Endocrine System
... Epinephrine and norepinephrine Increases heart rate, increased force of cardiac muscle contraction, increased breathing rate, elevated blood pressure, increased blood glucose, and decreased digestive ...
... Epinephrine and norepinephrine Increases heart rate, increased force of cardiac muscle contraction, increased breathing rate, elevated blood pressure, increased blood glucose, and decreased digestive ...
21 Endocrine Flashcards MtSAC
... Thyroid hormone and Calcitonin Thyroid hormone increases metabolism Calcitonin -lowers blood calcium levels in children, slows osteoclasts to allow for bone deposition. It does NOT increase intestinal calcium absorption. Vitamin D is synthesized in the dermis ...
... Thyroid hormone and Calcitonin Thyroid hormone increases metabolism Calcitonin -lowers blood calcium levels in children, slows osteoclasts to allow for bone deposition. It does NOT increase intestinal calcium absorption. Vitamin D is synthesized in the dermis ...
Endocrine System _2 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... release energy our cells get from the food we eat ...
... release energy our cells get from the food we eat ...
Endokrin Sistem - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... If muscles are not exercised after eating-stored as muscle glycogen ...
... If muscles are not exercised after eating-stored as muscle glycogen ...
The Endocrine System - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... If muscles are not exercised after eating-stored as muscle glycogen ...
... If muscles are not exercised after eating-stored as muscle glycogen ...
Endocrine Physio PPT
... • ATP is used to bring iodine into cells against its electrical gradient. ...
... • ATP is used to bring iodine into cells against its electrical gradient. ...
Endocrinology_2
... into a capillary network in the anterior gland. Via this pathway the hypothalamus releases substances that the blood carries to the anterior pituitary. Hormones of the anterior pituitary: growth hormone (GH) stimulates cells to increase in size and divide more frequently, prolactin (PRL) stimulates ...
... into a capillary network in the anterior gland. Via this pathway the hypothalamus releases substances that the blood carries to the anterior pituitary. Hormones of the anterior pituitary: growth hormone (GH) stimulates cells to increase in size and divide more frequently, prolactin (PRL) stimulates ...
Goserelin-induced transient thyrotoxicosis in a hypothyroid
... persisted during the whole study period. No data were shown after discontinuation of oestrogens. The difference in f T4 and TSH between the control groups and the women on thyroxine is explained by the notion that subjects on levothyroxine replacement are not able to adjust their serum f T4 concentr ...
... persisted during the whole study period. No data were shown after discontinuation of oestrogens. The difference in f T4 and TSH between the control groups and the women on thyroxine is explained by the notion that subjects on levothyroxine replacement are not able to adjust their serum f T4 concentr ...
Endocrine Review Package
... A. stop hormone secretions because the target cells are not working B. produce a more active form of the hormone that stimulates the target cells C. cause other endocrine glands to secrete hormones that stimulate the target cells D. increase the secretion of the appropriate hormone that stimulates t ...
... A. stop hormone secretions because the target cells are not working B. produce a more active form of the hormone that stimulates the target cells C. cause other endocrine glands to secrete hormones that stimulate the target cells D. increase the secretion of the appropriate hormone that stimulates t ...
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System
... – Prolactin stimulates mammary gland growth and milk synthesis in mammals. – Melanocyte stimulating hormone inhibits hunger b-endorphins dull the perception of pain (some drugs cause the brain to secrete) ...
... – Prolactin stimulates mammary gland growth and milk synthesis in mammals. – Melanocyte stimulating hormone inhibits hunger b-endorphins dull the perception of pain (some drugs cause the brain to secrete) ...
Endocrine system
... Abnormal resorption of water, hyponatremia and inability to excrete diluted urine Caused by ectopic ADH secretion: Non-endocrine neoplasms (small cell carcinoma of the lung) Non-neoplastic pulmonary diseases (TBC, pneumonia) Primary CNS lesions (infarcts, meningitis, haemorrhage) ...
... Abnormal resorption of water, hyponatremia and inability to excrete diluted urine Caused by ectopic ADH secretion: Non-endocrine neoplasms (small cell carcinoma of the lung) Non-neoplastic pulmonary diseases (TBC, pneumonia) Primary CNS lesions (infarcts, meningitis, haemorrhage) ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE THYROID GLAND
... ! Apply knowledge acquired from mastery of basic learning objectives concerning thyroid function, physiology and pathology. ! Understand the many and varied manifestations of thyroid disease in key sub-populations. Drug therapy options are limited, but abnormal thyroid function is prevalent in diffe ...
... ! Apply knowledge acquired from mastery of basic learning objectives concerning thyroid function, physiology and pathology. ! Understand the many and varied manifestations of thyroid disease in key sub-populations. Drug therapy options are limited, but abnormal thyroid function is prevalent in diffe ...
The role of the autonomic nervous system in the
... The contribution of the parasympathetic component to the tachycardia occurring in thyrotoxicosis has not been extensively evaluated. Studies carried out on hyperthyroid animals [22-241 have demonstrated that the negative chronotropic response of the heart during electrical stimulation of the vagus w ...
... The contribution of the parasympathetic component to the tachycardia occurring in thyrotoxicosis has not been extensively evaluated. Studies carried out on hyperthyroid animals [22-241 have demonstrated that the negative chronotropic response of the heart during electrical stimulation of the vagus w ...
Document
... Function of Endocrine Glands The Function of Endocrine Glands Glands of the human body, like sweat glands or tear glands, have specialized ducts to transport the substances secreted, like sweat glands expel sweat to the skin surface, and tear ducts transport tears to the eye. But hormones secreted b ...
... Function of Endocrine Glands The Function of Endocrine Glands Glands of the human body, like sweat glands or tear glands, have specialized ducts to transport the substances secreted, like sweat glands expel sweat to the skin surface, and tear ducts transport tears to the eye. But hormones secreted b ...
File
... The Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland requires iodine to make thyroid hormones. If there is insufficient iodine in the diet, thyroxine cannot be made, and there will be no signal to stop TSH secretion. Constant stimulation of the thyroid gland by TSH causes a goitre, which is an enlargement of the thy ...
... The Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland requires iodine to make thyroid hormones. If there is insufficient iodine in the diet, thyroxine cannot be made, and there will be no signal to stop TSH secretion. Constant stimulation of the thyroid gland by TSH causes a goitre, which is an enlargement of the thy ...
Endocrine System 2 - Napa Valley College
... 1. Insulin - secreted during absorptive state when blood glucose and a.a. levels are high - stimulates glucose uptake (facilitated diffusion) into most body cells - stimulates synthesis of glycogen, protein, and lipids (energy storage) - decreases plasma glucose concentration 2. Glucagon - secreted ...
... 1. Insulin - secreted during absorptive state when blood glucose and a.a. levels are high - stimulates glucose uptake (facilitated diffusion) into most body cells - stimulates synthesis of glycogen, protein, and lipids (energy storage) - decreases plasma glucose concentration 2. Glucagon - secreted ...
Neonatal TSH concentrations are positively correlated with insulin
... Background: Adult studies have identified significant inverse relationships between thyroid function, as determined by circulating thyroglobulin (Tg) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels, and body weight, body fat mass and body mass index (BMI), but whether thyroid status in infancy is relat ...
... Background: Adult studies have identified significant inverse relationships between thyroid function, as determined by circulating thyroglobulin (Tg) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels, and body weight, body fat mass and body mass index (BMI), but whether thyroid status in infancy is relat ...
Thyroid Physiology and Sick Euthyroid State
... • Hypercholesterolemic patients not at LDL target levels while on statins were given eprotirome (KB2115), a TR-beta selective agonist. Treatment for 12 weeks resulted in reduced total and LDL-cholesterol in all patients and also reduced triglycerides in those individuals with elevated baseline trigl ...
... • Hypercholesterolemic patients not at LDL target levels while on statins were given eprotirome (KB2115), a TR-beta selective agonist. Treatment for 12 weeks resulted in reduced total and LDL-cholesterol in all patients and also reduced triglycerides in those individuals with elevated baseline trigl ...
Q. Describe an activity to demonstrate phototropism. A. Fill a conical
... shoots bend towards the light and roots away from the light. Now turn the flask so that the shoots are away from light and the roots towards light. Leave it undisturbed in this condition for a few days. After few days, we will again find that the shoots bend towards the light and roots away from the ...
... shoots bend towards the light and roots away from the light. Now turn the flask so that the shoots are away from light and the roots towards light. Leave it undisturbed in this condition for a few days. After few days, we will again find that the shoots bend towards the light and roots away from the ...
Chapter 41 Endocrine System
... glucagon directly into the blood. Insulin is secreted when there is a high level of glucose in the blood, which usually occurs just after eating. Insulin has the three different actions: 1) It stimulates fat, liver, and muscle cells to take up and metabolize glucose; 2) It stimulates the liver and m ...
... glucagon directly into the blood. Insulin is secreted when there is a high level of glucose in the blood, which usually occurs just after eating. Insulin has the three different actions: 1) It stimulates fat, liver, and muscle cells to take up and metabolize glucose; 2) It stimulates the liver and m ...
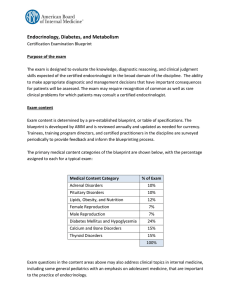
Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism
... Thyrotoxicosis with low radioactive iodine uptake Thyroiditis Factitious, accidental, and iatrogenic thyrotoxicosis Iodine-induced Struma ovarii Complicated thyrotoxicosis Subclinical hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Primary Secondary Subclinical hypothyroidism Complicated hypothyroidism TSH resistanc ...
... Thyrotoxicosis with low radioactive iodine uptake Thyroiditis Factitious, accidental, and iatrogenic thyrotoxicosis Iodine-induced Struma ovarii Complicated thyrotoxicosis Subclinical hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Primary Secondary Subclinical hypothyroidism Complicated hypothyroidism TSH resistanc ...
3 The endocrine system of a vertebrate
... • Adrenalin. It increases blood sugar levels, blood pressure and heart rate, preparing our bodies for action in situations in which we are alert or in danger. • Cortisol. This hormone is produced as a response to stress. It regulates the processes of producing and breaking down proteins and sugars i ...
... • Adrenalin. It increases blood sugar levels, blood pressure and heart rate, preparing our bodies for action in situations in which we are alert or in danger. • Cortisol. This hormone is produced as a response to stress. It regulates the processes of producing and breaking down proteins and sugars i ...
grave problem
... “Carrie, a subset of your immune system antibodies is mistakenly attacking your thyroid gland, causing an increase in hormone production. Common symptoms include insomnia, anxiety, fatigue, heat sensitivity, weight loss, and increased sweating. Your hair might get brittle, and your menstrual cycle m ...
... “Carrie, a subset of your immune system antibodies is mistakenly attacking your thyroid gland, causing an increase in hormone production. Common symptoms include insomnia, anxiety, fatigue, heat sensitivity, weight loss, and increased sweating. Your hair might get brittle, and your menstrual cycle m ...
Chapter 11: Endocrine System Theory Lecture Outline
... o Overdevelopment of the bones of the face, hands and feet • Hypofunction o Dwarfism – long bones are abnormally decreased due to inadequate production of growth hormone Disorders – Thyroid Because the thyroid gland controls metabolic activity, any disorder will affect other structures besides the g ...
... o Overdevelopment of the bones of the face, hands and feet • Hypofunction o Dwarfism – long bones are abnormally decreased due to inadequate production of growth hormone Disorders – Thyroid Because the thyroid gland controls metabolic activity, any disorder will affect other structures besides the g ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.