IMMUNOLOGY OF TRANSPLANTATION
... T cells are critical in graft rejection Rejection responses in molecular terms, are due to TCR-MHC interaction Graft and host MHC molecules present different peptides Different MHC molecules have different peptidebinding grooves T lymphocytes can directly recognize and respond to foreign MHC molecul ...
... T cells are critical in graft rejection Rejection responses in molecular terms, are due to TCR-MHC interaction Graft and host MHC molecules present different peptides Different MHC molecules have different peptidebinding grooves T lymphocytes can directly recognize and respond to foreign MHC molecul ...
Cells - Shelton State
... -word Cell coined in 1665 by Robert Hooke (latin for small room). --Cell Theory: 1. All organisms composed of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in life. 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. Why Organize into Cells? -individual cells can be lost and replaced -organis ...
... -word Cell coined in 1665 by Robert Hooke (latin for small room). --Cell Theory: 1. All organisms composed of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in life. 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. Why Organize into Cells? -individual cells can be lost and replaced -organis ...
Immune System Guided Notes
... Each receptor is capable of binding with only one type of antigen. These mature, but inactive, lymphocytes take up residence in lymphatic organs and wait to meet their antigen. Most never will. The lucky few lymphocytes that do bind to their antigen will undergo clonal selection so that they, and th ...
... Each receptor is capable of binding with only one type of antigen. These mature, but inactive, lymphocytes take up residence in lymphatic organs and wait to meet their antigen. Most never will. The lucky few lymphocytes that do bind to their antigen will undergo clonal selection so that they, and th ...
Document
... - WBCs normally circulate throughout the blood, but will enter the body’s tissues if invaders are detected ...
... - WBCs normally circulate throughout the blood, but will enter the body’s tissues if invaders are detected ...
The Immune System The immune system allows the body to defend
... The immune system allows the body to defend against disease-causing agent. This system recognizes and destroys “foreign” substances, such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa, viruses, toxins and cancer cells. The body has two ways to defend against these substances nonspecific and specific resistance or im ...
... The immune system allows the body to defend against disease-causing agent. This system recognizes and destroys “foreign” substances, such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa, viruses, toxins and cancer cells. The body has two ways to defend against these substances nonspecific and specific resistance or im ...
Tissues of the immune system
... The sites for cell proliferation and maturation Such as Bone marrow and thymus B- peripheral lymphoid organs or secondary organs Where lymphocytes responses to foreign Ags Such as :spleen ,lymph nodes,cutaneous and mucosal immune system . ...
... The sites for cell proliferation and maturation Such as Bone marrow and thymus B- peripheral lymphoid organs or secondary organs Where lymphocytes responses to foreign Ags Such as :spleen ,lymph nodes,cutaneous and mucosal immune system . ...
5 dent inflammation and mucosal immunity
... Migration of neutrophil and monocytes to site of infection I Selectins, Chemokines, Integrins ...
... Migration of neutrophil and monocytes to site of infection I Selectins, Chemokines, Integrins ...
Powerpoint version
... The MHC is a set of genes that code for glycoproteins on cell membranes and mark cells as “self” ...
... The MHC is a set of genes that code for glycoproteins on cell membranes and mark cells as “self” ...
Cell Signaling
... • Discuss with your partner how adaptive immunity could utilize cell signaling pathways. • How is your second line of defense like a signal transduction pathway? – What parts of the inflammatory response are represented in the cell signaling pathway? Can you draws parallels between the parts of this ...
... • Discuss with your partner how adaptive immunity could utilize cell signaling pathways. • How is your second line of defense like a signal transduction pathway? – What parts of the inflammatory response are represented in the cell signaling pathway? Can you draws parallels between the parts of this ...
Who Gets Lupus?
... 2. C1q binds to and clears apoptotic blebs (sources of autoantigens) 3. Absence of C1q permits sustained infections that could trigger autoimmune response. ...
... 2. C1q binds to and clears apoptotic blebs (sources of autoantigens) 3. Absence of C1q permits sustained infections that could trigger autoimmune response. ...
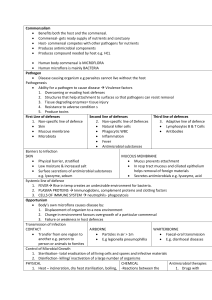
Ch 12 2nd and 3rd Lines of Defense
... Insert a toxic chemical (perforin) Helper T cells Recruit other cells to fight the invaders Interact directly with B cells Suppressor T cells Release chemicals to stop T and B cells Stop the immune response to prevent ...
... Insert a toxic chemical (perforin) Helper T cells Recruit other cells to fight the invaders Interact directly with B cells Suppressor T cells Release chemicals to stop T and B cells Stop the immune response to prevent ...
AMS_PowerPoint_The_Lymphatic_System_and_Immunity
... •Two properties distinguish specific immunity from non- specific immunity: • (a) specificity for particular foreign molecules (allow self to distinguish between non-self). • (b) Memory for most previously encountered antigens so that a second encounter prompts an even more rapid and vigorous respo ...
... •Two properties distinguish specific immunity from non- specific immunity: • (a) specificity for particular foreign molecules (allow self to distinguish between non-self). • (b) Memory for most previously encountered antigens so that a second encounter prompts an even more rapid and vigorous respo ...
powerpoint is here
... identical twins 20-30% fraternal same-sex twins 2-5% African Americans less susceptible than Caucasian Americans HLA-DRB1 gene on chromosome 6p21 ...
... identical twins 20-30% fraternal same-sex twins 2-5% African Americans less susceptible than Caucasian Americans HLA-DRB1 gene on chromosome 6p21 ...
Ch. 43 Immune System 9e v2 (1)
... • T cells: mature in thymus – helper T, cytotoxic T • B cells: mature in bone marrow – plasma cells make antibodies ...
... • T cells: mature in thymus – helper T, cytotoxic T • B cells: mature in bone marrow – plasma cells make antibodies ...
Commensalism • Benefits both the host and the commensal
... Produces compound needed by host e.g. HCL Human body commensal is MICROFLORA Human microflora is mainly BACTERIA Pathogen Disease causing organism e.g parasites cannot live without the host Pathogenesis Ability for a pathogen to cause disease Virulence factors 1. Overcoming or evading ho ...
... Produces compound needed by host e.g. HCL Human body commensal is MICROFLORA Human microflora is mainly BACTERIA Pathogen Disease causing organism e.g parasites cannot live without the host Pathogenesis Ability for a pathogen to cause disease Virulence factors 1. Overcoming or evading ho ...
Type II Hypersensitivity: Antibody mediated cytotoxicity
... • Both processes result in lysis of the Ab-coated cell • Clinical examples of Type II responses include: – Certain autoimmune diseases where Ab’s produced vs membrane Ag’s • Grave’s Disease – Ab’s produced vs thyroid hormone receptor • Myasthenia Gravis – Ab’s produced vs acetylcholine recpetors • A ...
... • Both processes result in lysis of the Ab-coated cell • Clinical examples of Type II responses include: – Certain autoimmune diseases where Ab’s produced vs membrane Ag’s • Grave’s Disease – Ab’s produced vs thyroid hormone receptor • Myasthenia Gravis – Ab’s produced vs acetylcholine recpetors • A ...
Fall 2004 - Antelope Valley College
... In the ELISA test, Ab/Ag binding is detected by ____________________________________________. ...
... In the ELISA test, Ab/Ag binding is detected by ____________________________________________. ...
Chapter 17
... Ag fragments + ____________________________ (MHC II) proteins together = presented or “processed” antigen Triggers __________________ (IL-2) production from T cells This stimulates B cells further and creates memory cells Known as _______________________, usually proteins ...
... Ag fragments + ____________________________ (MHC II) proteins together = presented or “processed” antigen Triggers __________________ (IL-2) production from T cells This stimulates B cells further and creates memory cells Known as _______________________, usually proteins ...