TOPIC 11.1
... – Immunity due to the production of antibodies after the body has been challenged by the presence of an antigen – Production of memory cells leading to long-term, full immunity – ex. vaccination or having the illness ...
... – Immunity due to the production of antibodies after the body has been challenged by the presence of an antigen – Production of memory cells leading to long-term, full immunity – ex. vaccination or having the illness ...
Immune system notes - St Paul`s School Intranet
... outside of a virus. What is important is that the lymphocyte can recognize it as a foreign molecule i.e. one that would not normally be found in the body. Each antigen has a particular molecular shape, which will activate certain lymphocytes to secrete proteins called antibodies. Lymphocytes have re ...
... outside of a virus. What is important is that the lymphocyte can recognize it as a foreign molecule i.e. one that would not normally be found in the body. Each antigen has a particular molecular shape, which will activate certain lymphocytes to secrete proteins called antibodies. Lymphocytes have re ...
The immune system - Mount Mansfield Union High School
... into different types of blood cells Travel through both blood and lymphatic systems, pass from blood through lymph nodes, pass from lymphatic system through thoracic duct Two types ...
... into different types of blood cells Travel through both blood and lymphatic systems, pass from blood through lymph nodes, pass from lymphatic system through thoracic duct Two types ...
word - marric.us
... 2. Expectant parents now have the option to save their baby's "cord blood" (blood from the umbilical cord) immediately following birth. This cord blood can be transplanted into individuals whose blood has been damaged by diseases such as leukemia, Hodgkin's lymphoma, and sickle cell anemia. Saved co ...
... 2. Expectant parents now have the option to save their baby's "cord blood" (blood from the umbilical cord) immediately following birth. This cord blood can be transplanted into individuals whose blood has been damaged by diseases such as leukemia, Hodgkin's lymphoma, and sickle cell anemia. Saved co ...
MORPHOLOGIE DES HEMATIES Normales et Pathologiques
... A protein (immunoglobulin) produced by a B-cell that binds to a specific foreign antigen in the blood or body fluids. This leads to attack by the immune system. Belong to a group of serum proteins called immunoglobulins (Igs). ...
... A protein (immunoglobulin) produced by a B-cell that binds to a specific foreign antigen in the blood or body fluids. This leads to attack by the immune system. Belong to a group of serum proteins called immunoglobulins (Igs). ...
Immunity - De Anza College
... Phagocytic cells: WBC’s Natural killer cells: perforins Resident bacteria and fungi Defensive proteins: interferons & complement ...
... Phagocytic cells: WBC’s Natural killer cells: perforins Resident bacteria and fungi Defensive proteins: interferons & complement ...
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... substance capable of triggering an immune response is known as an antigen. • An antigen can be a whole non-self cell, a bacterium, or a virus. ...
... substance capable of triggering an immune response is known as an antigen. • An antigen can be a whole non-self cell, a bacterium, or a virus. ...
dr._mather-brown_presentation
... antigens (peptides) to naïve T cells MHC I -> produced by almost all nucleated cells, present antigen to CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) MHC II -> produced by “professional” antigen presenting cells, present antigen to CD4+ lymphocytes (T helper cells) ...
... antigens (peptides) to naïve T cells MHC I -> produced by almost all nucleated cells, present antigen to CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) MHC II -> produced by “professional” antigen presenting cells, present antigen to CD4+ lymphocytes (T helper cells) ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
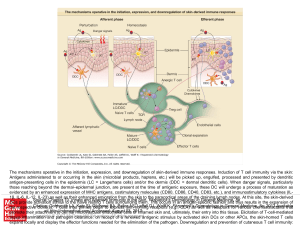
... The mechanisms operative in the initiation, expression, and downregulation of skin-derived immune responses. Induction of T cell immunity via the skin: Antigens administered to or occurring in the skin (microbial products, haptens, etc.) will be picked up, engulfed, processed and presented by dendri ...
... The mechanisms operative in the initiation, expression, and downregulation of skin-derived immune responses. Induction of T cell immunity via the skin: Antigens administered to or occurring in the skin (microbial products, haptens, etc.) will be picked up, engulfed, processed and presented by dendri ...
Fairytale Creative Writing to Improve
... The activated B cell, produces antibodies (Ig)… usually IgM at first. (T helper cells secrete cytokines that can class switch B cells to make other Ig types). B cell matures to become either plasma cell (makes tons of Ig), or a memory B cell. Antibodies (Ig) opsonize antigens. These complexes be ...
... The activated B cell, produces antibodies (Ig)… usually IgM at first. (T helper cells secrete cytokines that can class switch B cells to make other Ig types). B cell matures to become either plasma cell (makes tons of Ig), or a memory B cell. Antibodies (Ig) opsonize antigens. These complexes be ...
May 13, 2015
... NY-ESO-1 cancer testis antigen were administered to patients with synovial sarcoma and multiple myeloma. The data being presented relates to the phenotypic and functional evaluation of the engineered T cells administered to patients and the data may suggest that the engineered autologous T cells adm ...
... NY-ESO-1 cancer testis antigen were administered to patients with synovial sarcoma and multiple myeloma. The data being presented relates to the phenotypic and functional evaluation of the engineered T cells administered to patients and the data may suggest that the engineered autologous T cells adm ...
You - Dickinson ISD
... inflammatory response - Capillaries dilate - Pyrogens released, and temperature rises - Pain receptors activate - WBCs flock to infected area like sharks to blood ...
... inflammatory response - Capillaries dilate - Pyrogens released, and temperature rises - Pain receptors activate - WBCs flock to infected area like sharks to blood ...
Immune System Disorders
... Autograft: Use of one's own tissue Isograft: Use of identical twin's tissue Allograft: Use of tissue from another ...
... Autograft: Use of one's own tissue Isograft: Use of identical twin's tissue Allograft: Use of tissue from another ...
Immunity AIM: How does the immune system protect the body
... 3. Describe • It works against specific pathogens. the function of the immune system. ...
... 3. Describe • It works against specific pathogens. the function of the immune system. ...
File
... • Our immune system “remembers” bad pathogens it has fought in the past • It has weapons built up so the next time the pathogen enters your body, you are ready to defend ...
... • Our immune system “remembers” bad pathogens it has fought in the past • It has weapons built up so the next time the pathogen enters your body, you are ready to defend ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.