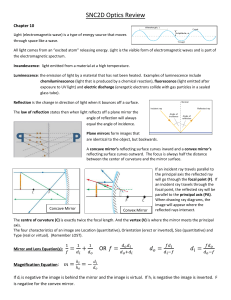
Magneto Optical Kerr Effect (MOKE)
... the electric field directions with respect to the plane of incidence of the light, as shown in Fig. 1 When the p or s-polarized light is reflected from a metallic surface the reflected light will still be linearly polarized (p or s). This is because the reflecting surface is a plane of symmetry for ...
... the electric field directions with respect to the plane of incidence of the light, as shown in Fig. 1 When the p or s-polarized light is reflected from a metallic surface the reflected light will still be linearly polarized (p or s). This is because the reflecting surface is a plane of symmetry for ...
Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani and Elite School of Optometry
... Course Objective: The objectives of this course are to describe the wave nature of light and apply the wave theory to explain classic phenomena such as interference, diffraction and polarization. Working of some optical instruments and a brief description of scattering and laser will also be include ...
... Course Objective: The objectives of this course are to describe the wave nature of light and apply the wave theory to explain classic phenomena such as interference, diffraction and polarization. Working of some optical instruments and a brief description of scattering and laser will also be include ...
Waves and Radiation
... In this case the light rays are slowed down by the water and are _____, causing the pen to look odd. The two mediums in this example are ______ and _______. Words – speed up, water, air, bent, medium ...
... In this case the light rays are slowed down by the water and are _____, causing the pen to look odd. The two mediums in this example are ______ and _______. Words – speed up, water, air, bent, medium ...
File
... Single slit diffraction pattern : It consist of central bright band surrounded on either side by alternate dark and bright bands with decreasing intensity. Half angular width of the central bright band θ = λ/a = x/ D where λ is wavelength of light a is width of slit x is half linear width of centra ...
... Single slit diffraction pattern : It consist of central bright band surrounded on either side by alternate dark and bright bands with decreasing intensity. Half angular width of the central bright band θ = λ/a = x/ D where λ is wavelength of light a is width of slit x is half linear width of centra ...
没有幻灯片标题
... natural light (unpolarized light) • The waves emitted by any one molecule may be linearly polarized, but any actual light source contains a tremendous number of molecules with random orientations, so the emitted light is a random mixture of waves linearly polarized in all possible transverse direct ...
... natural light (unpolarized light) • The waves emitted by any one molecule may be linearly polarized, but any actual light source contains a tremendous number of molecules with random orientations, so the emitted light is a random mixture of waves linearly polarized in all possible transverse direct ...
Refraction - Snell`s Law, Internal Reflection, Dispersion (PowerPoint)
... The fact that rainbows are semicircular tells you that the light from one has to come from the water drops at the right angle angle*. When white light enters a water drop light is refracted and disperses into its component colors. Violet is bent the most and red the least. When the rays reach the op ...
... The fact that rainbows are semicircular tells you that the light from one has to come from the water drops at the right angle angle*. When white light enters a water drop light is refracted and disperses into its component colors. Violet is bent the most and red the least. When the rays reach the op ...
Soleil-Babinet Compensator
... The variable retardance is achieved by adjusting the position of a long birefringent wedge with respect to a short fixed birefringent wedge. The wedge angle and fast axis orientation is the same for both wedges so that the retardance is uniform across the entire clear aperture of the Soleil-Babinet ...
... The variable retardance is achieved by adjusting the position of a long birefringent wedge with respect to a short fixed birefringent wedge. The wedge angle and fast axis orientation is the same for both wedges so that the retardance is uniform across the entire clear aperture of the Soleil-Babinet ...
physics
... 5. How does the diffraction limit the resolving power of an optical instrument? 6. What is a wavefront? What is the geometrical shape of the wavefront of light emerging out of a convex lens, when a point source is placed at its focus? 7. A ray of light is incident on the surface of a spherical glass ...
... 5. How does the diffraction limit the resolving power of an optical instrument? 6. What is a wavefront? What is the geometrical shape of the wavefront of light emerging out of a convex lens, when a point source is placed at its focus? 7. A ray of light is incident on the surface of a spherical glass ...
Optics - Mr. Gallagher's Physics
... • The reflected ray is the light ray that bounces off the mirror • Between the incident and reflected rays, there is an imaginary line called the normal line which is perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. • The angle between the incident ray and the normal line is called the angle of incidence ...
... • The reflected ray is the light ray that bounces off the mirror • Between the incident and reflected rays, there is an imaginary line called the normal line which is perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. • The angle between the incident ray and the normal line is called the angle of incidence ...
Here - Liquid Crystals and Photonics Group
... In today’s liquid crystal displays, white light is generated by LEDs, coupled to a waveguide plate and scattered towards the viewer with homogeneous intensity. This part of the display is called the backlight and then the light has to pass a scatter-free component with color filters, polarizers, liq ...
... In today’s liquid crystal displays, white light is generated by LEDs, coupled to a waveguide plate and scattered towards the viewer with homogeneous intensity. This part of the display is called the backlight and then the light has to pass a scatter-free component with color filters, polarizers, liq ...
Slow light in room-temperature optical waveguides
... Duke University, Department of Physics, Box 90305, Durham, NC, 27708, USA Over the last decade, there has been great progress in devising methods for tailoring the dispersion of optical materials, such as electromagnetically induced transparency, photonic crystals, and nano-optic resonators [1]. By ...
... Duke University, Department of Physics, Box 90305, Durham, NC, 27708, USA Over the last decade, there has been great progress in devising methods for tailoring the dispersion of optical materials, such as electromagnetically induced transparency, photonic crystals, and nano-optic resonators [1]. By ...
total internal reflection
... internal reflection. The critical angle for total internal reflection can be found by sin c = n2/n1. Total internal reflection can only occur on the side of an interface that has the greater index of refraction. Dr. Jie Zou ...
... internal reflection. The critical angle for total internal reflection can be found by sin c = n2/n1. Total internal reflection can only occur on the side of an interface that has the greater index of refraction. Dr. Jie Zou ...
4.3 Wave characteristics
... • The intensity of polarised light that passes through a polarizer is proportional to the square of the cosine of the angle between the electric field of the polarized light and the angle of the polarizer! ...
... • The intensity of polarised light that passes through a polarizer is proportional to the square of the cosine of the angle between the electric field of the polarized light and the angle of the polarizer! ...
Anisotropy - IIT Kanpur
... Possible Explanation Optical Alignment can also be explained by a pseudoscalar field. As the EM wave passes through large scale magnetic field, photons (polarized parallel to transverse magnetic field) ...
... Possible Explanation Optical Alignment can also be explained by a pseudoscalar field. As the EM wave passes through large scale magnetic field, photons (polarized parallel to transverse magnetic field) ...
Single Slit Diffraction & Gratings
... the information on the CD The two first-order maxima are used for steering ...
... the information on the CD The two first-order maxima are used for steering ...
Image formation with broad bundles of rays
... The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same for the different rays. The optical path length y is the same for all these rays. ...
... The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same for the different rays. The optical path length y is the same for all these rays. ...
Energy Flow and Poynting Vector
... intuitively clear linear polarization and now progressed to circular polarization by superimposing two special linearly polarized waves. Of course, we can produce two basic kinds of circular polarization: left-handed and right-handed circular polarized light this way. Equally of course, we can now s ...
... intuitively clear linear polarization and now progressed to circular polarization by superimposing two special linearly polarized waves. Of course, we can produce two basic kinds of circular polarization: left-handed and right-handed circular polarized light this way. Equally of course, we can now s ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).