BIOL212Test3Guide30MAY2012
... Immune System Innate Immunity Recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens Invertebrates vs. vertebrates Barrier defenses Cellular Innate Defenses Toll-like Receptors Neutrophils Macrophages Eosinophils Dendritic cells Natural Killer Cells Antimicrobial Peptides & Proteins I ...
... Immune System Innate Immunity Recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens Invertebrates vs. vertebrates Barrier defenses Cellular Innate Defenses Toll-like Receptors Neutrophils Macrophages Eosinophils Dendritic cells Natural Killer Cells Antimicrobial Peptides & Proteins I ...
Immunology for Surgeons: The Basics 101
... Class II: D region, on APCs, recognized CD4+ helper T-cells --> activation and proliferation of helper T-cells (-> cytokines), cytotoxic T-cells (--> lysis), and B-cells (-> plasma cells --> Ab) ...
... Class II: D region, on APCs, recognized CD4+ helper T-cells --> activation and proliferation of helper T-cells (-> cytokines), cytotoxic T-cells (--> lysis), and B-cells (-> plasma cells --> Ab) ...
Lymphatic System
... Species resistant: the development of diseases unique to that organism. Mechanical barriers: Prevent entry of infectious agents, in areas such as the respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems (Skin and mucus membranes, and sweat). Chemical barriers: Enzymes in body fluid that provide the barr ...
... Species resistant: the development of diseases unique to that organism. Mechanical barriers: Prevent entry of infectious agents, in areas such as the respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems (Skin and mucus membranes, and sweat). Chemical barriers: Enzymes in body fluid that provide the barr ...
Immune System - Mr. Mazza's BioResource
... thymus, tonsils, and lymphoid tissue in digestive and respiratory tracts Lymph nodes filter lymph of pathogens and activates immune response against an antigen ...
... thymus, tonsils, and lymphoid tissue in digestive and respiratory tracts Lymph nodes filter lymph of pathogens and activates immune response against an antigen ...
Adv
... the innate immune system, which can be thought of as the first line of defense against any invading pathogen. In fact, most pathogens are kept out of the body by anatomic barriers, including the skin, mucosal membranes, saliva, and tears. Those pathogens that do gain access to the body also encounte ...
... the innate immune system, which can be thought of as the first line of defense against any invading pathogen. In fact, most pathogens are kept out of the body by anatomic barriers, including the skin, mucosal membranes, saliva, and tears. Those pathogens that do gain access to the body also encounte ...
Riggs_Signal_Transduction-_PAMP_Presentation[1]
... INNATE IMMUNITY There are many types of pattern recognition receptors in different locations in tissues that respond to invading organisms Recognition molecules are expressed by: ...
... INNATE IMMUNITY There are many types of pattern recognition receptors in different locations in tissues that respond to invading organisms Recognition molecules are expressed by: ...
Cell-mediated immunity
... Hyperacute rejection, mediated by preexisting recipient (host) antibodies to graft antigens. Acute graft rejection, in which TH cells and/or cytotoxic T cells mediate tissue damage. Chronic rejection, which involves both cellular and humoral immune components. •The immune response to antigens encode ...
... Hyperacute rejection, mediated by preexisting recipient (host) antibodies to graft antigens. Acute graft rejection, in which TH cells and/or cytotoxic T cells mediate tissue damage. Chronic rejection, which involves both cellular and humoral immune components. •The immune response to antigens encode ...
Lesson 1: The Immune System - Lecture Notes | Vaccine Education
... pathogens that cause an immune response are called antigens. 7. The two parts of the adaptive immune system are the humoral immune system and the cell-mediated immune system. 8. The humoral immune system, also known as antibody-mediated response, protects against micro-organisms present in the fluid ...
... pathogens that cause an immune response are called antigens. 7. The two parts of the adaptive immune system are the humoral immune system and the cell-mediated immune system. 8. The humoral immune system, also known as antibody-mediated response, protects against micro-organisms present in the fluid ...
Immune System
... broken down by incredibly strong acids in the stomach that break down your food - The stomach must produce a coating of special mucus or this acid would eat through the stomach! ...
... broken down by incredibly strong acids in the stomach that break down your food - The stomach must produce a coating of special mucus or this acid would eat through the stomach! ...
Immune System - ilovebiology
... Your body has been exposed to the antigen You make antibodies that eventually destroy it The next time that same antigen tries to come around, those same antibodies will destroy it ...
... Your body has been exposed to the antigen You make antibodies that eventually destroy it The next time that same antigen tries to come around, those same antibodies will destroy it ...
You should be able to find the information necessary to answer
... 12. Describe the role of the major histocompatibility complex class I and class II proteins in humoral and cell-mediated immunity. ...
... 12. Describe the role of the major histocompatibility complex class I and class II proteins in humoral and cell-mediated immunity. ...
Antibodies - blobs.org
... and cells to label them as invaders and stop them attacking the body. They are produced by special cells in the immune system called plasma cells, which are mature B lymphocytes. Each antibody is made up of light chains and heavy chains, connected by a disulphide bond. The structure of the antibody ...
... and cells to label them as invaders and stop them attacking the body. They are produced by special cells in the immune system called plasma cells, which are mature B lymphocytes. Each antibody is made up of light chains and heavy chains, connected by a disulphide bond. The structure of the antibody ...
Transplants
... find more precise methods of immunosuppression in order to prevent rejection without the dangerous side effects of infection. Both these problems may be helped by xenotransplantation the use of organs from other animals. A number of attempts have been made to use hearts, livers, and kidneys from s ...
... find more precise methods of immunosuppression in order to prevent rejection without the dangerous side effects of infection. Both these problems may be helped by xenotransplantation the use of organs from other animals. A number of attempts have been made to use hearts, livers, and kidneys from s ...
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
... The sac containing the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed. May lead to chest pain, arterial thickening, and heart attack. ...
... The sac containing the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed. May lead to chest pain, arterial thickening, and heart attack. ...
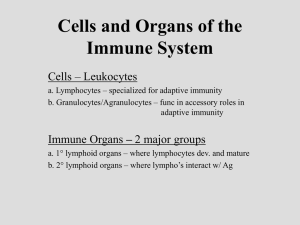
Cells and Organs of the Immune System
... • Cytokine influences -> stimulated by activated MØ and T cells • Genetic regulation – see Table 2-1. • Hematopoietic homeostasis – req’d to maintain certain [c] of cells balance between cells removed by cell death and those produced -for WBC’s: a human must produce ~3.7 x 1011/day ! ...
... • Cytokine influences -> stimulated by activated MØ and T cells • Genetic regulation – see Table 2-1. • Hematopoietic homeostasis – req’d to maintain certain [c] of cells balance between cells removed by cell death and those produced -for WBC’s: a human must produce ~3.7 x 1011/day ! ...
Specific Immunity POGIL
... The Facts on HIV/AIDS AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) was first recognized in North America in the early 1980s. It is caused by a virus known as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV infection has become a worldwide epidemic. About 33 million people are currently infected with the virus ...
... The Facts on HIV/AIDS AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) was first recognized in North America in the early 1980s. It is caused by a virus known as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV infection has become a worldwide epidemic. About 33 million people are currently infected with the virus ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.





![Riggs_Signal_Transduction-_PAMP_Presentation[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008651685_1-7a9da834997c5984d78c99bc734baadf-300x300.png)