Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester Lecture 27 – Geometric Optics
... to describe propagation of rays through any compound system Note: any ray passing through the first principal plane will emerge at the same height at the second principal plane For 2 lenses (above): Example: page 246 ...
... to describe propagation of rays through any compound system Note: any ray passing through the first principal plane will emerge at the same height at the second principal plane For 2 lenses (above): Example: page 246 ...
Unusually large polarizabilities of excited states of Ba
... A test of the spin statistics theorem (SST) for photons. What is the SST? ...
... A test of the spin statistics theorem (SST) for photons. What is the SST? ...
A1982PU06800001
... we received letters from Tatarski, M. Beran, and D.M. Chase pointing out that we had not correctly proved our solution to be the only one possible. Chase’s discussion was the most com3 plete and the one published. “The problem was caused by an extra term in the solution arising from a possible stati ...
... we received letters from Tatarski, M. Beran, and D.M. Chase pointing out that we had not correctly proved our solution to be the only one possible. Chase’s discussion was the most com3 plete and the one published. “The problem was caused by an extra term in the solution arising from a possible stati ...
Chromatic Dispersion
... you grind your particles into, there will be enough grazing-incidence surfaces to guarantee satisfactory discrimination between index-matched and non-indexmatched rays. The use of Christansen filters as passband filters was common before the second World War. It’s easy to see why, if you look at a b ...
... you grind your particles into, there will be enough grazing-incidence surfaces to guarantee satisfactory discrimination between index-matched and non-indexmatched rays. The use of Christansen filters as passband filters was common before the second World War. It’s easy to see why, if you look at a b ...
Polymer Based Photonic Crystals
... co-extruded films is the occurrence of undesired thickness variations, which result in a broadening of the reflection spectrum and also unwanted higher order reflections. The addition of a third material of interFig. 1. a) Top: Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of spherical domains produced i ...
... co-extruded films is the occurrence of undesired thickness variations, which result in a broadening of the reflection spectrum and also unwanted higher order reflections. The addition of a third material of interFig. 1. a) Top: Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of spherical domains produced i ...
Effect of temperature on the refractive index and Kerr effect of the
... electric breakdown, the sample is often placed in a bath containing a liquid which does not solve the crystal. In measurements of electrooptic properties based on interferometric methods the use of two immersion media with different refractive indices makes also possible to evaluate changes in the o ...
... electric breakdown, the sample is often placed in a bath containing a liquid which does not solve the crystal. In measurements of electrooptic properties based on interferometric methods the use of two immersion media with different refractive indices makes also possible to evaluate changes in the o ...
Determination of Absolute Values of Refractive Index of Liquids
... where θ and θ0 are the incidence angles of the reference and signal beam, α is the inner incidence angle of the signal and x, y are the distances between reflections (compare Fig. 3). The constants s1 and s2 represent contributions from glass plates which will not enter the final result. The inciden ...
... where θ and θ0 are the incidence angles of the reference and signal beam, α is the inner incidence angle of the signal and x, y are the distances between reflections (compare Fig. 3). The constants s1 and s2 represent contributions from glass plates which will not enter the final result. The inciden ...
Optical Low-pass Filter
... Pseudo-signal: Generated by solid-state image pickup devices, pseudo-signals causes horizontal lines to look jagged or the black-and-white lattice fringe to be colored. ...
... Pseudo-signal: Generated by solid-state image pickup devices, pseudo-signals causes horizontal lines to look jagged or the black-and-white lattice fringe to be colored. ...
Martti Kauranen , 1182 (2013); DOI: 10.1126/science.1247622
... beam. To maximize macroscopic nonlinear sig- Phase matching for second harmonic (SH) generation. The spatial oscillations of the fundamental wave and SH source polarizanals, the wavelets emitted tion are shown by red and blue lines, respectively; green lines indicate SH wavelets. (A) An elementary S ...
... beam. To maximize macroscopic nonlinear sig- Phase matching for second harmonic (SH) generation. The spatial oscillations of the fundamental wave and SH source polarizanals, the wavelets emitted tion are shown by red and blue lines, respectively; green lines indicate SH wavelets. (A) An elementary S ...
Chapter 37 Wave Optics (I)
... When light is incident normally on the boundary between air (n=1) and glass (n=1.5), about 4% of the energy is reflected and 96% is transmitted. Thus, a camera with 6 lenses has 12 air-glass interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize ...
... When light is incident normally on the boundary between air (n=1) and glass (n=1.5), about 4% of the energy is reflected and 96% is transmitted. Thus, a camera with 6 lenses has 12 air-glass interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize ...
Why do scientists grow crystals? - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web
... X-ray crystallography is a method for determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal. ...
... X-ray crystallography is a method for determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal. ...
Lab 11 - Optical Ray Tracing
... In the previous exercise, the phenomenon of spherical aberration was observed as a slight divergence at the ideal focal point. This is due to the fact that rays striking the edges of the len are refracted more strongly that the paraxial ones. A quick remedy is to use an iris to block off the perimet ...
... In the previous exercise, the phenomenon of spherical aberration was observed as a slight divergence at the ideal focal point. This is due to the fact that rays striking the edges of the len are refracted more strongly that the paraxial ones. A quick remedy is to use an iris to block off the perimet ...
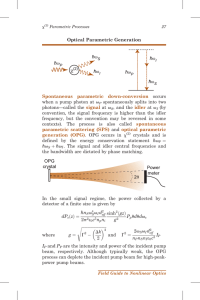
Optical Parametric Generation Spontaneous parametric down
... is chosen to allow rotation of the phase-matching angle, while keeping the azimuthal angle (angle between X axis and k vector) fixed. For interactions confined to the principal planes of a biaxial crystal, the phase-matching angle is defined to be between one of the principal axes and the laser k ve ...
... is chosen to allow rotation of the phase-matching angle, while keeping the azimuthal angle (angle between X axis and k vector) fixed. For interactions confined to the principal planes of a biaxial crystal, the phase-matching angle is defined to be between one of the principal axes and the laser k ve ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester Lecture 28 – Geometric Optics
... to describe propagation of rays through any compound system Note: any ray passing through the first principal plane will emerge at the same height at the second principal plane For 2 lenses (above): Example: page 246 ...
... to describe propagation of rays through any compound system Note: any ray passing through the first principal plane will emerge at the same height at the second principal plane For 2 lenses (above): Example: page 246 ...
PowerPoint lectures on Optical Mineralogy, by J. Winter
... Plane polarized light enters xl. & resolved into 2 rays (if not || optic axis), which vibrate ^ each other & travel at different velocities (since have different n) Will thus travel diff # of l (even if frequency same or similar) So if in phase when enter, won't be when exit!! The path diff (D ...
... Plane polarized light enters xl. & resolved into 2 rays (if not || optic axis), which vibrate ^ each other & travel at different velocities (since have different n) Will thus travel diff # of l (even if frequency same or similar) So if in phase when enter, won't be when exit!! The path diff (D ...
9-5 Huygens principle
... Snell’s law Light traveling from a low-index material to a high-index material will bend towards the normal ...
... Snell’s law Light traveling from a low-index material to a high-index material will bend towards the normal ...
ECE 463/626: Optoelectronics Instructor: Prof. H. Grebel, Rm 302
... 40%; Final: 40%; Research paper: 15%; HW: 5% Honor code: The NJIT honor code will be upheld and that any violations will be brought to the immediate attention of the Dean of Students. Week ...
... 40%; Final: 40%; Research paper: 15%; HW: 5% Honor code: The NJIT honor code will be upheld and that any violations will be brought to the immediate attention of the Dean of Students. Week ...
GRADE 10 SA2 PHYSICS revision worksheet-2
... Use lens formula of determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm. 9.(a) An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the position and nature of the image. (b) Define refractive index. Light en ...
... Use lens formula of determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm. 9.(a) An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the position and nature of the image. (b) Define refractive index. Light en ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).