Light Propagation in optical Fibres
... The ray theory appears to allow rays at any angle ϕ greater than the critical angle ϕc to propagate along the fibre. However, when the interference effect due to the phase of the plane associated with the ray is taken into account, it is seen that only waves at certain discrete angles greater than o ...
... The ray theory appears to allow rays at any angle ϕ greater than the critical angle ϕc to propagate along the fibre. However, when the interference effect due to the phase of the plane associated with the ray is taken into account, it is seen that only waves at certain discrete angles greater than o ...
Low threshold edge emitting polymer distributed feedback laser based on
... We report the demonstration of a low-threshold, edge-emitting polymer distributed feedback laser based on a square lattice. The lattice constant was 268 nm, which corresponds to a lattice line spacing in the ⌫M symmetry direction of the Brillouin zone of 189 nm. The latter was employed to provide fe ...
... We report the demonstration of a low-threshold, edge-emitting polymer distributed feedback laser based on a square lattice. The lattice constant was 268 nm, which corresponds to a lattice line spacing in the ⌫M symmetry direction of the Brillouin zone of 189 nm. The latter was employed to provide fe ...
ECE 4362: Modern Optics for Engineers Credit / Contact hours: Course coordinator:
... Catalog description: Modern concepts in optics related to engineering applications. Geometrical optics, matrix methods in optics; Polarization, interference, coherence, and lasers; Fourier optics, Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction. Pre-requisite(s) or co-requisite: ECE 3323, ECE 3342 Designation: E ...
... Catalog description: Modern concepts in optics related to engineering applications. Geometrical optics, matrix methods in optics; Polarization, interference, coherence, and lasers; Fourier optics, Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction. Pre-requisite(s) or co-requisite: ECE 3323, ECE 3342 Designation: E ...
Introduction to Metamaterials
... refractive index of a substance, solid or liquid, to that of air — so far as all practical purposes are ...
... refractive index of a substance, solid or liquid, to that of air — so far as all practical purposes are ...
Three-year WMAP Observations: Method and Results
... During the radiation dominated epoch, even CDM fluctuations cannot grow (the expansion of the Universe is too fast); thus, dark matter potential gets shallower and shallower as the Universe expands --> potential decay --> ISW --> Boost Cl. ...
... During the radiation dominated epoch, even CDM fluctuations cannot grow (the expansion of the Universe is too fast); thus, dark matter potential gets shallower and shallower as the Universe expands --> potential decay --> ISW --> Boost Cl. ...
Direct index of refraction measurement at extreme
... The absorptive part β(ω) of the refractive index at EUV wavelengths is well-tabulated by photoabsorption measurements. However, the real (dispersive) part of the refractive index δ(ω) at EUV wavelengths is less accurately known. Interferometry, which can provide independent measurements of δ and β, ...
... The absorptive part β(ω) of the refractive index at EUV wavelengths is well-tabulated by photoabsorption measurements. However, the real (dispersive) part of the refractive index δ(ω) at EUV wavelengths is less accurately known. Interferometry, which can provide independent measurements of δ and β, ...
Introduction to Optics Frank L. Pedrotti Leno M. Pedrotti Leno S
... Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk © Pearson Education Limited 2014 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without ...
... Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk © Pearson Education Limited 2014 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without ...
Soleil-Babinet Compensator
... LabVIEW drivers and a stand-alone micrometer program. Once the Soleil-Babinet compensator is calibrated at a single wavelength, the software can output the micrometer position required for any retardance at any wavelength within the operating range. The calibration procedure, which is necessary for ...
... LabVIEW drivers and a stand-alone micrometer program. Once the Soleil-Babinet compensator is calibrated at a single wavelength, the software can output the micrometer position required for any retardance at any wavelength within the operating range. The calibration procedure, which is necessary for ...
Resonators and Mode Matching
... Beam parameter for a resonator Beam in resonator must be self-consistent, i.e., the same after one round trip. Determine the ABCD matrix for one round trip in the resonator matrix depends on starting point Solve equation ...
... Beam parameter for a resonator Beam in resonator must be self-consistent, i.e., the same after one round trip. Determine the ABCD matrix for one round trip in the resonator matrix depends on starting point Solve equation ...
Interferometric back focal plane microellipsometry
... in Fig. 5. In the Au and Al data, d increases and decreases along the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, as expected from Eqs. ~17!, and the nodal lines along the diagonals as predicted in Eq. ~18! are clearly visible. The averages of the four d lines given in Eqs. ~17! from the diffe ...
... in Fig. 5. In the Au and Al data, d increases and decreases along the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, as expected from Eqs. ~17!, and the nodal lines along the diagonals as predicted in Eq. ~18! are clearly visible. The averages of the four d lines given in Eqs. ~17! from the diffe ...
Iceland spar
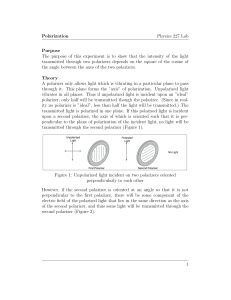
... • E.L. Malus discovered in 1808 that reflection from smooth nonmetallic surfaces changed a light beam in much the same way as its passage through Iceland spar. He called it “polarization” of light • D. Brewster found experimentally for many materials in 1811-15, that this polarization by reflection ...
... • E.L. Malus discovered in 1808 that reflection from smooth nonmetallic surfaces changed a light beam in much the same way as its passage through Iceland spar. He called it “polarization” of light • D. Brewster found experimentally for many materials in 1811-15, that this polarization by reflection ...
Reflecting And Refracting Light
... • We describe the path of light as straight-line rays • Reflection off a flat surface follows a simple rule: – angle in (incidence) equals angle out (reflection) – angles measured from surface “normal” (perpendicular) ...
... • We describe the path of light as straight-line rays • Reflection off a flat surface follows a simple rule: – angle in (incidence) equals angle out (reflection) – angles measured from surface “normal” (perpendicular) ...
Bright Field Microscopy
... brighter, while regions where the path differences decrease appear in reverse contrast. ...
... brighter, while regions where the path differences decrease appear in reverse contrast. ...
1. Which of the following statement are true about "LED life" term?
... enters that will be captured and propagate as a bound mode proportional with Cos of the critical angle of a ray enters that will be captured and propagate as a bound mode A measure related to the refractive index of the core and cladding Related to half angle of a ray’s “cone” of acceptance 4. Becau ...
... enters that will be captured and propagate as a bound mode proportional with Cos of the critical angle of a ray enters that will be captured and propagate as a bound mode A measure related to the refractive index of the core and cladding Related to half angle of a ray’s “cone” of acceptance 4. Becau ...
289-1028-1
... its optical and electrical properties . Much work has been done on the molecular design ,synthesis ,and assembly of structures with desired properties[1].Phenols resin are polymers used in a wide variety of application in different areas as the construction , electronic .. etc. [2].Some common uses ...
... its optical and electrical properties . Much work has been done on the molecular design ,synthesis ,and assembly of structures with desired properties[1].Phenols resin are polymers used in a wide variety of application in different areas as the construction , electronic .. etc. [2].Some common uses ...
Midway High School Science TAKS Review
... Polarized waves are transverse waves that are in the same plane. Notice, the vertical wave may pass through the vertical analyzer and the horizontal wave may pass through the horizontal analyzer. ...
... Polarized waves are transverse waves that are in the same plane. Notice, the vertical wave may pass through the vertical analyzer and the horizontal wave may pass through the horizontal analyzer. ...
Imaging properties of supercritical angle
... A fundamental goal of physical optics is the characterization of the imaging properties of a given optical system. When dealing with imaging of non-coherent fluorescent sources, this is equivalent to calculating the image of single dipole emitters as a function of their position in sample space. For ...
... A fundamental goal of physical optics is the characterization of the imaging properties of a given optical system. When dealing with imaging of non-coherent fluorescent sources, this is equivalent to calculating the image of single dipole emitters as a function of their position in sample space. For ...
Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach
... as a function of frequency, and the chromatic dispersion is calculated as a numerical derivative of the group delay. The spectral features of a link are typically very broad, having dominant features that vary on the order of tens of nanometers. As a result, over any particular channel the CD will b ...
... as a function of frequency, and the chromatic dispersion is calculated as a numerical derivative of the group delay. The spectral features of a link are typically very broad, having dominant features that vary on the order of tens of nanometers. As a result, over any particular channel the CD will b ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).