AOM2017 Abstract Template
... in plasmonic focusing and manipulation. As special cases of the vectorial optical field, radially and azimuthally polarized beams with spatially variant states of polarization have attracted much interest as a SPP excitation sources. Radial polarization, whose local electric field is linearly polari ...
... in plasmonic focusing and manipulation. As special cases of the vectorial optical field, radially and azimuthally polarized beams with spatially variant states of polarization have attracted much interest as a SPP excitation sources. Radial polarization, whose local electric field is linearly polari ...
r - Nano[studijní] materiály - Technical University of Liberec
... • Applied electric field E=(0,0,E) along optical axis z, perpendicular to laser beam. The values of the principal refractive indices with field E are ne(E) and no(E) • The change of refractive index causes the optical phase shift of light wave in the sample. The electric field in optical axis direct ...
... • Applied electric field E=(0,0,E) along optical axis z, perpendicular to laser beam. The values of the principal refractive indices with field E are ne(E) and no(E) • The change of refractive index causes the optical phase shift of light wave in the sample. The electric field in optical axis direct ...
Syllabus
... Introduction to optical waveguides and fibers, propagation characteristics of fibers, characterization methods, LEDs, laser diodes, optical receivers, optical amplifiers, all-optical switching and fiber optic communication systems. The objective is to give students a comprehensive understanding of t ...
... Introduction to optical waveguides and fibers, propagation characteristics of fibers, characterization methods, LEDs, laser diodes, optical receivers, optical amplifiers, all-optical switching and fiber optic communication systems. The objective is to give students a comprehensive understanding of t ...
Light Rays
... Light from the sky is gradually refracted more towards the horizontal as the air near the ground has a lower refractive index (optically less dense). Total internal reflection takes place when it meets a layer of air at an angle greater than the critical angle. The image of the sky is then formed on ...
... Light from the sky is gradually refracted more towards the horizontal as the air near the ground has a lower refractive index (optically less dense). Total internal reflection takes place when it meets a layer of air at an angle greater than the critical angle. The image of the sky is then formed on ...
Polarization Study 1 Introduction
... phase difference between the two orthogonal polarization components A0k and A0⊥ . As a result, linearly polarized light becomes elliptically polarized. There are two noteworthy cases where tan(αr ) is real and the light remains linearly polarized upon reflection: 1. Normal Incidence: θ1 = 0, which r ...
... phase difference between the two orthogonal polarization components A0k and A0⊥ . As a result, linearly polarized light becomes elliptically polarized. There are two noteworthy cases where tan(αr ) is real and the light remains linearly polarized upon reflection: 1. Normal Incidence: θ1 = 0, which r ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... • Opically anisotropic crystal : the refractive index n of a crystal depends on the direction of the electric field in the propagating light beam. • Birefringence : optically anisotropic crystals are called birefringence because an incident light beam ...
... • Opically anisotropic crystal : the refractive index n of a crystal depends on the direction of the electric field in the propagating light beam. • Birefringence : optically anisotropic crystals are called birefringence because an incident light beam ...
Sect.3
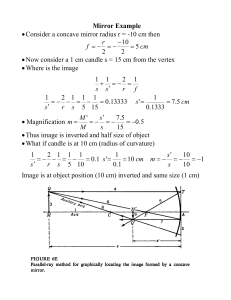
... Concave mirrors - a mirror with a surface that curves inward like the inside of a bowl ...
... Concave mirrors - a mirror with a surface that curves inward like the inside of a bowl ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... This course explores the production and nature of light including: the laws of reflection and refraction, theory of image formation, principles of wave optics (including interference, diffraction and polarization), fundamentals of fiber optic theory, principles of lasers and laser safety, and the ba ...
... This course explores the production and nature of light including: the laws of reflection and refraction, theory of image formation, principles of wave optics (including interference, diffraction and polarization), fundamentals of fiber optic theory, principles of lasers and laser safety, and the ba ...
Reflection,Refraction, Lenses
... a perfect mirror, depending on the angle at which light strikes it. When an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle, the light cannot pass through the surface - it is all reflected. This is called total internal reflection. ...
... a perfect mirror, depending on the angle at which light strikes it. When an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle, the light cannot pass through the surface - it is all reflected. This is called total internal reflection. ...
CNOT on polarization states of coherent light
... polarized light passes through a solution of an optically active compound – chiral or optical isomers or optical polymers – the direction of polarization is rotated to the right or to the left. Recent development in the chemistry of such dipole molecules with controlled optical properties opens the ...
... polarized light passes through a solution of an optically active compound – chiral or optical isomers or optical polymers – the direction of polarization is rotated to the right or to the left. Recent development in the chemistry of such dipole molecules with controlled optical properties opens the ...
Module Descriptor - What is FlexiLearn?
... Synthesis of new Lens Designs Indicative Learning Outcomes: On successful completion of this module, students should be able to: Understand basic principles of optical design Develop a basic optical design for an research application in lasers and optics Evaluate optical designs of commercia ...
... Synthesis of new Lens Designs Indicative Learning Outcomes: On successful completion of this module, students should be able to: Understand basic principles of optical design Develop a basic optical design for an research application in lasers and optics Evaluate optical designs of commercia ...
Ref. “Optical Materials”
... Ellipsometry An ellipsometer is usually used to measure the thickness and refractive index of films deposited on a substrate. With an appropriate standard, the same method can be applied to index measurements on bulk samples. ...
... Ellipsometry An ellipsometer is usually used to measure the thickness and refractive index of films deposited on a substrate. With an appropriate standard, the same method can be applied to index measurements on bulk samples. ...
Ch. 35: Reflection and Refraction of Light
... This is valid as long as the light does not change the medium through which it propagates (air, water, glass, plastic), or finds an obstacle (interface). The velocity of light in air is c c = 3x108 m/s The velocity of light in other media may be different from c (less than c). ...
... This is valid as long as the light does not change the medium through which it propagates (air, water, glass, plastic), or finds an obstacle (interface). The velocity of light in air is c c = 3x108 m/s The velocity of light in other media may be different from c (less than c). ...
Tunable properties of light propagation in photonic liquid crystal fibers
... air holes in the cladding. In PCFs, light can be guided either by effective index mechanism related to the modified total internal reflection (TIR) or through light confinement by the photonic band gap (PBG) phenomenon. The size and the location of the air holes allow for tailoring PCF parameters in ...
... air holes in the cladding. In PCFs, light can be guided either by effective index mechanism related to the modified total internal reflection (TIR) or through light confinement by the photonic band gap (PBG) phenomenon. The size and the location of the air holes allow for tailoring PCF parameters in ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 16. Explain the construction and working of Huygens eyepiece with the help of a neat diagram and indicate the positions of its cardinal points. ...
... 16. Explain the construction and working of Huygens eyepiece with the help of a neat diagram and indicate the positions of its cardinal points. ...
Interference I - Galileo and Einstein
... light is much shorter than the distance between slits, First dark place from center: so there are many dark and first-order minimum bright fringes within very small angles from the d center, so it’s bright where d sin d n n is called the order of the (bright) fringe ...
... light is much shorter than the distance between slits, First dark place from center: so there are many dark and first-order minimum bright fringes within very small angles from the d center, so it’s bright where d sin d n n is called the order of the (bright) fringe ...
... In this work we present two examples applying an analytical formalism, which allows us to describe various non linear optical phenomena in liquid crystals. First, we analyze the propagation of plane waves in rectangular cells with nematic liquid crystal cores, by taking into account its cupling with ...
Topic 4.5 - Aurora City School
... • If the pulses are 180o () out of phase then the net resultant of the string will be zero. This is called complete destructive ...
... • If the pulses are 180o () out of phase then the net resultant of the string will be zero. This is called complete destructive ...
Read more (docx 14 kB)
... Nonlinear Photonic Crystals Abstract: Photonic crystals are materials patterned with periodic dielectric structures. Since they were first proposed, in 1987, they have grown into a burgeoning research field. Nowadays, their engineerable response is already used in a broad range of applications, rang ...
... Nonlinear Photonic Crystals Abstract: Photonic crystals are materials patterned with periodic dielectric structures. Since they were first proposed, in 1987, they have grown into a burgeoning research field. Nowadays, their engineerable response is already used in a broad range of applications, rang ...
4.8 Acceptance Angle and Numerical Aperture
... The fibre output is a cone of light that spreads out wider as the distance from the fibre exit increases. The grid slide or screen and ruler can be used to measure diameters. The edges of the cone of light may appear fuzzy so there will be an error introduced into your measurements. Measurement of t ...
... The fibre output is a cone of light that spreads out wider as the distance from the fibre exit increases. The grid slide or screen and ruler can be used to measure diameters. The edges of the cone of light may appear fuzzy so there will be an error introduced into your measurements. Measurement of t ...
Chapter 23 Ray Optics
... Our everyday experience that light travels in straight lines is the basis of the ray model of light. Ray optics apply to a variety of situations, including mirrors, lenses, and shiny spoons. Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. In this chapter you will learn: • Use the ray m ...
... Our everyday experience that light travels in straight lines is the basis of the ray model of light. Ray optics apply to a variety of situations, including mirrors, lenses, and shiny spoons. Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. In this chapter you will learn: • Use the ray m ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).
![r - Nano[studijní] materiály - Technical University of Liberec](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007925985_1-5e55f54db686ed86c2131eb21f7dd098-300x300.png)