million Americans suffer from thyroid dysfunction and over half are unaware that their thyroid is affected. Even more alarming is the fact that more than half of these cases are due to autoimmunity (where the immune system ...
Endocrinology - Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center
... c. Increased BMR generates heat through the sodium-potassium pump. d. Heart rate is increased because thyroid hormones increase the heart’s receptors for Norepinephrine and Epinephrine. 4. Regulations of Secretion a. TRH increases TSH which stimulates T4 and T 3. b. T4 and T 3 have negative feedback ...
... c. Increased BMR generates heat through the sodium-potassium pump. d. Heart rate is increased because thyroid hormones increase the heart’s receptors for Norepinephrine and Epinephrine. 4. Regulations of Secretion a. TRH increases TSH which stimulates T4 and T 3. b. T4 and T 3 have negative feedback ...
Path 24- Endocrine System [3-20
... d. increased basal metalloidc rate (weight loss, heat intolerance, flushed skin), cardiac (tach, palpitations, cardiomegally), tremor, hyperactivity, anxiety, insomnia, staring gaze, GI motility increase, osteoporosis What is thyroid storm? What is apathetic hyperthyroidism? How is hyperthyroidism d ...
... d. increased basal metalloidc rate (weight loss, heat intolerance, flushed skin), cardiac (tach, palpitations, cardiomegally), tremor, hyperactivity, anxiety, insomnia, staring gaze, GI motility increase, osteoporosis What is thyroid storm? What is apathetic hyperthyroidism? How is hyperthyroidism d ...
Endocrine system powerpoint
... pancreas secretes insulin to move blood-sugar into cells, thus decreasing levels ...
... pancreas secretes insulin to move blood-sugar into cells, thus decreasing levels ...
TSH Secreting Pituitary Adenoma
... pituitary adenomas is transsphenoidal resection of the tumor. The outcome is not very poor as only one-third patients are cured and one-third show improvement and one-third show no change. Pituitary radiation alone or in conjunction with pituitary surgery has not been found useful. Octerotide, a som ...
... pituitary adenomas is transsphenoidal resection of the tumor. The outcome is not very poor as only one-third patients are cured and one-third show improvement and one-third show no change. Pituitary radiation alone or in conjunction with pituitary surgery has not been found useful. Octerotide, a som ...
Endocrine system Hormones
... Function: stimulation of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria (resorption in intestine, regulation of lipid metabolism, growth, development of CNS) Parafollicular cells– calcitonin –decrease of Ca level in blood –storage into bone and release into urine. ...
... Function: stimulation of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria (resorption in intestine, regulation of lipid metabolism, growth, development of CNS) Parafollicular cells– calcitonin –decrease of Ca level in blood –storage into bone and release into urine. ...
Chapter 6 The Thyroid Type
... makes these animals grow faster and plumper. It is more costly, for example, to grow hormone-free chickens for twenty-two weeks than to grow hormone-fed chickens for only six weeks. I believe out of all the things that go into your body, commercial milk contains the highest amount of estrogen. Alway ...
... makes these animals grow faster and plumper. It is more costly, for example, to grow hormone-free chickens for twenty-two weeks than to grow hormone-fed chickens for only six weeks. I believe out of all the things that go into your body, commercial milk contains the highest amount of estrogen. Alway ...
Endocrine Pharmacology Adrenal
... A. Too much IGF-1 will cause acromegaly B. FSH surge causes ovulation C. Most prolactinomas are medically treated D. Sarcoidosis can cause adrenal ...
... A. Too much IGF-1 will cause acromegaly B. FSH surge causes ovulation C. Most prolactinomas are medically treated D. Sarcoidosis can cause adrenal ...
PPT File
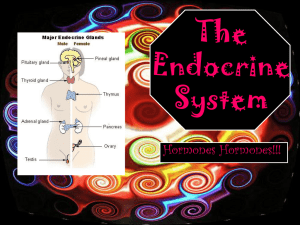
... Major endocrine glands (Male left, female on the right.) 1. Pineal gland 2. Pituitary gland 3. Thyroid gland 4. Thymus 5. Adrenal gland 6. Pancreas 7. Ovary 8.Testis ...
... Major endocrine glands (Male left, female on the right.) 1. Pineal gland 2. Pituitary gland 3. Thyroid gland 4. Thymus 5. Adrenal gland 6. Pancreas 7. Ovary 8.Testis ...
Treatment of Resistance to Thyroid Hormone
... data regarding the long-term outcome. General guidelines for the treatment with TH, usually L-T4, are: 1) elevated serum TSH levels; 2) failure to thrive that cannot be explained on the basis of another illness or defect; 3) unexplained seizures; 4) developmental delay; and 5) history of growth or m ...
... data regarding the long-term outcome. General guidelines for the treatment with TH, usually L-T4, are: 1) elevated serum TSH levels; 2) failure to thrive that cannot be explained on the basis of another illness or defect; 3) unexplained seizures; 4) developmental delay; and 5) history of growth or m ...
The Endocrine System
... • Due to low or non-functional insulin • Since sugar cannot be absorbed into body cells: – Blood sugar levels rise (hyperglycemia) – This stress causes the body to release MORE glucose into the blood! • Gluconeogenesis from fat and protein conversion, the waste products of which lead to ketoacidosis ...
... • Due to low or non-functional insulin • Since sugar cannot be absorbed into body cells: – Blood sugar levels rise (hyperglycemia) – This stress causes the body to release MORE glucose into the blood! • Gluconeogenesis from fat and protein conversion, the waste products of which lead to ketoacidosis ...
Pituitary Agents. Thyroid and Antithyroid Agents. Antidiabe
... • Leads to excessive blood glucose levels • Normal: 100 mg/dL ...
... • Leads to excessive blood glucose levels • Normal: 100 mg/dL ...
Chapter 15: Endocrine System
... The Thyroid secretes: • Thyroid Hormone (____) which is actually two iodinecontaining amine hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). • T4 – is secreted from the thyroid __________ • TH affects virtually every cell in the body except for the adult _____, ________, _______, _______, and the ...
... The Thyroid secretes: • Thyroid Hormone (____) which is actually two iodinecontaining amine hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). • T4 – is secreted from the thyroid __________ • TH affects virtually every cell in the body except for the adult _____, ________, _______, _______, and the ...
Iris 29 - Body Glyphix Studio
... Manage your stress levels. Practicing deep, slow diaphragmatic breathing every day for 5 to 10 minutes helps your nervous system know how to get from the “fight or flight” state to the “rest and digest” state. Regular practice (not just when you feel overwhelmed) makes that relaxed state more access ...
... Manage your stress levels. Practicing deep, slow diaphragmatic breathing every day for 5 to 10 minutes helps your nervous system know how to get from the “fight or flight” state to the “rest and digest” state. Regular practice (not just when you feel overwhelmed) makes that relaxed state more access ...
the thyroid and how it works
... The function of the thyroid gland is to take the iodine from food we eat, and convert it into thyroid hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid cells are the only cells in the body that can absorb iodine. These cells combine iodine and the amino acid tyrosine to make T3 and T4. Th ...
... The function of the thyroid gland is to take the iodine from food we eat, and convert it into thyroid hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid cells are the only cells in the body that can absorb iodine. These cells combine iodine and the amino acid tyrosine to make T3 and T4. Th ...
Essays for a Large Medical School Class?
... Patricia Moran is a 26-year-old woman who is seeing her primary care physician for the first time. She has been treated for Graves‟ disease with propylthiouracil (PTU) in the past. She stopped taking the pill about a year ago because she felt fine and didn‟t think she needed it. Since then she has l ...
... Patricia Moran is a 26-year-old woman who is seeing her primary care physician for the first time. She has been treated for Graves‟ disease with propylthiouracil (PTU) in the past. She stopped taking the pill about a year ago because she felt fine and didn‟t think she needed it. Since then she has l ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.