Chapter 45 Notes
... Mineralocorticoids act principally on salt and water balance. SEE FIGURE 45.20 p. 2007 ***Both glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids help deal with long term stress as opposed to epinephrine and norepinephrine that work on short term stress.*** GONADS Sex hormones regulate growth, development, ...
... Mineralocorticoids act principally on salt and water balance. SEE FIGURE 45.20 p. 2007 ***Both glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids help deal with long term stress as opposed to epinephrine and norepinephrine that work on short term stress.*** GONADS Sex hormones regulate growth, development, ...
questions for the endocrine system chapter 16
... 6. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. 7. When is norepinephrine a neurotransmitter? When is it a hormone? 8. Trace/Draw neatly the diagram on page 486 and label the endocrine glands. 9. Hormones can be classified by general __-name and describe 3 of these. 10. Another way that hormon ...
... 6. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. 7. When is norepinephrine a neurotransmitter? When is it a hormone? 8. Trace/Draw neatly the diagram on page 486 and label the endocrine glands. 9. Hormones can be classified by general __-name and describe 3 of these. 10. Another way that hormon ...
thyroid gland - Pharmacy Fun
... The second zone is called zona fasciculata, is the widest of the three zones and consists of cells arranged in long, straight columns. Mainly secret glucocorticoids The inner most zone is called zona reticularis which secrets androgens ...
... The second zone is called zona fasciculata, is the widest of the three zones and consists of cells arranged in long, straight columns. Mainly secret glucocorticoids The inner most zone is called zona reticularis which secrets androgens ...
Origin and Location of Thyroid Gland - eCurriculum
... – Thin CT capsule with septae (trabeculae) that divide gland into lobes – Adipose Tissue which may be up to 70% of the gland in aged individuals – Fenestrated capillaries ...
... – Thin CT capsule with septae (trabeculae) that divide gland into lobes – Adipose Tissue which may be up to 70% of the gland in aged individuals – Fenestrated capillaries ...
Endocrine System Revision Notes
... The arterial blood supply to the gland is through the superior and inferior thyroid arteries o Superior thyroid artery is a branch of the external carotid artery o Inferior thyroid artery is a branch of the subclavian artery Venous return is by the thyroid veins o Drain into the internal jugular ...
... The arterial blood supply to the gland is through the superior and inferior thyroid arteries o Superior thyroid artery is a branch of the external carotid artery o Inferior thyroid artery is a branch of the subclavian artery Venous return is by the thyroid veins o Drain into the internal jugular ...
Endocrine - Austin Community College
... Gonadotropic cells - secrete follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) Tropic hormones TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH Regulate the secretion of hormones by other endocrine glands Hormones of the Adenohypophysis Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) triggers the release of thyroid hormones ...
... Gonadotropic cells - secrete follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) Tropic hormones TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH Regulate the secretion of hormones by other endocrine glands Hormones of the Adenohypophysis Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) triggers the release of thyroid hormones ...
PMHS
... Activate genes that result in __________________ Nonsteroid Hormone Action Hormone binds to a membrane receptor Hormone _________________________________ Sets off a series of reactions that activates an enzyme Catalyzes a reaction that produces a second messenger ...
... Activate genes that result in __________________ Nonsteroid Hormone Action Hormone binds to a membrane receptor Hormone _________________________________ Sets off a series of reactions that activates an enzyme Catalyzes a reaction that produces a second messenger ...
Lesson 2.3: Chemical Communication Preface While the nervous
... involved in maintaining the body’s homeostasis. These chemical messengers carry signals from one cell to another and regulate many of the body’s functions, including growth and development, metabolism and reproduction. Hormones are secreted by tissues in the body referred to as glands. Endocrine gla ...
... involved in maintaining the body’s homeostasis. These chemical messengers carry signals from one cell to another and regulate many of the body’s functions, including growth and development, metabolism and reproduction. Hormones are secreted by tissues in the body referred to as glands. Endocrine gla ...
Chapter 18 - Illini West High School
... or tubeless organs or group of cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream • Hormones – are chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate many of the body’s functions ...
... or tubeless organs or group of cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream • Hormones – are chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate many of the body’s functions ...
Endocrine System - UNT's College of Education
... bloodstream directly. • Horomones – products deliver messages to body • Target cells – have specific receptors for specific hormones ...
... bloodstream directly. • Horomones – products deliver messages to body • Target cells – have specific receptors for specific hormones ...
The Endocrine System - FW Johnson Collegiate
... of the pancreas in dogs lead to what we now identify as symptoms of diabetes. Although this shed some light on the endocrine system, many glands produce more than one hormone, and levels of some hormones affect the level of other hormones. - To study hormones today, scientists inject radioactive tra ...
... of the pancreas in dogs lead to what we now identify as symptoms of diabetes. Although this shed some light on the endocrine system, many glands produce more than one hormone, and levels of some hormones affect the level of other hormones. - To study hormones today, scientists inject radioactive tra ...
ADRENAL GLAND Medulla
... show evidence of catecholamine production. – During fetal life, the chromaffine cells secrete only nor-epinephrine but just before birth, some cells begin to synthesize epinephrine. ...
... show evidence of catecholamine production. – During fetal life, the chromaffine cells secrete only nor-epinephrine but just before birth, some cells begin to synthesize epinephrine. ...
Endocrine System
... bloodstream directly. • Horomones – products deliver messages to body • Target cells – have specific receptors for specific hormones ...
... bloodstream directly. • Horomones – products deliver messages to body • Target cells – have specific receptors for specific hormones ...
Endocrine System
... • Anterior Pituitary Gland – Secretes peptide hormones that act on target organs including the adrenal gland, liver, bone, thyroid gland, and gonads. • Parathyroid - Releases parathyroid hormone, which regulates the level of calcium in the blood with the help of calcitonin, which is produced in the ...
... • Anterior Pituitary Gland – Secretes peptide hormones that act on target organs including the adrenal gland, liver, bone, thyroid gland, and gonads. • Parathyroid - Releases parathyroid hormone, which regulates the level of calcium in the blood with the help of calcitonin, which is produced in the ...
presentation source
... regulated by the hypothalamus. 4. describe the production and actions of the thyroid hormones and explain how thyroid secretion is regulated. 5. describe the location of the parathyroid glands and explain the actions of PTH and the regulation of its secretion. 6. describe the types and actions of co ...
... regulated by the hypothalamus. 4. describe the production and actions of the thyroid hormones and explain how thyroid secretion is regulated. 5. describe the location of the parathyroid glands and explain the actions of PTH and the regulation of its secretion. 6. describe the types and actions of co ...
ES Note Booklet - Morinville Community High School
... A2. Defining endocrine glands, hormones, and negative feedback A3. Location of endocrine glands Key Concept B: The hypothalamus and pituitary complex controls the secretion of many of the bodyʼs hormones B1. Hormones of the Hypothalamus, posterior and anterior pituitary glands B2. Growth Hormone • g ...
... A2. Defining endocrine glands, hormones, and negative feedback A3. Location of endocrine glands Key Concept B: The hypothalamus and pituitary complex controls the secretion of many of the bodyʼs hormones B1. Hormones of the Hypothalamus, posterior and anterior pituitary glands B2. Growth Hormone • g ...
Chapter 11: The Endocrine System (pp
... The endocrine system, like the nervous system, controls body activities to maintain a relatively constant internal environment. The methods used by these two systems are different. This chapter describes the location of the endocrine glands and the hormones they secrete. It Explains the nature of ho ...
... The endocrine system, like the nervous system, controls body activities to maintain a relatively constant internal environment. The methods used by these two systems are different. This chapter describes the location of the endocrine glands and the hormones they secrete. It Explains the nature of ho ...
Endocrine Notes PPT
... and deal with stress Location: “Suprarenal” glands because found above each kidney Hormones of the Adrenal Gland ...
... and deal with stress Location: “Suprarenal” glands because found above each kidney Hormones of the Adrenal Gland ...
Endocrine Overview - Solon City Schools
... Exocrine glands- external secretions onto surface or other organ; sweat, mammary, lacrimal, salivary glands ...
... Exocrine glands- external secretions onto surface or other organ; sweat, mammary, lacrimal, salivary glands ...
Typical disorders of the endocrine system 1. Choose the correct
... + a) acromegaly; + b) gigantism; + c) hypercortisolism; d) secondary aldosteronism; e) primary aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome). 37. Excessive production of ACTH leads to increased secretion of: + a) androgenic corticosteroids; b) norepinephrine; c) insulin; d) epinephrine; + e) cortisol. 38. Insuffi ...
... + a) acromegaly; + b) gigantism; + c) hypercortisolism; d) secondary aldosteronism; e) primary aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome). 37. Excessive production of ACTH leads to increased secretion of: + a) androgenic corticosteroids; b) norepinephrine; c) insulin; d) epinephrine; + e) cortisol. 38. Insuffi ...
Topic: The Endocrine System
... What are the Parathyroid Glands? • There are FOUR parathyroid glands, which are embedded in the thyroid gland • Release a hormone that controls the amount of calcium in the blood and body ...
... What are the Parathyroid Glands? • There are FOUR parathyroid glands, which are embedded in the thyroid gland • Release a hormone that controls the amount of calcium in the blood and body ...
Endocrine Glands and Hormones
... 2. Gland that produces two hormones that regulate the female reproductive system. 4. Hormone which is produced in the pineal gland. 7. Gland that is responsible for the maturation and development of T-cells. 10. A group of hormones produced in the adrenals that regulates electrolyte and mineral bala ...
... 2. Gland that produces two hormones that regulate the female reproductive system. 4. Hormone which is produced in the pineal gland. 7. Gland that is responsible for the maturation and development of T-cells. 10. A group of hormones produced in the adrenals that regulates electrolyte and mineral bala ...
Endocrine System
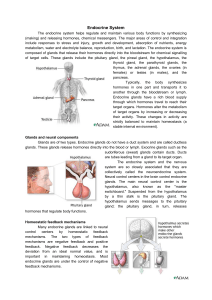
... calcium by stimulating bone calcium release into the bloodstream and by increasing the calcium absorption rate in the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. Adrenal glands The adrenal glands are on top of each kidney. Each gland has a cortex (outer region) and a medulla (inner region). The cortex secr ...
... calcium by stimulating bone calcium release into the bloodstream and by increasing the calcium absorption rate in the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. Adrenal glands The adrenal glands are on top of each kidney. Each gland has a cortex (outer region) and a medulla (inner region). The cortex secr ...
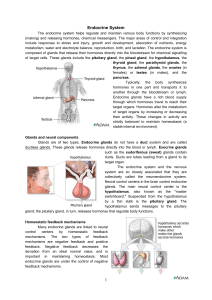
Endocrine System
... calcium by stimulating bone calcium release into the bloodstream and by increasing the calcium absorption rate in the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. Adrenal glands The adrenal glands are on top of each kidney. Each gland has a cortex (outer region) and a medulla (inner region). The cortex secr ...
... calcium by stimulating bone calcium release into the bloodstream and by increasing the calcium absorption rate in the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. Adrenal glands The adrenal glands are on top of each kidney. Each gland has a cortex (outer region) and a medulla (inner region). The cortex secr ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.