Final Exam Review Guide
... 2. Dimensional analysis must be used to convert between measurement units. 3. Chemicals have both physical and chemical properties that can be used to tell them apart, and also to separate components of a mixture. 4. When it comes to evaluating a solute/solvent relationship, remember the phrase “lik ...
... 2. Dimensional analysis must be used to convert between measurement units. 3. Chemicals have both physical and chemical properties that can be used to tell them apart, and also to separate components of a mixture. 4. When it comes to evaluating a solute/solvent relationship, remember the phrase “lik ...
Activity 4 Are Atoms Indivisible?
... atoms will have different boiling points, melting points, color, and relative mass. ...
... atoms will have different boiling points, melting points, color, and relative mass. ...
The Atom
... Serves as the glue that holds the nucleus together as well as a buffer between the charges of protons and electrons ...
... Serves as the glue that holds the nucleus together as well as a buffer between the charges of protons and electrons ...
Section 4.3 Notes
... 1. Describe periodic trends in the ionization energy, atomic radius, and electronegativity. 2. Relate the periodic trends to the atomic structures of the elements. 3. Describe periodic trends in ionic size, electron affinity, and melting and boiling points, and relate them to periodic trends in the ...
... 1. Describe periodic trends in the ionization energy, atomic radius, and electronegativity. 2. Relate the periodic trends to the atomic structures of the elements. 3. Describe periodic trends in ionic size, electron affinity, and melting and boiling points, and relate them to periodic trends in the ...
Name the three parts of an atom and where they are located
... What is the atomic mass? The mass of an atom; the # protons + # of neutrons What parts of the atom account for the atomic mass? protons & neutrons What is an isotope? An atom that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons Are isotopes always the same element? Why? Yes, the # ...
... What is the atomic mass? The mass of an atom; the # protons + # of neutrons What parts of the atom account for the atomic mass? protons & neutrons What is an isotope? An atom that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons Are isotopes always the same element? Why? Yes, the # ...
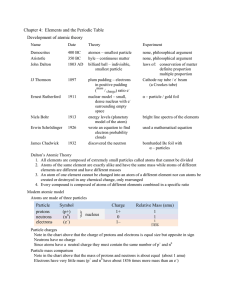
Chapter 4: Elements and the Periodic Table Development of atomic
... They are often used to make alloys Nd and Sm are used to make very powerful magnets used for modern speakers Actinides – the bottom row of which only Ac, Th, Pa, and U occur naturally on earth Most of the actinides are synthetic elements formed in particle accelerators Mixed group metals – metals fo ...
... They are often used to make alloys Nd and Sm are used to make very powerful magnets used for modern speakers Actinides – the bottom row of which only Ac, Th, Pa, and U occur naturally on earth Most of the actinides are synthetic elements formed in particle accelerators Mixed group metals – metals fo ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... c. some MATTER exists in elemental form [(e.g.) gold [Au] = not chemically REACTIVE)] *d. ELEMENTS individually or combined form everything in the universe including HUMANS *1. Human body’s most abundant ELEMENTS: carbon [C], oxygen [O], hydrogen [H], and nitrogen [N]; for teeth & BONES = calcium [C ...
... c. some MATTER exists in elemental form [(e.g.) gold [Au] = not chemically REACTIVE)] *d. ELEMENTS individually or combined form everything in the universe including HUMANS *1. Human body’s most abundant ELEMENTS: carbon [C], oxygen [O], hydrogen [H], and nitrogen [N]; for teeth & BONES = calcium [C ...
Composition and Structure of the Atom Atom: basic unit of an
... How many Neon atoms are required to give the same mass as one calcium atom? Dalton’s Atomic Theory (Mostly true, with a few modifications) •All matter consists of atoms •Atoms cannot be created or destroyed, divided* or changed* to a different atom ...
... How many Neon atoms are required to give the same mass as one calcium atom? Dalton’s Atomic Theory (Mostly true, with a few modifications) •All matter consists of atoms •Atoms cannot be created or destroyed, divided* or changed* to a different atom ...
CHM_101_TUTORIAL_QUESTIONS_1
... 4. Stability: In stable configuration we require more energy to release the electron as compared to non stable configuration.Therefore, Ionization energy is directly proportional to Stability.Ionization Energy is more of full-filled shell as compared to half-filled shell. 5. Screening & Shielding ef ...
... 4. Stability: In stable configuration we require more energy to release the electron as compared to non stable configuration.Therefore, Ionization energy is directly proportional to Stability.Ionization Energy is more of full-filled shell as compared to half-filled shell. 5. Screening & Shielding ef ...
Mass/Mole Conversions
... the _______ of the masses of the second element combined with a certain _________ of the first element is always a ratio of ______________________. ...
... the _______ of the masses of the second element combined with a certain _________ of the first element is always a ratio of ______________________. ...
Hein and Arena - faculty at Chemeketa
... 2000 years after Aristotle, John Dalton, an English schoolmaster, proposed his model of the atom–which was based on experimentation. ...
... 2000 years after Aristotle, John Dalton, an English schoolmaster, proposed his model of the atom–which was based on experimentation. ...
Unit 1: Chapter 3
... same number of valence electrons, and thus have similar properties. 2. Where are the metalloids? Where are the Transition Metals? The Lanthanides? The Actinides? The Halogens? The Nobel Gases? The Alkali Metals? The Alkaline Earth Metals? 3. Describe the origins of the modern periodic table. Describ ...
... same number of valence electrons, and thus have similar properties. 2. Where are the metalloids? Where are the Transition Metals? The Lanthanides? The Actinides? The Halogens? The Nobel Gases? The Alkali Metals? The Alkaline Earth Metals? 3. Describe the origins of the modern periodic table. Describ ...
chp 6 ppt - brown - edited - APchem-MCC
... proportional to the magnitude of each of the two charges (q1 and q2), and inversely proportional to the square of the distance, r, between them. If the two charges are of opposite sign, the force between them is attractive; if they are of the same sign, the force is repulsive. • What this has to do ...
... proportional to the magnitude of each of the two charges (q1 and q2), and inversely proportional to the square of the distance, r, between them. If the two charges are of opposite sign, the force between them is attractive; if they are of the same sign, the force is repulsive. • What this has to do ...
Chapter 1
... magnitude of the charges, the greater the electrostatic repulsion or attraction. As the charge on the plates is increased, the bending will increase. 11. How does Dalton’s atomic theory account for the fact that when 1.000 g of water is decomposed into its elements, 0.111 g of hydrogen and 0889 g of ...
... magnitude of the charges, the greater the electrostatic repulsion or attraction. As the charge on the plates is increased, the bending will increase. 11. How does Dalton’s atomic theory account for the fact that when 1.000 g of water is decomposed into its elements, 0.111 g of hydrogen and 0889 g of ...
Atomic Structure
... uncertain and only a probability of its location is mapped This idea lends to the analogy of a cloud (the more dense the cloud, the higher the probability of finding the electron there) ...
... uncertain and only a probability of its location is mapped This idea lends to the analogy of a cloud (the more dense the cloud, the higher the probability of finding the electron there) ...
Atomic Theory, Mole Relationships, Percent Compositions, and
... • Elements are made up of tiny particles called atoms. • Each element is characterized by the mass of its atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same mass, but atoms of different elements have different masses. • The chemical combination of elements to make different chemical compounds occurs whe ...
... • Elements are made up of tiny particles called atoms. • Each element is characterized by the mass of its atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same mass, but atoms of different elements have different masses. • The chemical combination of elements to make different chemical compounds occurs whe ...
Unit 2: Atomic Structure Practice Packet
... hard sphere ---> plum pudding ---> empty space ---> electron shell ---> modern model ...
... hard sphere ---> plum pudding ---> empty space ---> electron shell ---> modern model ...
S2 Chemistry - Aberdeen Grammar School
... graphs. A final mass of product occurs faster with graph 2. Comparing graph 1 and graph 2, the greater rate of reaction in graph 2 could have been due to: a greater concentration of reactants in 2, a greater temperature of reactants in 2, a smaller particle size in the reactants in 2, or, th ...
... graphs. A final mass of product occurs faster with graph 2. Comparing graph 1 and graph 2, the greater rate of reaction in graph 2 could have been due to: a greater concentration of reactants in 2, a greater temperature of reactants in 2, a smaller particle size in the reactants in 2, or, th ...
bonding, structure, properties and energy changes
... If heat energy is absorbed during a reaction, the temperature of the surroundings decreases and the reaction is described as being endothermic. When methylated spirits (‘meths’) is spilt on the skin it quickly evaporates. This is an endothermic process – the meths absorbs heat energy from the skin a ...
... If heat energy is absorbed during a reaction, the temperature of the surroundings decreases and the reaction is described as being endothermic. When methylated spirits (‘meths’) is spilt on the skin it quickly evaporates. This is an endothermic process – the meths absorbs heat energy from the skin a ...
chapter 4
... but different than A and BA element Atoms of element A and B can be can be physically chemically combined mixed together as a compound ...
... but different than A and BA element Atoms of element A and B can be can be physically chemically combined mixed together as a compound ...
Wine Country Lodging near San Luis Obispo CA
... (molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, and maybe other elements) in order to give a better idea of how the atoms are connected: C2H6O is the molecular formula for ethanol, but nobody ever writes it this way—instead the formula is written C2H5OH to indicate one H atom is connected to the O atom. ...
... (molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, and maybe other elements) in order to give a better idea of how the atoms are connected: C2H6O is the molecular formula for ethanol, but nobody ever writes it this way—instead the formula is written C2H5OH to indicate one H atom is connected to the O atom. ...
Gen Chem--Chapter 3 lecture notes.ppt (Read
... (molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, and maybe other elements) in order to give a better idea of how the atoms are connected: C2H6O is the molecular formula for ethanol, but nobody ever writes it this way—instead the formula is written C2H5OH to indicate one H atom is connected to the O atom. ...
... (molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, and maybe other elements) in order to give a better idea of how the atoms are connected: C2H6O is the molecular formula for ethanol, but nobody ever writes it this way—instead the formula is written C2H5OH to indicate one H atom is connected to the O atom. ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2013 - Chapter 7 Homework 7 (Chapter 7: Periodic
... 12) Alkali metals tend to be more reactive than alkaline earth metals because __________. A) alkali metals have lower densities B) alkali metals have greater electron affinities C) alkali metals have lower ionization energies D) alkali metals have lower melting points E) alkali metals are not more r ...
... 12) Alkali metals tend to be more reactive than alkaline earth metals because __________. A) alkali metals have lower densities B) alkali metals have greater electron affinities C) alkali metals have lower ionization energies D) alkali metals have lower melting points E) alkali metals are not more r ...
2 - DanaFrank
... changes that occur when matter interacts in an open and closed container. 8.P.1.1 Classify matter as elements, compounds, or mixtures based on how the atoms are packed together in arrangements. ...
... changes that occur when matter interacts in an open and closed container. 8.P.1.1 Classify matter as elements, compounds, or mixtures based on how the atoms are packed together in arrangements. ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.