CHEMISTRY 103 – Practice Problems #3 Chapters 8 – 10 http
... 17. A central atom with 2 lone pairs and 3 bonding pairs of e- will have a molecular shape of: a. linear b. trigonal pyramid c. trigonal planar d. T-shape e. trigonal bipyramid 18. In Lewis dot structures, which electron interactions repel the most? a. bonding pair–bonding pair b. bonding pair–lone ...
... 17. A central atom with 2 lone pairs and 3 bonding pairs of e- will have a molecular shape of: a. linear b. trigonal pyramid c. trigonal planar d. T-shape e. trigonal bipyramid 18. In Lewis dot structures, which electron interactions repel the most? a. bonding pair–bonding pair b. bonding pair–lone ...
Study guide for percent abundance chapter 4 spaced out
... c. State and explain which is the more abundant isotope. d. State the name and the number of the isotope relative to which all atomic masses are measured. ...
... c. State and explain which is the more abundant isotope. d. State the name and the number of the isotope relative to which all atomic masses are measured. ...
Answer
... atoms (atomic size decreases across a period as the nuclear charge increases). In each period, the halogen is the element with the highest number of protons in the nucleus that also has an incomplete shell. As a result, they will readily gain a single electron to form the X– ion. Similarly, the high ...
... atoms (atomic size decreases across a period as the nuclear charge increases). In each period, the halogen is the element with the highest number of protons in the nucleus that also has an incomplete shell. As a result, they will readily gain a single electron to form the X– ion. Similarly, the high ...
Answer
... atoms (atomic size decreases across a period as the nuclear charge increases). In each period, the halogen is the element with the highest number of protons in the nucleus that also has an incomplete shell. As a result, they will readily gain a single electron to form the X– ion. Similarly, the high ...
... atoms (atomic size decreases across a period as the nuclear charge increases). In each period, the halogen is the element with the highest number of protons in the nucleus that also has an incomplete shell. As a result, they will readily gain a single electron to form the X– ion. Similarly, the high ...
minerals - Tulane University
... Each of these rock forming processes results in distinctive mineral assemblages and textures in the resulting rock. Thus, the different mineral assemblages and textures give us clues to how the rock formed. An understanding of the rock forming processes and the resulting mineral assemblage and textu ...
... Each of these rock forming processes results in distinctive mineral assemblages and textures in the resulting rock. Thus, the different mineral assemblages and textures give us clues to how the rock formed. An understanding of the rock forming processes and the resulting mineral assemblage and textu ...
CHAPTER 11 Introduction to Atoms
... Read the following section highlights. Then, in your own words, write the highlights in your ScienceLog. • A proton is a positively charged particle with a mass of 1 amu. • A neutron is a particle with no charge that has a mass of 1 amu. • An electron is a negatively charged particle with an extreme ...
... Read the following section highlights. Then, in your own words, write the highlights in your ScienceLog. • A proton is a positively charged particle with a mass of 1 amu. • A neutron is a particle with no charge that has a mass of 1 amu. • An electron is a negatively charged particle with an extreme ...
Atoms- Building Blocks TG quark.qxd
... 10. The greatest difficulty that scientists faced in their study of atoms was their incredibly tiny size, but there were other difficulties. The behavior of electrons does not follow predictable patterns, the orbital shapes are complicated, and one of the most difficult problems was that electrons a ...
... 10. The greatest difficulty that scientists faced in their study of atoms was their incredibly tiny size, but there were other difficulties. The behavior of electrons does not follow predictable patterns, the orbital shapes are complicated, and one of the most difficult problems was that electrons a ...
Atoms Matter Energy Notes
... o The periodic table is organized by physical properties. Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into smaller substances by ordinary chemical means. Atom: The basic particle from which all elements are made. Molecule: two or more atoms that are chemically combined to form a larger particle. ...
... o The periodic table is organized by physical properties. Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into smaller substances by ordinary chemical means. Atom: The basic particle from which all elements are made. Molecule: two or more atoms that are chemically combined to form a larger particle. ...
Chapter 7 Chemical Formulas
... write the symbols for the ions side by side, cations first: Al3+ O22. Cross over the charges by using the absolute value of each ion’s charge as the subscript for the other ion: Al23+ O3-2 3. Check the subscripts and simplify if necessary. Final answer = Al2 O3 ...
... write the symbols for the ions side by side, cations first: Al3+ O22. Cross over the charges by using the absolute value of each ion’s charge as the subscript for the other ion: Al23+ O3-2 3. Check the subscripts and simplify if necessary. Final answer = Al2 O3 ...
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3)
... 4. Types of Chemical Formulas (e.g., see Table 3.1) empirical formula shows the simplest ratio of the elements present molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in one molecule structural formula shows how the atoms are connected e.g., for "hydrogen peroxide" the three formulas are: ...
... 4. Types of Chemical Formulas (e.g., see Table 3.1) empirical formula shows the simplest ratio of the elements present molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in one molecule structural formula shows how the atoms are connected e.g., for "hydrogen peroxide" the three formulas are: ...
Chemistry Module 1- Basic Revision Notes 1.1a Atomic Structure 1.1
... 1.1.3 Elements (H, He, Li, Be,…..) are the basic building blocks of all matter, and cannot be broken down into simpler parts by chemical means. 1.1.4 There is a clear relationship between an elements electronic structure and its position in the periodic table. P E r i o d ...
... 1.1.3 Elements (H, He, Li, Be,…..) are the basic building blocks of all matter, and cannot be broken down into simpler parts by chemical means. 1.1.4 There is a clear relationship between an elements electronic structure and its position in the periodic table. P E r i o d ...
KENTUCKY TECH ELIZABETHTOWN
... Has been used practically only about 100 years Amber became charged when rubbed with other materials Attracted things like leaves, feathers, bits of cloth Word “Electric” comes from Greek word “Elektron” Positive Charges (List A) ...
... Has been used practically only about 100 years Amber became charged when rubbed with other materials Attracted things like leaves, feathers, bits of cloth Word “Electric” comes from Greek word “Elektron” Positive Charges (List A) ...
Chemistry Stoichiometry Standard Set 3 Review
... 3b. Students know the quantity one mole is set by defining one mole of carbon-12 atoms to have a mass of exactly 12 grams. Description The mole concept is often difficult at first, but the concept is convenient in chemistry just as a dozen is a convenient concept, or measurement unit, in the grocer ...
... 3b. Students know the quantity one mole is set by defining one mole of carbon-12 atoms to have a mass of exactly 12 grams. Description The mole concept is often difficult at first, but the concept is convenient in chemistry just as a dozen is a convenient concept, or measurement unit, in the grocer ...
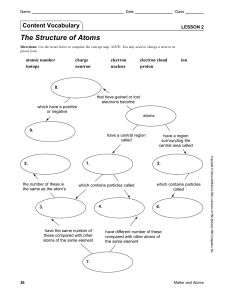
Lesson 2 | The Structure of Atoms
... 2. Atoms are composed of several basic types of very small particles; the number of each of these particles gives the different kinds of atoms their unique identity. 3. The region at the center of an atom that contains most of the mass of the atom is called the nucleus. a. A positively charged parti ...
... 2. Atoms are composed of several basic types of very small particles; the number of each of these particles gives the different kinds of atoms their unique identity. 3. The region at the center of an atom that contains most of the mass of the atom is called the nucleus. a. A positively charged parti ...
Atomic Theory: History - stpats-sch4u-sem1-2013
... 1. Start adding electrons into the lowest energy level and build up form the bottom until the limit on the number of electrons for the particle is reached. 2. No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers; if an electron is in the same orbital with another electron, it must have opposite s ...
... 1. Start adding electrons into the lowest energy level and build up form the bottom until the limit on the number of electrons for the particle is reached. 2. No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers; if an electron is in the same orbital with another electron, it must have opposite s ...
Atoms
... of an element when you take into account all naturally occurring isotopes. No mater how you what compound your element is bound in, or how you get your sample, the ratio of all isotopes will be the same and so you can forget about isotopes and use average mass… ...
... of an element when you take into account all naturally occurring isotopes. No mater how you what compound your element is bound in, or how you get your sample, the ratio of all isotopes will be the same and so you can forget about isotopes and use average mass… ...
Atoms and Molecules - E
... number 10 because electronic configuration of atomic number 11 will be 2, 8, 1 so, it has to loose only 1e- from its outermost shall to be stable which is more easy than the element with atomic number 10 because its electronic configuration is 2, 8 and has 8e- in the outermost shell and hence is alr ...
... number 10 because electronic configuration of atomic number 11 will be 2, 8, 1 so, it has to loose only 1e- from its outermost shall to be stable which is more easy than the element with atomic number 10 because its electronic configuration is 2, 8 and has 8e- in the outermost shell and hence is alr ...
INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY - Chapter 1
... Average value that varies significantly from core to edge ...
... Average value that varies significantly from core to edge ...
Practice exam - Dynamic Science
... The screws are too soft and will not support the window. Both the window frame and the screw will rust away. The screws will rust. The metal around the screw will corrode and the screw will fall out. ...
... The screws are too soft and will not support the window. Both the window frame and the screw will rust away. The screws will rust. The metal around the screw will corrode and the screw will fall out. ...
Chapter 2
... bonding partners • An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine • After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have charges ...
... bonding partners • An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine • After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have charges ...
Atomic Worksheet
... Where would you find a proton in an atom? ___________________________________ What is the charge of an electron?__________ Where would you find an electron in an atom?_________________________________ What is the charge of a neutron?___________ Where would you find a neutron in an atom? ____________ ...
... Where would you find a proton in an atom? ___________________________________ What is the charge of an electron?__________ Where would you find an electron in an atom?_________________________________ What is the charge of a neutron?___________ Where would you find a neutron in an atom? ____________ ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.