Document
... Flint glass is an optical glass that has relatively high refractive index and low Abbe number. Flint glasses are arbitrarily defined as having an Abbe number of 50 to 55 or less. The currently known flint glasses have refractive indices ranging between 1.45-2.00. A concave lens of flint glass is com ...
... Flint glass is an optical glass that has relatively high refractive index and low Abbe number. Flint glasses are arbitrarily defined as having an Abbe number of 50 to 55 or less. The currently known flint glasses have refractive indices ranging between 1.45-2.00. A concave lens of flint glass is com ...
Observation of optical polarization Möbius strips
... propagates, the polarization ellipses change in the transverse plane because TEM00 and LG0,T1 possess different Gouy phases (8). The polarization topology of the beam remains unchanged but undergoes a global rotation that depends on the propagation distance. Furthermore, the C-line coincides with th ...
... propagates, the polarization ellipses change in the transverse plane because TEM00 and LG0,T1 possess different Gouy phases (8). The polarization topology of the beam remains unchanged but undergoes a global rotation that depends on the propagation distance. Furthermore, the C-line coincides with th ...
slides - Smith Lab
... Two basic types of lenses are convex and concave. A convex lens, also known as a plus power lens, focuses light behind the lens; whereas, a concave lens, also known as a minus power lens, focuses light in front of the lens. The power of a lens is measured in Diopters (D) and reflects the focusing di ...
... Two basic types of lenses are convex and concave. A convex lens, also known as a plus power lens, focuses light behind the lens; whereas, a concave lens, also known as a minus power lens, focuses light in front of the lens. The power of a lens is measured in Diopters (D) and reflects the focusing di ...
Optical Fiber Communication
... Maxwells eqs are solved with the BC defined by above to find the mode of propagation. ...
... Maxwells eqs are solved with the BC defined by above to find the mode of propagation. ...
Training modules for an advanced interactive course on
... 3.2. The internet version of the same material Material presented on the internet has advantages of the possibility of the use of unlimited colour at no extra cost. It gives the opportunity for the user to flick through images sufficiently fast to give the impression of motion, thereby in effect add ...
... 3.2. The internet version of the same material Material presented on the internet has advantages of the possibility of the use of unlimited colour at no extra cost. It gives the opportunity for the user to flick through images sufficiently fast to give the impression of motion, thereby in effect add ...
Titel
... Gratings Transmission gratings The incident light is transmitted through the slits Due to diffraction (narrow slits) the light is Transmission transmitted in all direction gratings Each slit becomes a secondary source of light A constructive interference will be created on the image plane o ...
... Gratings Transmission gratings The incident light is transmitted through the slits Due to diffraction (narrow slits) the light is Transmission transmitted in all direction gratings Each slit becomes a secondary source of light A constructive interference will be created on the image plane o ...
Miniaturized Fiber-Optic Fabry-Perot Interferometer for Highly
... interests include fiber-optic passive and active optical sensors. Tao Zhu was born in Sichuan Province, China, in 1976. He received the M.S. and Ph.D. degrees from the Chongqing University, Chongqing, in 2003 and 2008, respectively, both in optical engineering. He is a member of the Optical Society ...
... interests include fiber-optic passive and active optical sensors. Tao Zhu was born in Sichuan Province, China, in 1976. He received the M.S. and Ph.D. degrees from the Chongqing University, Chongqing, in 2003 and 2008, respectively, both in optical engineering. He is a member of the Optical Society ...
Tristate and Gate Using Photonic Crystal
... when intense light propagates in crystals and glasses, but also in other media such as gases. Its physical origin is a nonlinear polarization generated in the medium, which itself modifies the propagation properties of the light. In particular, the refractive index for the high intensity light beam ...
... when intense light propagates in crystals and glasses, but also in other media such as gases. Its physical origin is a nonlinear polarization generated in the medium, which itself modifies the propagation properties of the light. In particular, the refractive index for the high intensity light beam ...
Electromagnetic processes in dispersive media
... electromagnetic wave pass through a media? • Mechanical properties of the media • Concepts like grope velocity, dispersion, birefringence, … Electric field ...
... electromagnetic wave pass through a media? • Mechanical properties of the media • Concepts like grope velocity, dispersion, birefringence, … Electric field ...
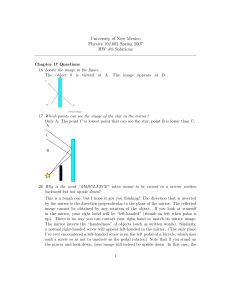
HW #8 Solutions
... (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is equal to the incident intensity. 15 Waves that are refracted towards the normal at a boundary have a shorter wavelength than the wave incident to the boundary. What does this say about the speed of light in glass versus air? Since the frequency is constant, the r ...
... (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is equal to the incident intensity. 15 Waves that are refracted towards the normal at a boundary have a shorter wavelength than the wave incident to the boundary. What does this say about the speed of light in glass versus air? Since the frequency is constant, the r ...
ray_optics_su2014
... •Run straight to river, then swim •Run further to shore adjacent swimmer then swim ...
... •Run straight to river, then swim •Run further to shore adjacent swimmer then swim ...
Optical processes
... normals populates the annulus of solid angle sin(α)dα will be proportional to a gaussian of SigmaAlpha: theOpSurface -> SetSigmaAlpha(0.1); where sigma_alpha is in [rad] In the GLISUR model this is indicated by the value of polish; when it is <1, then a random point is generated in a sphere of radiu ...
... normals populates the annulus of solid angle sin(α)dα will be proportional to a gaussian of SigmaAlpha: theOpSurface -> SetSigmaAlpha(0.1); where sigma_alpha is in [rad] In the GLISUR model this is indicated by the value of polish; when it is <1, then a random point is generated in a sphere of radiu ...
Geometrical Optics
... then it is refracted toward the normal. If the ray enters from the optically more dense medium, it is refracted away from the normal. In that case, the maximum possible angle of refraction is 90° (along the interface) and the corresponding angle of incidence is then (from Eq. 1): ...
... then it is refracted toward the normal. If the ray enters from the optically more dense medium, it is refracted away from the normal. In that case, the maximum possible angle of refraction is 90° (along the interface) and the corresponding angle of incidence is then (from Eq. 1): ...
Refraction
... Total internal reflection and optical fibres Light enters the fibre at an angle greater than the critical angle. Total internal reflection occurs and the ray is reflected in such a way as to ensure continued total internal reflection. ...
... Total internal reflection and optical fibres Light enters the fibre at an angle greater than the critical angle. Total internal reflection occurs and the ray is reflected in such a way as to ensure continued total internal reflection. ...
The Critical Angle and Beyond - The Society of Vacuum Coaters
... The mean power transported by a plane harmonic light wave is proportional to the product of the electric and magnetic field amplitudes and the cosine of their phase difference. The wave that is evanescent in the z-direction does have components of both electric and magnetic field in the x-y plane bu ...
... The mean power transported by a plane harmonic light wave is proportional to the product of the electric and magnetic field amplitudes and the cosine of their phase difference. The wave that is evanescent in the z-direction does have components of both electric and magnetic field in the x-y plane bu ...
Ray Optics at a Deep-Subwavelength Scale: A Transformation Optics Approach Seunghoon Han,
... Information). Thin multilayers made up of positive index material (ε1 ) 2, µ1 ) 1, e.g., glass) and negative index material (ε2 ) -1.98 + 0.02i, µ2 ) -0.99 - 0.01i) were considered with the filling ratio p set as 1:2. Regarding the constitutional low-loss homogeneous negative index material, there a ...
... Information). Thin multilayers made up of positive index material (ε1 ) 2, µ1 ) 1, e.g., glass) and negative index material (ε2 ) -1.98 + 0.02i, µ2 ) -0.99 - 0.01i) were considered with the filling ratio p set as 1:2. Regarding the constitutional low-loss homogeneous negative index material, there a ...
6.1 Electromagnetic Waves
... which in turn is determined by the refractive index • electromagnetic radiation is characterized by both an electric field and magnetic field ...
... which in turn is determined by the refractive index • electromagnetic radiation is characterized by both an electric field and magnetic field ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).