Greg A. Smith - curriculum vitae
... - depolarization - stress birefringence - rigorous coupled wave analysis (RCWA) Computer Skills - Solidwoks certified (CSWA - August 2009 - #C-93URMTLMYW) - ASAP & Photon Engineering tutorials - Mathematica / MatLab / C / MathCad - LabView hardware (GPIB, NI-DAQ) & user-interface improvements - PCs ...
... - depolarization - stress birefringence - rigorous coupled wave analysis (RCWA) Computer Skills - Solidwoks certified (CSWA - August 2009 - #C-93URMTLMYW) - ASAP & Photon Engineering tutorials - Mathematica / MatLab / C / MathCad - LabView hardware (GPIB, NI-DAQ) & user-interface improvements - PCs ...
Optical Fiber Communications Assignments From Senior.pdf
... © 1999 S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics (Prentice Hall) ...
... © 1999 S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics (Prentice Hall) ...
I news & views
... number generation at bit rates several orders of magnitude higher than those of electronic schemes has been achieved using chaotic lasers by exploiting their random-like output and applying suitable post-processing 6. Finally, the high entropy of chaotic light scattering in asymmetric optical resona ...
... number generation at bit rates several orders of magnitude higher than those of electronic schemes has been achieved using chaotic lasers by exploiting their random-like output and applying suitable post-processing 6. Finally, the high entropy of chaotic light scattering in asymmetric optical resona ...
Laser and its applications
... ray keeps passing through the center of the fiber it is known as a meridional ray. Other guided rays are possible which do not pass through the center. These are known as skew rays, and they describe angular helices as sketched in Fig. 3. Let us now examine what happens to a meridional ray when it l ...
... ray keeps passing through the center of the fiber it is known as a meridional ray. Other guided rays are possible which do not pass through the center. These are known as skew rays, and they describe angular helices as sketched in Fig. 3. Let us now examine what happens to a meridional ray when it l ...
2.1. Specifications and designs
... graded index designs need more thickness for the same optical density then the HL stack. However, the advantage of the gradient index approach is better sidelobes and ripple suppression, specially in the case of the rugate design. The hybrid design has simpler refractive index profile compared to th ...
... graded index designs need more thickness for the same optical density then the HL stack. However, the advantage of the gradient index approach is better sidelobes and ripple suppression, specially in the case of the rugate design. The hybrid design has simpler refractive index profile compared to th ...
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Grating Interference by Thin
... incident ray • Ray 2, which is reflected from the lower surface, undergoes no phase change with respect to the incident wave ...
... incident ray • Ray 2, which is reflected from the lower surface, undergoes no phase change with respect to the incident wave ...
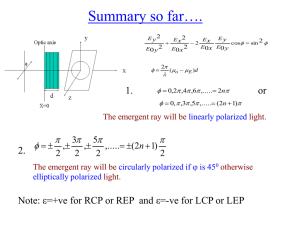
optically active substances.
... Fresnel’s theory of optical rotation On emergence from an optically active substance the two circular vibrations recombine to give plane polarized light whose plane of vibration has been rotated w.r.t that of incident light through a certain angle depends on the phase diff between the two vibration ...
... Fresnel’s theory of optical rotation On emergence from an optically active substance the two circular vibrations recombine to give plane polarized light whose plane of vibration has been rotated w.r.t that of incident light through a certain angle depends on the phase diff between the two vibration ...
In the figure shown above, an object is placed a distance in front of a
... determine the location of the image due to the lens (technically two rays should suffice): 1. Parallel to the optical axis through the focus 2. Through the focus and then parallel to the optical axis 3. Through the optical center ...
... determine the location of the image due to the lens (technically two rays should suffice): 1. Parallel to the optical axis through the focus 2. Through the focus and then parallel to the optical axis 3. Through the optical center ...
Two arfvedsonitic rhyolite intrusions from Cloghaneely, Co
... and fl; and, instead of having y - b and negative sign, would now have fi -- b with positive sign. Since type (ii) bears just this sort of relationship to type (i), it seems reasonable that both should be termed arfvedsonite. It is clear from the absorption formulae given above that, but for the re- ...
... and fl; and, instead of having y - b and negative sign, would now have fi -- b with positive sign. Since type (ii) bears just this sort of relationship to type (i), it seems reasonable that both should be termed arfvedsonite. It is clear from the absorption formulae given above that, but for the re- ...
Refractive Index Measurement within a Photonic Crystal Fibre Based on Short Wavelength Diffraction
... structure. The amount of evanescent field is negligible in comparison to the scattered light, as was demonstrated with a HeNe laser. However, a small amount of error will be introduced though the final results indicate this is not significant and can in principle be calibrated out. The hole fraction ...
... structure. The amount of evanescent field is negligible in comparison to the scattered light, as was demonstrated with a HeNe laser. However, a small amount of error will be introduced though the final results indicate this is not significant and can in principle be calibrated out. The hole fraction ...
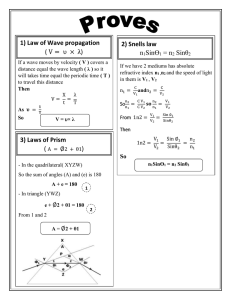
Ray Theory
... Huygen's Principle: An expanding wavefront is generated as the sum of contributions of individual point sources. ...
... Huygen's Principle: An expanding wavefront is generated as the sum of contributions of individual point sources. ...
DISPERSIVE BIREFRINGENT FILTERS Pochi YEH 1. Introduction
... polarized parallel to the fast and slow axes of the crystal when radiation passes through it. Since the phase retardation introduced by a wave plate is proportional to the birefringence of the crystal. It is desirable to have crystals with large birefringence (n, -. no) for filter construction. Curr ...
... polarized parallel to the fast and slow axes of the crystal when radiation passes through it. Since the phase retardation introduced by a wave plate is proportional to the birefringence of the crystal. It is desirable to have crystals with large birefringence (n, -. no) for filter construction. Curr ...
The page, which you have just visited, was created for students of
... Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects are made however in practice there is no single correct scientific meaning; each field uses the term in different and often contradictory ways. As we know, matter is existed in four states (or phases): solid, liquid, gas and pl ...
... Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects are made however in practice there is no single correct scientific meaning; each field uses the term in different and often contradictory ways. As we know, matter is existed in four states (or phases): solid, liquid, gas and pl ...
Stellar Activity with SONG
... ALFOSC has a polarimetry unit FAPOL which can be equiped either with half wave plate (linear polarisation) or quater wave plate (cicular + linear polarisation) A calcite plate is needed in the aperture wheel to provide a simultaneous measurement of the ordinary and the extraordinary components. The ...
... ALFOSC has a polarimetry unit FAPOL which can be equiped either with half wave plate (linear polarisation) or quater wave plate (cicular + linear polarisation) A calcite plate is needed in the aperture wheel to provide a simultaneous measurement of the ordinary and the extraordinary components. The ...
Document
... successive compressions or rarefactions 19- Wave length ( λ ) : it is the distance between any 2 successive points having the same phase - it’s the distance covered by the wave in one periodic time 20- Electromagnetic waves: they are transverse waves consist of electric field and magnetic fields hav ...
... successive compressions or rarefactions 19- Wave length ( λ ) : it is the distance between any 2 successive points having the same phase - it’s the distance covered by the wave in one periodic time 20- Electromagnetic waves: they are transverse waves consist of electric field and magnetic fields hav ...
OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS
... energies beginning effectively from zero energy. This usually involves the absorption or emission of phonons to conserve momentum. In this process the electrons move between energy states in the same band. The intraband transitions can only occur in metals, and they are responsible for the high refl ...
... energies beginning effectively from zero energy. This usually involves the absorption or emission of phonons to conserve momentum. In this process the electrons move between energy states in the same band. The intraband transitions can only occur in metals, and they are responsible for the high refl ...
Full Article
... One reason for silicone’s versatility is due to the relatively large bond angles2 of the repeating helical silicon-oxygen (Si-O) bonds on the polymer backbone and the variability of the substituent, or R’, groups attached to the open valences of the silicon atoms. The bond angles yield large amounts ...
... One reason for silicone’s versatility is due to the relatively large bond angles2 of the repeating helical silicon-oxygen (Si-O) bonds on the polymer backbone and the variability of the substituent, or R’, groups attached to the open valences of the silicon atoms. The bond angles yield large amounts ...
Rev.Sci.Instrum.
... layer system. In favorable cases the thickness can be determined to within sub-nm accuracy. Despite the apparent similarities between these techniques as far as the parameters measured are concerned, individual features of each technique can be exploited for a given experimental task. Due to each me ...
... layer system. In favorable cases the thickness can be determined to within sub-nm accuracy. Despite the apparent similarities between these techniques as far as the parameters measured are concerned, individual features of each technique can be exploited for a given experimental task. Due to each me ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).