Cheng - The University of Akron
... • Photonics: “The technology of generating and harnessing light and other forms of radiant energy whose quantum unit is the photon.”1 • Photonic Crystals: (photonic band gap materials), are materials with periodic variation of refractive index. A photonic crystal can control the flow of electromagne ...
... • Photonics: “The technology of generating and harnessing light and other forms of radiant energy whose quantum unit is the photon.”1 • Photonic Crystals: (photonic band gap materials), are materials with periodic variation of refractive index. A photonic crystal can control the flow of electromagne ...
Physics - No Brain Too Small
... When light travels from a medium to a less dense medium, a certain angle of incidence will produce an angle of refraction of 90o. This angle of incidence is the critical angle for this material. If the angle of incidence > critical angle, then total internal reflection occurs. Less than the critic ...
... When light travels from a medium to a less dense medium, a certain angle of incidence will produce an angle of refraction of 90o. This angle of incidence is the critical angle for this material. If the angle of incidence > critical angle, then total internal reflection occurs. Less than the critic ...
optical fiber communication - GTU e
... LEDs are suitable primarily for local-area-network applications with bit rates of 10-100 Mbit/s and transmission distances of a few kilometers. ...
... LEDs are suitable primarily for local-area-network applications with bit rates of 10-100 Mbit/s and transmission distances of a few kilometers. ...
Sample
... fibers (using the total internal reflection model), and other properties of fibers and optical components. ...
... fibers (using the total internal reflection model), and other properties of fibers and optical components. ...
The Very Basics of Geometric Optics 5.1.2 Basic Geometric Optics
... lenses allow to manipulate the light path, e.g. by focusing a parallel beam of light as shown. Let's clarify the terms at this point: Reflection is, well, reflection; always with "angle in" = "angle out". Refraction is the sudden "bending" or "flexing" of light beams at the interface between two dif ...
... lenses allow to manipulate the light path, e.g. by focusing a parallel beam of light as shown. Let's clarify the terms at this point: Reflection is, well, reflection; always with "angle in" = "angle out". Refraction is the sudden "bending" or "flexing" of light beams at the interface between two dif ...
a collection of problems about light rays, refraction and rainbows
... and rainbows get their colour. (i) Estimate the angular width of a rainbow. (ii) Why is a rainbow darkest just outside the blue band? (b) We have considered a drop in the sky at an angle χm to the direction of the Sun’s rays. Drops anywhere on a circle subtending χm to the eye with the Sun shining p ...
... and rainbows get their colour. (i) Estimate the angular width of a rainbow. (ii) Why is a rainbow darkest just outside the blue band? (b) We have considered a drop in the sky at an angle χm to the direction of the Sun’s rays. Drops anywhere on a circle subtending χm to the eye with the Sun shining p ...
Optical properties
... Here impurities such as boron oxide (B2O3) or germanium dioxide /GeO2) are added to the silica glass such that the index of refraction varied gradually in parabolic manner across the cross section. This enables light to travel faster while close to the periphery than at the center. This avoids pul ...
... Here impurities such as boron oxide (B2O3) or germanium dioxide /GeO2) are added to the silica glass such that the index of refraction varied gradually in parabolic manner across the cross section. This enables light to travel faster while close to the periphery than at the center. This avoids pul ...
PDF Link
... The dispersion relation is fundamental to a physical phenomenon that develops in both space and time. This equation connects the spatial and temporal frequencies involved in the dynamic process through the material constants. Electromagnetic plane waves propagating in homogeneous media are bound by ...
... The dispersion relation is fundamental to a physical phenomenon that develops in both space and time. This equation connects the spatial and temporal frequencies involved in the dynamic process through the material constants. Electromagnetic plane waves propagating in homogeneous media are bound by ...
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Polarization
... light immediately after the second polarizer and repeat the experiment that you just did, measuring the intensity of the light reflected off of the front surface of the prism for a variety of angles. Calculate where you expect Brewster’s angle to be (Prism 1 has an index of refraction n(520.8 nm) = ...
... light immediately after the second polarizer and repeat the experiment that you just did, measuring the intensity of the light reflected off of the front surface of the prism for a variety of angles. Calculate where you expect Brewster’s angle to be (Prism 1 has an index of refraction n(520.8 nm) = ...
Week4-figs
... Historical Development: Ray Optics → Wave Optics → EM Optics → Quantum Optics. • Ray Optics is an approximation of Wave Optics in which wavelength short compared to other dimensions (focal lengths, diameter of optical components, etc.) so that Diffraction can be ignored. ...
... Historical Development: Ray Optics → Wave Optics → EM Optics → Quantum Optics. • Ray Optics is an approximation of Wave Optics in which wavelength short compared to other dimensions (focal lengths, diameter of optical components, etc.) so that Diffraction can be ignored. ...
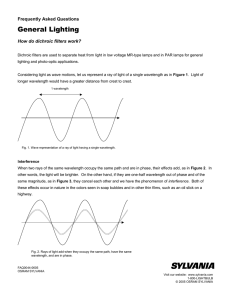
How do Dichroic Filters work?
... When the film has a thickness equal to ¼ wavelength, the ray c will be reflected with change of phase, and will therefore add to ray a, increasing the brightness of the reflection. These results also occur when the thickness is multiple of ¼ wavelength. As a general rule, therefore, for a particular ...
... When the film has a thickness equal to ¼ wavelength, the ray c will be reflected with change of phase, and will therefore add to ray a, increasing the brightness of the reflection. These results also occur when the thickness is multiple of ¼ wavelength. As a general rule, therefore, for a particular ...
20170327_AH_Interference
... Two waves are said to be coherent if they have a constant phase relationship. For two waves travelling in air to have a constant phase relationship, they must have the same frequency and wavelength. At any given point, the phase difference between the two waves will be fixed. For us to see interfere ...
... Two waves are said to be coherent if they have a constant phase relationship. For two waves travelling in air to have a constant phase relationship, they must have the same frequency and wavelength. At any given point, the phase difference between the two waves will be fixed. For us to see interfere ...
NON-LINEAR MATERIALS Definition
... absorption and scattering when the light pulse propagates through the fibre. It is, now-a-days, possible to fabricate fibres which amplify the light signal propagating through it. They are called fibre amplifiers. By pumping the atoms inside the fibre by sending a pump beam, population inversion is ...
... absorption and scattering when the light pulse propagates through the fibre. It is, now-a-days, possible to fabricate fibres which amplify the light signal propagating through it. They are called fibre amplifiers. By pumping the atoms inside the fibre by sending a pump beam, population inversion is ...
Needle-based reflection refractometry of scattering samples using
... ng = l / d. In addition to its use for bulk measurement, this method has been combined with direct and computed tomography techniques to form cross-sectional refractive index images.[16-18] In addition to precise pathlength sensing, coherent techniques may also be used map reflection amplitudes, a ...
... ng = l / d. In addition to its use for bulk measurement, this method has been combined with direct and computed tomography techniques to form cross-sectional refractive index images.[16-18] In addition to precise pathlength sensing, coherent techniques may also be used map reflection amplitudes, a ...
Polarization radiation from the accretion disk and
... rotating accretion disk . Temperature in the inner parts of the disk can reach 106 K. The accretion rate is so high that the material does not have time to settle on the surface of the white dwarf. Accumulation of material in the disk leads to its instability and explosion, observed as New flash . I ...
... rotating accretion disk . Temperature in the inner parts of the disk can reach 106 K. The accretion rate is so high that the material does not have time to settle on the surface of the white dwarf. Accumulation of material in the disk leads to its instability and explosion, observed as New flash . I ...
Non-Linear Optics Lecture 3: Achieving Phase Matching Learning
... importance for non-linear optics. Remember that phase matching occurs when a constant phase relationship is maintained between the generated and propagating waves. In general, this does not occur, so a repeated build up and decline of radiation is observed with a characteristic length given by the c ...
... importance for non-linear optics. Remember that phase matching occurs when a constant phase relationship is maintained between the generated and propagating waves. In general, this does not occur, so a repeated build up and decline of radiation is observed with a characteristic length given by the c ...
POLARIZATION
... components as shown in Figure 1. This may be due to the arrangement of power input leads to various points on a flat antenna, or due to an interaction of active elements in an array, or many other reasons. The geometric figure traced by the sum of the electric field vectors over time is, in general, ...
... components as shown in Figure 1. This may be due to the arrangement of power input leads to various points on a flat antenna, or due to an interaction of active elements in an array, or many other reasons. The geometric figure traced by the sum of the electric field vectors over time is, in general, ...
Optical Scientist - Corning
... Design, execute and support ongoing projects in the general area of light management, waveguides and devices. Specific projects include characterization and optimization of light scattering from thin films, measurement of glass optical properties, fiber optics and optical communications. Areas of sp ...
... Design, execute and support ongoing projects in the general area of light management, waveguides and devices. Specific projects include characterization and optimization of light scattering from thin films, measurement of glass optical properties, fiber optics and optical communications. Areas of sp ...
Shaping optical space with metamaterials
... The fabrication of miniature metal helices as a metamaterial sensitive to optical or IR frequencies, however, remained out of reach until last year. Thanks to direct laser writing (DLW), which can be viewed as the 3D analog of 2D electron-beam lithography, one can tightly focus femtosecond laser pul ...
... The fabrication of miniature metal helices as a metamaterial sensitive to optical or IR frequencies, however, remained out of reach until last year. Thanks to direct laser writing (DLW), which can be viewed as the 3D analog of 2D electron-beam lithography, one can tightly focus femtosecond laser pul ...
POLARIZATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
... The LPlp modes count the group of modes appearing together as a single mode and they are an example of pseudo-modes with the property of changing their cross-sectional intensity and polarization pattern as the mode propagates. However, the LPl p modes are superpositions of the true, generally hybrid ...
... The LPlp modes count the group of modes appearing together as a single mode and they are an example of pseudo-modes with the property of changing their cross-sectional intensity and polarization pattern as the mode propagates. However, the LPl p modes are superpositions of the true, generally hybrid ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).