March 24 (PP)
... Hypersensitivity – immune responses that causes tissue damage Autoimmune disease – immune responses to self-antigens Immunodeficiency – insufficient immune response ...
... Hypersensitivity – immune responses that causes tissue damage Autoimmune disease – immune responses to self-antigens Immunodeficiency – insufficient immune response ...
your body`s defense against infection lesson 2
... antibodies Proteins that attach to antigens, keeping them from harming the body ...
... antibodies Proteins that attach to antigens, keeping them from harming the body ...
Immunology Notes
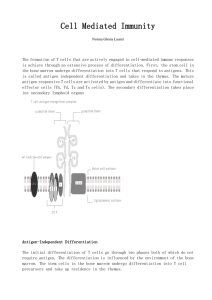
... Helper cells stimulate B cells to mature into plasma cells, which begin to synthesize and secrete immunoglobulin (proteins with known antibody activity) Suppressor cells reduce the humoral immunity B. Humoral immunity: also called immunoglobulin-mediated immunity Associated with circulating anti ...
... Helper cells stimulate B cells to mature into plasma cells, which begin to synthesize and secrete immunoglobulin (proteins with known antibody activity) Suppressor cells reduce the humoral immunity B. Humoral immunity: also called immunoglobulin-mediated immunity Associated with circulating anti ...
Slide 1
... them together Neutralize toxins by glomming onto them on the surface of pathogens Stick to surface of pathogen so it can be recognized by phagocytic cells Immunoglobulins are classes of antibodies—each class has more specific immune function ...
... them together Neutralize toxins by glomming onto them on the surface of pathogens Stick to surface of pathogen so it can be recognized by phagocytic cells Immunoglobulins are classes of antibodies—each class has more specific immune function ...
Document
... D. lymph nodes. E. skin. 47. A molecule that can be covalently linked to a non-immunogenic antigen to make it an immunogen is called a(n) A. adjuvant. B. carrier. C. hapten. D. mitogen. E. superantigen. 48. Which statement about antigen epitopes is FALSE? A. An epitope may be shared by two different ...
... D. lymph nodes. E. skin. 47. A molecule that can be covalently linked to a non-immunogenic antigen to make it an immunogen is called a(n) A. adjuvant. B. carrier. C. hapten. D. mitogen. E. superantigen. 48. Which statement about antigen epitopes is FALSE? A. An epitope may be shared by two different ...
Unit 2 Biology Test Chapter 31.2
... - Some complement proteins weaken a pathogen’s cell membrane, allowing water to enter the cell and cause it to burst. Others attract phagocytes to the infected area. ...
... - Some complement proteins weaken a pathogen’s cell membrane, allowing water to enter the cell and cause it to burst. Others attract phagocytes to the infected area. ...
1) if the response to an antigen
... fluids of the body can be recognized by immune system as self ( i.e. own tissues), and so do not stimulate immune response. If foreign substances are introduced in the body, immune system recognizes them as nonself and immune response will occur. 3- Structural complexity: A molecule must posses a ...
... fluids of the body can be recognized by immune system as self ( i.e. own tissues), and so do not stimulate immune response. If foreign substances are introduced in the body, immune system recognizes them as nonself and immune response will occur. 3- Structural complexity: A molecule must posses a ...
Defense against Disease: White Blood Cells
... more blood into the area and more WBCs out into the infected tissues where they can battle pathogens 3. WBCs battle with pathogen by phagocytosis and releasing chemical to damage and mark pathogens 4. This all results in “inflammation” - redness and ...
... more blood into the area and more WBCs out into the infected tissues where they can battle pathogens 3. WBCs battle with pathogen by phagocytosis and releasing chemical to damage and mark pathogens 4. This all results in “inflammation” - redness and ...
6.3 Immune system notes
... There are many different types of plasma cells, and each type can only produce ________________ of antibody. Primary Immune Response A specific _____________ is identified A specific _____________ is identified to produce an antibody against the pathogen The specific plasma cell begins ____________ ...
... There are many different types of plasma cells, and each type can only produce ________________ of antibody. Primary Immune Response A specific _____________ is identified A specific _____________ is identified to produce an antibody against the pathogen The specific plasma cell begins ____________ ...
The Immune System
... – A Pathogen invades and multiplies, making the host sick. – The body makes antibodies that fight off antigens and get the host well again. – This is why you only get sick once from some pathogens, such as Chicken Pox! ...
... – A Pathogen invades and multiplies, making the host sick. – The body makes antibodies that fight off antigens and get the host well again. – This is why you only get sick once from some pathogens, such as Chicken Pox! ...
Preventing Communicable Diseases
... Meningitis – Virus or bacteria cause inflammation of the membranes that cover the brain. Fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck ...
... Meningitis – Virus or bacteria cause inflammation of the membranes that cover the brain. Fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck ...
Aseptic Technique: Media and Equipment
... immune system and provoking immune responses • Large complex molecules not normally present in the body • They are anything non-self: Mo’s, Cells, Cells containing MO’s, or chemicals • Epitope – small area of antigen that stimulates the immune response ...
... immune system and provoking immune responses • Large complex molecules not normally present in the body • They are anything non-self: Mo’s, Cells, Cells containing MO’s, or chemicals • Epitope – small area of antigen that stimulates the immune response ...
Overview of Adaptive Immunity 01/24/06
... Cell-mediated Immunity Conferred via lymphocyte exchange Cell dependent Modulates humoral immunity Cytotoxic ...
... Cell-mediated Immunity Conferred via lymphocyte exchange Cell dependent Modulates humoral immunity Cytotoxic ...
Unit 2.2.2 – Health and Disease Immunity
... B and T-lymphocytes recognise specific pathogens that have invaded the body and set in motion mechanisms to destroy them: thus protecting the body from harm. This is known as the immune response. The function of B-lymphocytes B-lymphocytes are involved in the production of antibodies in response to ...
... B and T-lymphocytes recognise specific pathogens that have invaded the body and set in motion mechanisms to destroy them: thus protecting the body from harm. This is known as the immune response. The function of B-lymphocytes B-lymphocytes are involved in the production of antibodies in response to ...
Antibody
... thymus removal (thymectomy) to have on the ability of host immunity against infection? Ans: 1. Total lymphocytes are drastically reduced. T cell development was blocked. B cells are also reduced => require T helper cells for their proliferation. LN size is reduced. => Get infections easier. 2. DiGeo ...
... thymus removal (thymectomy) to have on the ability of host immunity against infection? Ans: 1. Total lymphocytes are drastically reduced. T cell development was blocked. B cells are also reduced => require T helper cells for their proliferation. LN size is reduced. => Get infections easier. 2. DiGeo ...
Autoimmune Disease
... Why would the body attack itself? What is the mistake made by the immune system? Hint: In order for the immune system to be successful in defending the body, what two things must it be able to distinguish? ...
... Why would the body attack itself? What is the mistake made by the immune system? Hint: In order for the immune system to be successful in defending the body, what two things must it be able to distinguish? ...
your body`s defense against infection lesson 2
... antibodies Proteins that attach to antigens, keeping them from harming the body ...
... antibodies Proteins that attach to antigens, keeping them from harming the body ...
IMMUNITY CELLULAR AND HUMORAL IMMUNITY
... But early in the process, infected cells display fragments of the viral proteins in their surface class I molecules. CTLs specific for that antigen bind to the infected cell and often will be able to destroy it before it can release a fresh crop of viruses. In general, the role of the T cells is to ...
... But early in the process, infected cells display fragments of the viral proteins in their surface class I molecules. CTLs specific for that antigen bind to the infected cell and often will be able to destroy it before it can release a fresh crop of viruses. In general, the role of the T cells is to ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.