2. Building a new atomic model from scratch
... separated due to the fact that they each occupy a particular amount of space and cannot merge into each other. This can be pictured like two Lego bricks stuck together. This atomic model is so similar to the building toy that these pictures were rendered using Lego’s 3-D Digital Designer software. [ ...
... separated due to the fact that they each occupy a particular amount of space and cannot merge into each other. This can be pictured like two Lego bricks stuck together. This atomic model is so similar to the building toy that these pictures were rendered using Lego’s 3-D Digital Designer software. [ ...
Slide 1
... oxygen for every 1.00 g of carbon carbon dioxide contains 2.67 g of oxygen for every 1.00 g of carbon since there are twice as many oxygen atoms per carbon atom in carbon dioxide than in carbon monoxide, the oxygen mass ratio should be 2 mass of oxygen that combines with 1 g of carbon in carbon diox ...
... oxygen for every 1.00 g of carbon carbon dioxide contains 2.67 g of oxygen for every 1.00 g of carbon since there are twice as many oxygen atoms per carbon atom in carbon dioxide than in carbon monoxide, the oxygen mass ratio should be 2 mass of oxygen that combines with 1 g of carbon in carbon diox ...
Chapt3
... 4. Types of Chemical Formulas (e.g., see Table 3.1) empirical formula shows the simplest ratio of the elements present molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in one molecule structural formula shows how the atoms are connected e.g., for "hydrogen peroxide" the three formulas are: ...
... 4. Types of Chemical Formulas (e.g., see Table 3.1) empirical formula shows the simplest ratio of the elements present molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in one molecule structural formula shows how the atoms are connected e.g., for "hydrogen peroxide" the three formulas are: ...
Two valence electrons.
... Our class wall table shows man-made elements with a white chemical symbol, all others are natural. ...
... Our class wall table shows man-made elements with a white chemical symbol, all others are natural. ...
Darlington High School EDI Lesson Plan Teacher: L. Grooms
... PS2.1 Compare the subatomic particles, protons, neutrons and electrons in regard to the mass, location, and charge and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom. PS 2.3 Explain the trends of the periodic table based on the elements’ valence electrons and atomic number. PS 2.4 Use ...
... PS2.1 Compare the subatomic particles, protons, neutrons and electrons in regard to the mass, location, and charge and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom. PS 2.3 Explain the trends of the periodic table based on the elements’ valence electrons and atomic number. PS 2.4 Use ...
Chem. Review Notes
... Think of a football stadium… • as a giant model of a hydrogen atom – football would be nucleus • 1 proton and 1 neutron inside ...
... Think of a football stadium… • as a giant model of a hydrogen atom – football would be nucleus • 1 proton and 1 neutron inside ...
atomic number - Mrs.Yu Science Class
... Neutrons (n0) have no charge and a mass of 1. Protons and neutrons are located in the center of the atom in an area called the nucleus. The nucleus is tiny, dense ...
... Neutrons (n0) have no charge and a mass of 1. Protons and neutrons are located in the center of the atom in an area called the nucleus. The nucleus is tiny, dense ...
Part of a Molecular Compound
... Calculating Molar Mass • Use the atomic masses on the periodic table. • On many of them you can round to the nearest gram, except for elements that atomic masses end in 0.5 • Use as many significant figures needed to maintain the number of significant figures given in the problem. ...
... Calculating Molar Mass • Use the atomic masses on the periodic table. • On many of them you can round to the nearest gram, except for elements that atomic masses end in 0.5 • Use as many significant figures needed to maintain the number of significant figures given in the problem. ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter2
... • Protons are located in the nucleus of an atom. They carry a +1 electrical charge and have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (u). • Neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. They carry no electrical charge and have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (u). • Electrons are located outside the nucleus of an ...
... • Protons are located in the nucleus of an atom. They carry a +1 electrical charge and have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (u). • Neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. They carry no electrical charge and have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (u). • Electrons are located outside the nucleus of an ...
1 - Cobb Learning
... 36. A chemical bond that forms when two atoms share electrons is called a(n) A. ionic bond. B. covalent bond. C. polyatomic bond. D. crystal bond. Two or 37 m Two or more substances that are NOT chemically combined are called? a. elements b. compounds ...
... 36. A chemical bond that forms when two atoms share electrons is called a(n) A. ionic bond. B. covalent bond. C. polyatomic bond. D. crystal bond. Two or 37 m Two or more substances that are NOT chemically combined are called? a. elements b. compounds ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... 3) Naturally occurring silicon consists of 92.23% Si-‐28 (mass = 27.976927 g), 4.76% Si-‐29 (mass = 28.976495 g) and 3.10% Si-‐30 (mass = 29.973770 g). What is the expected average mola ...
... 3) Naturally occurring silicon consists of 92.23% Si-‐28 (mass = 27.976927 g), 4.76% Si-‐29 (mass = 28.976495 g) and 3.10% Si-‐30 (mass = 29.973770 g). What is the expected average mola ...
Chapter 20 Resource: Chemical Bonds
... C. __________________ are neutral particles formed as a result of sharing electrons. 1. A ______________________ is the force of attraction between atoms sharing electrons. 2. Atoms can form double or triple ______________ depending on whether they share two or three pairs of electrons. 3. Electrons ...
... C. __________________ are neutral particles formed as a result of sharing electrons. 1. A ______________________ is the force of attraction between atoms sharing electrons. 2. Atoms can form double or triple ______________ depending on whether they share two or three pairs of electrons. 3. Electrons ...
Atomic Math
... – The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom. – The atomic mass only measures the nucleus. – Unreacted atoms should be neutral, meaning they should have the same number of protons and electrons. ...
... – The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom. – The atomic mass only measures the nucleus. – Unreacted atoms should be neutral, meaning they should have the same number of protons and electrons. ...
100610 chem a GALL
... not hole-punched and placed in the binder, do that; Portfolios are collected today. Homework: Finish 2 assigned atom models, due Friday. AIMS: TLW continue to apply knowledge of phase changes, kinetic energy, and the structure of the atom. ...
... not hole-punched and placed in the binder, do that; Portfolios are collected today. Homework: Finish 2 assigned atom models, due Friday. AIMS: TLW continue to apply knowledge of phase changes, kinetic energy, and the structure of the atom. ...
Review of Major Concepts Taught in Grade 9 Chemistry
... Valence electrons are the electrons found in the outermost electron orbit or shell. ...
... Valence electrons are the electrons found in the outermost electron orbit or shell. ...
Matter - tompkinsmath
... 1. Ionic- combinations of cations/anions metal/non-metal Ex. sodium chloride (NaCl) 2. Molecular – non-metal / non-metal combinations. Ex. sulfur dioxide - SO2(g) Water → H2O 3. Intermetallic – metal / metal combination ...
... 1. Ionic- combinations of cations/anions metal/non-metal Ex. sodium chloride (NaCl) 2. Molecular – non-metal / non-metal combinations. Ex. sulfur dioxide - SO2(g) Water → H2O 3. Intermetallic – metal / metal combination ...
Group IV Elements
... Reactions with transition metals. The metals occupy tetrahedral holes in the close packed arrays of metal atoms. Materials are very hard, conducting, and have high melting points (3000-4800 deg C). WC is hard, used for machining steel. Cr,Mn,Fe,Co,Ni are between ionic and interstitial. Hydrolysed by ...
... Reactions with transition metals. The metals occupy tetrahedral holes in the close packed arrays of metal atoms. Materials are very hard, conducting, and have high melting points (3000-4800 deg C). WC is hard, used for machining steel. Cr,Mn,Fe,Co,Ni are between ionic and interstitial. Hydrolysed by ...
Classification of Matter
... or more atoms that are chemically bonded Smallest part of a compound that has the same properties of that compound ...
... or more atoms that are chemically bonded Smallest part of a compound that has the same properties of that compound ...
Document
... • The atomic number of an atom is given by its number of protons. The mass number of an atom is the sum of its neutrons and protons. atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons mass number = atomic number + number of neutrons ...
... • The atomic number of an atom is given by its number of protons. The mass number of an atom is the sum of its neutrons and protons. atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons mass number = atomic number + number of neutrons ...
Date: ______ Properties of the Physical Universe: Matter Relative
... The main properties of an atom are defined by the contents of its nucleus. In fact, the type of element an atom is defined to be is dictated by the number of protons in the nucleus. This property is called the atomic number (Z). For example, the element Hydrogen is defined as an atom that possesses ...
... The main properties of an atom are defined by the contents of its nucleus. In fact, the type of element an atom is defined to be is dictated by the number of protons in the nucleus. This property is called the atomic number (Z). For example, the element Hydrogen is defined as an atom that possesses ...
Properties of the Physical Universe
... The main properties of an atom are defined by the contents of its nucleus. In fact, the type of element an atom is defined to be is dictated by the number of protons in the nucleus. This property is called the atomic number (Z). For example, the element Hydrogen is defined as an atom that possesses ...
... The main properties of an atom are defined by the contents of its nucleus. In fact, the type of element an atom is defined to be is dictated by the number of protons in the nucleus. This property is called the atomic number (Z). For example, the element Hydrogen is defined as an atom that possesses ...
Redox
... This method is typically used for organic compounds, which contain many carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms The advantage of the effective charge method is that you can determine which atom has been oxidized or reduced To determine effective charges, we will need to use some more advanced topics, suc ...
... This method is typically used for organic compounds, which contain many carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms The advantage of the effective charge method is that you can determine which atom has been oxidized or reduced To determine effective charges, we will need to use some more advanced topics, suc ...
Chapter 5
... • All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but differing numbers of neutrons. • The mass number for an isotope is the total number of protons plus neutrons. • The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masse ...
... • All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but differing numbers of neutrons. • The mass number for an isotope is the total number of protons plus neutrons. • The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masse ...
Word - The Chemistry Book
... Below the football field at the University of Chicago, the United States developed the very first working nuclear fission reactor. The Manhattan Project was in process. ...
... Below the football field at the University of Chicago, the United States developed the very first working nuclear fission reactor. The Manhattan Project was in process. ...
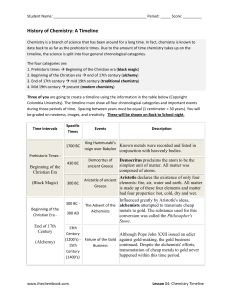
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.