3.6 Immune System
... down along with any human cells damaged by the pathogen. Fragments of dead pathogen and white blood cells form _________________ ...
... down along with any human cells damaged by the pathogen. Fragments of dead pathogen and white blood cells form _________________ ...
Molecular Immunology
... - 25 gennaio 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 08 febbraio 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 22 febbraio 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 15 giugno 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 28 giugno 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 12 luglio 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 30 settembre 12.00-14.00 aula da definire ...
... - 25 gennaio 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 08 febbraio 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 22 febbraio 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 15 giugno 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 28 giugno 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 12 luglio 12.00-14.00 aula da definire - 30 settembre 12.00-14.00 aula da definire ...
Immune System
... 1. Active Immunity - the body produces its own antibodies or killer T cells. - develops as the result of having had the disease - may also developed through the use of a vaccine Vaccines consist of dead or weakened bacteria or viruses or modified poisons 2. Passive Immunity - antibodies obtained fro ...
... 1. Active Immunity - the body produces its own antibodies or killer T cells. - develops as the result of having had the disease - may also developed through the use of a vaccine Vaccines consist of dead or weakened bacteria or viruses or modified poisons 2. Passive Immunity - antibodies obtained fro ...
Document
... general function. • Describe three types of neurons. • How can a hormone have different responses in different cells? • List three evolutionary trends of nervous system formation in animals. Describe each • List the types of ions and their locations that participate in forming the resting potential. ...
... general function. • Describe three types of neurons. • How can a hormone have different responses in different cells? • List three evolutionary trends of nervous system formation in animals. Describe each • List the types of ions and their locations that participate in forming the resting potential. ...
Helminth derived Immunodmodulator A therapeutic for immune-related diseases Overview
... Overview The technology relates to novel compositions and methods for modulating an immune response in order to prevent or treat disease and/or conditions where T lymphocyte cells have a pathogenic role, such as Th1 or ThIL-17 mediated inflammatory conditions, chronic inflammatory conditions and aut ...
... Overview The technology relates to novel compositions and methods for modulating an immune response in order to prevent or treat disease and/or conditions where T lymphocyte cells have a pathogenic role, such as Th1 or ThIL-17 mediated inflammatory conditions, chronic inflammatory conditions and aut ...
Cell-mediated immunity
... – What are Th1 vs. Th2 cells? What do they do and what do they make? In what systems is one more important than the others? ...
... – What are Th1 vs. Th2 cells? What do they do and what do they make? In what systems is one more important than the others? ...
Viruses - Ms. Franklin`s Classroom
... Viral DNA/RNA is able to mutate at a quick rate which in turn allows the virus to ‘mask’ itself and enter the host cell. The host’s immune system will not recognize the new protein coat and in turn not attack the viral invasion. ...
... Viral DNA/RNA is able to mutate at a quick rate which in turn allows the virus to ‘mask’ itself and enter the host cell. The host’s immune system will not recognize the new protein coat and in turn not attack the viral invasion. ...
Immunology Introductory course Series of lectures outlining
... Any substance which • causes a lymphocyte reaction • reaction is specific to that lymphocyte • clone - single type of lymphocyte which reacts to an individual antigen ...
... Any substance which • causes a lymphocyte reaction • reaction is specific to that lymphocyte • clone - single type of lymphocyte which reacts to an individual antigen ...
Immune System Summmary
... Immediately blood flows from the wound. Flowing out through the wound are all kinds of blood cells, red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). As the platelets flow over the jagged edges of the cut vessels they break apart and release platelet facto ...
... Immediately blood flows from the wound. Flowing out through the wound are all kinds of blood cells, red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). As the platelets flow over the jagged edges of the cut vessels they break apart and release platelet facto ...
Autoimmune diseases
... selection in the central- thymic phase Second possibility: The weak binding of self peptides in the positive phase of repertoire selection in the thymus means that only T cells with very high affinity for self peptides are selected via normal positive selection mechanisms: these clones are not elimi ...
... selection in the central- thymic phase Second possibility: The weak binding of self peptides in the positive phase of repertoire selection in the thymus means that only T cells with very high affinity for self peptides are selected via normal positive selection mechanisms: these clones are not elimi ...
Immunity
... Non-specific mechanisms Barriers to disease Epidermis of skin Layers of dead cells prevent invasion ...
... Non-specific mechanisms Barriers to disease Epidermis of skin Layers of dead cells prevent invasion ...
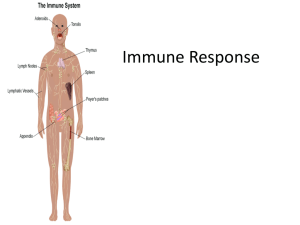
Immune Response
... • Immunology- the study of host defense mechanisms • Immunity- ability of the host to protect itself against foreign organisms. Resistance to disease. • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the bod ...
... • Immunology- the study of host defense mechanisms • Immunity- ability of the host to protect itself against foreign organisms. Resistance to disease. • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the bod ...
Immune System
... -Body temp increases in response to infection -pathogenic bacteria don’t grow well at higher temp ...
... -Body temp increases in response to infection -pathogenic bacteria don’t grow well at higher temp ...
AP Biology Chapter 43
... AP Bio Bellringer 1/11 • If you did the homework please get it out so I can pick it up. • Question: As animals are heterotrophic organisms, the ability to move and find food is important. Movement on earth, for animals, occurs basically in three different environments (Air, land, or water). Each env ...
... AP Bio Bellringer 1/11 • If you did the homework please get it out so I can pick it up. • Question: As animals are heterotrophic organisms, the ability to move and find food is important. Movement on earth, for animals, occurs basically in three different environments (Air, land, or water). Each env ...
Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity
... These cells must home to an environment wherein they wait for exposure to the antigen that they are preprogrammed to recognize. After exposure to the antigen they proliferate, leave the lymph node and migrate to infected tissues where they function as effector cells. ...
... These cells must home to an environment wherein they wait for exposure to the antigen that they are preprogrammed to recognize. After exposure to the antigen they proliferate, leave the lymph node and migrate to infected tissues where they function as effector cells. ...
Genetics of Immunity
... against that pathogen • Protection of having a previous attack without actually having the risk • Once some diseases have been removed with vaccines there is no longer any need to administer them: ...
... against that pathogen • Protection of having a previous attack without actually having the risk • Once some diseases have been removed with vaccines there is no longer any need to administer them: ...
The biochemistry and genetics of autoimmune disease
... Tolerance ◦ Discrimination of self vs non-self ...
... Tolerance ◦ Discrimination of self vs non-self ...