MOCT(Magneto Optic Current Transformer)
... A polarizer is used to convert the randomly polarized incident light into linearly polarized light. The orientation of the linearly polarized light rotates an angle after the light has passed through the magneto-optical material because of Faraday Effect. Then another polarization prism is used as ...
... A polarizer is used to convert the randomly polarized incident light into linearly polarized light. The orientation of the linearly polarized light rotates an angle after the light has passed through the magneto-optical material because of Faraday Effect. Then another polarization prism is used as ...
Interference
... Poisson’s Spot - a curious tale! • By the early 19th century the wave model was becoming accepted and the French Physicist Fresnel had worked out an elaborate mathematical theory of light. However, the famous physicist Poisson claimed to have found a fatal flaw in the ...
... Poisson’s Spot - a curious tale! • By the early 19th century the wave model was becoming accepted and the French Physicist Fresnel had worked out an elaborate mathematical theory of light. However, the famous physicist Poisson claimed to have found a fatal flaw in the ...
124-07_Reflection_and_Refraction
... the bottom) and compare your number to the marked focal length. To do this set put the painted arrow close to the lamp, fix the screen some distance away from the arrow and then move the lens until the image on the screen is most focused. At this point lock the lens into place and measure the distan ...
... the bottom) and compare your number to the marked focal length. To do this set put the painted arrow close to the lamp, fix the screen some distance away from the arrow and then move the lens until the image on the screen is most focused. At this point lock the lens into place and measure the distan ...
Research Directions
... Nonlinear Magneto-Optical Rotation • Linear Faraday rotation is independent of light intensity. • Nonlinear magneto-optical rotation possible when light modifies the properties of the medium. Small-field rotation can be enhanced by many orders of magnitude compared to the linear case due to nonline ...
... Nonlinear Magneto-Optical Rotation • Linear Faraday rotation is independent of light intensity. • Nonlinear magneto-optical rotation possible when light modifies the properties of the medium. Small-field rotation can be enhanced by many orders of magnitude compared to the linear case due to nonline ...
Axial birefringence in high-numerical-aperture optical
... light of wavelength and numerical aperture (NA) on the information layer through a protective cover layer of thickness d. To increase the information density the wavelength is decreased and the numerical aperture is increased, as the spot size scales with /NA. To that end the existing compact dis ...
... light of wavelength and numerical aperture (NA) on the information layer through a protective cover layer of thickness d. To increase the information density the wavelength is decreased and the numerical aperture is increased, as the spot size scales with /NA. To that end the existing compact dis ...
lecture5web
... the more the “ray” will bend towards the normal. • Different optical materials are differently “muddy”, which we identify using the index of refraction. • Higher index materials are “muddier” and bend the ray more than lower index materials ...
... the more the “ray” will bend towards the normal. • Different optical materials are differently “muddy”, which we identify using the index of refraction. • Higher index materials are “muddier” and bend the ray more than lower index materials ...
Optical Activity
... right, and average. In each case, you are looking for the smallest rotation angle between the reference minimum without the sample, and with the sample. The left and right reference minima differ by 180 degrees, but the magnitudes of the rotations should be equal. 3. Plot this data as a function of ...
... right, and average. In each case, you are looking for the smallest rotation angle between the reference minimum without the sample, and with the sample. The left and right reference minima differ by 180 degrees, but the magnitudes of the rotations should be equal. 3. Plot this data as a function of ...
Wave optics
... The top drawing was used to determine the angles at which dark fringes occur, since any two waves #1 and #2 which originate from positions a/2 apart in the slit are out of phase by /2. ...
... The top drawing was used to determine the angles at which dark fringes occur, since any two waves #1 and #2 which originate from positions a/2 apart in the slit are out of phase by /2. ...
polarization_magnifier
... sight, one might expect that 0 since for a single pass propagation through the plate, the phase shift is the same for parallel and perpendicular polarizations. However, experimentally, a linear incident polarization acquires an ellipticity after crossing such a pile of parallel plates, showing ...
... sight, one might expect that 0 since for a single pass propagation through the plate, the phase shift is the same for parallel and perpendicular polarizations. However, experimentally, a linear incident polarization acquires an ellipticity after crossing such a pile of parallel plates, showing ...
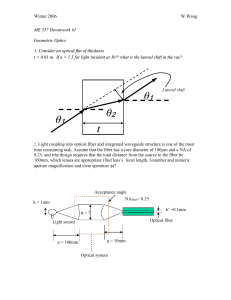
Chapter 2 Optical fibers
... Most optical fiber consist of a cylindrical piece of glass surrounded by an acrylic (made from a thermoplastic resin) jacket. The glass consists of a core, of refractive index n1, and a surrounding cladding, of refractive index n2, with n1 > n2. The index of the jacket is such that any light reachin ...
... Most optical fiber consist of a cylindrical piece of glass surrounded by an acrylic (made from a thermoplastic resin) jacket. The glass consists of a core, of refractive index n1, and a surrounding cladding, of refractive index n2, with n1 > n2. The index of the jacket is such that any light reachin ...
lecture_five_2016
... sheet. The sheet is stretched aligning molecules and causing them to be birefringent. The molecules selectively attach themselves to aligned polymer molecules, so that absorption is high in one plane and weak in the other. The transmitted beam is linearly polarized. 5.2.4 Polarization of scattered l ...
... sheet. The sheet is stretched aligning molecules and causing them to be birefringent. The molecules selectively attach themselves to aligned polymer molecules, so that absorption is high in one plane and weak in the other. The transmitted beam is linearly polarized. 5.2.4 Polarization of scattered l ...
... right, and average. In each case, you are looking for the smallest rotation angle between the reference minimum without the sample, and with the sample. The left and right reference minima differ by 180 degrees, but the magnitudes of the rotations should be equal. 3. Plot this data as a function of ...
Understanding Polarization
... Suppose the two components have equal amplitudes again, but now consider the case where these two components are not in phase, such that the angles of the sine functions are different. In particular, suppose there is a constant phase difference of /2 between them, which corresponds to a distance of ...
... Suppose the two components have equal amplitudes again, but now consider the case where these two components are not in phase, such that the angles of the sine functions are different. In particular, suppose there is a constant phase difference of /2 between them, which corresponds to a distance of ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester
... • constructive interference of wavelets scattered in forward direction. • Destructive interference of wavelets and incident light in the backward direction. True for low and high density substance ...
... • constructive interference of wavelets scattered in forward direction. • Destructive interference of wavelets and incident light in the backward direction. True for low and high density substance ...
Liquid Crystals
... Twisted Nematics and Light • The two components will experience different refraction indices, because both the two indices of refraction are perpendicular to one another and the two components of the wave are perpendicular to one another. • Therefore, by the very definition of refraction indices, o ...
... Twisted Nematics and Light • The two components will experience different refraction indices, because both the two indices of refraction are perpendicular to one another and the two components of the wave are perpendicular to one another. • Therefore, by the very definition of refraction indices, o ...
Polarization and Optical Properties of n-Layer Doped with Au Nanoparticles
... a deeper understanding of thin film structures. Antireflection coatings are the most common optical coating. They reduce the surface reflectivity and are usually designed for particular wavelength range and angle of incidence. In this paper, this subject is investigated. Multilayer structures that a ...
... a deeper understanding of thin film structures. Antireflection coatings are the most common optical coating. They reduce the surface reflectivity and are usually designed for particular wavelength range and angle of incidence. In this paper, this subject is investigated. Multilayer structures that a ...
Triple Refraction_and_Total_Internal_Reflection
... 1. Do the waves speed up or slow down as they move from the light blue medium to the dark blue medium? They slow down as they move from the light blue to the dark blue medium. 2. Do the waves change direction and what is this called? Yes, the waves do change direction. This is called refraction. 3. ...
... 1. Do the waves speed up or slow down as they move from the light blue medium to the dark blue medium? They slow down as they move from the light blue to the dark blue medium. 2. Do the waves change direction and what is this called? Yes, the waves do change direction. This is called refraction. 3. ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).