Portal Placement for Shoulder Arthroscopy
... the lateral edge of the acromion and there are no lateral knots to get caught either. When tying knots for Bankart repair, it is possible to engage the labral tissue and roll it up onto the glenoid rim creating a soft tissue buttress. This is much more difficult with the knotless design. The length ...
... the lateral edge of the acromion and there are no lateral knots to get caught either. When tying knots for Bankart repair, it is possible to engage the labral tissue and roll it up onto the glenoid rim creating a soft tissue buttress. This is much more difficult with the knotless design. The length ...
an introduction to human body - eSSUIR
... 1. Tubular bones are composed of spongy and compact substance forming a tube with a marrow cavity. Long tubular bones (arm bones, forearm bones, thigh bones, and leg bones) are supports and long levelers of movement. The process of endochondral ossification occurs in both epiphyses (biepiphyseal pla ...
... 1. Tubular bones are composed of spongy and compact substance forming a tube with a marrow cavity. Long tubular bones (arm bones, forearm bones, thigh bones, and leg bones) are supports and long levelers of movement. The process of endochondral ossification occurs in both epiphyses (biepiphyseal pla ...
Injuries
... -The only muscle supplied by the musculocutaneous nerve that can be examined accurately is the biceps; the brachialis and the coracobrachialis are difficult to palpate. -Complete division of the nerve may be overlooked because the sensory loss may be ill defined and flexion of the elbow by the brach ...
... -The only muscle supplied by the musculocutaneous nerve that can be examined accurately is the biceps; the brachialis and the coracobrachialis are difficult to palpate. -Complete division of the nerve may be overlooked because the sensory loss may be ill defined and flexion of the elbow by the brach ...
THE NECK BONES Skeleton is formed by cervical vertebrae, hyoid
... closed superiorly by cranial base and on each side by carotid sheath o opens inferiorly into superior mediastinum PARALYSIS OF PLATYSMA o Causes skin to fall away from neck in folds o Is caused by damage to cervical branch of facial nerve SPREAD OF INFECTION IN NECK o Investing layer of deep cervica ...
... closed superiorly by cranial base and on each side by carotid sheath o opens inferiorly into superior mediastinum PARALYSIS OF PLATYSMA o Causes skin to fall away from neck in folds o Is caused by damage to cervical branch of facial nerve SPREAD OF INFECTION IN NECK o Investing layer of deep cervica ...
Chapter (I) Anatomy of cervical spine
... vertebra below. The upper surface is concave transversely, and presents a projecting lip on either side; the lower surface is concave from before backward, convex from side to side, and presents laterally shallow concavities which receive the corresponding projecting lips of the subjacent vertebra. ...
... vertebra below. The upper surface is concave transversely, and presents a projecting lip on either side; the lower surface is concave from before backward, convex from side to side, and presents laterally shallow concavities which receive the corresponding projecting lips of the subjacent vertebra. ...
unilateral variation in biceps brachii muscle with four heads
... Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India. ABSTRACT Biceps brachii is one of the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm. Normally it has two heads; long head which originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of glenoid cavity and short head from the tip of coracoid process of scapula. During routine Anato ...
... Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India. ABSTRACT Biceps brachii is one of the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm. Normally it has two heads; long head which originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of glenoid cavity and short head from the tip of coracoid process of scapula. During routine Anato ...
Accessory Tendon and Tripartite Insertion Pattern of Fibularis
... and attachments of peroneal muscles (longus and brevis) were studied and appropriate photographs were taken. The peroneus longus and brevis originated in the form of a fused mass from the upper half of lateral surface of fibula. However, at the middle third of leg, the two muscles were separated. Th ...
... and attachments of peroneal muscles (longus and brevis) were studied and appropriate photographs were taken. The peroneus longus and brevis originated in the form of a fused mass from the upper half of lateral surface of fibula. However, at the middle third of leg, the two muscles were separated. Th ...
Kaan Yücel MD, Ph.D.
... Contain and protect the pelvic viscera Provide support for the abdominopelvic viscera and gravid (pregnant) uterus Provide attachment for the erectile bodies of the external genitalia. Provide attachment for the muscles and membranes ...
... Contain and protect the pelvic viscera Provide support for the abdominopelvic viscera and gravid (pregnant) uterus Provide attachment for the erectile bodies of the external genitalia. Provide attachment for the muscles and membranes ...
Unit #3 Lecture Syllabus 2008 (PDF version)
... Posterior cerebral arteries- terminal branches of the basilar artery, supply the occipital lobes of the cerebrum Posterior communication artery- connects the middle cerebral artery with the posterior cerebral arteries ...
... Posterior cerebral arteries- terminal branches of the basilar artery, supply the occipital lobes of the cerebrum Posterior communication artery- connects the middle cerebral artery with the posterior cerebral arteries ...
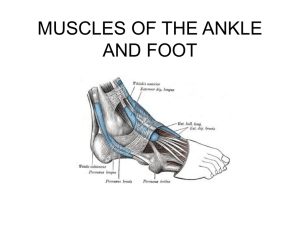
muscles of the ankle and foot
... He allowed his beloved cousin Patroclus to fight in his armor, and when Hector slew Patroclus, Achilles returned to battle, killed Hector, and dragged his body around the walls of Troy. Homer mentions Achilles' funeral but not the circumstances of his death; the ...
... He allowed his beloved cousin Patroclus to fight in his armor, and when Hector slew Patroclus, Achilles returned to battle, killed Hector, and dragged his body around the walls of Troy. Homer mentions Achilles' funeral but not the circumstances of his death; the ...
Indicate structure that belongs to pelvis as a whole
... The inguinal canal in patient is so wide that the internal organs extend from it. What is the upper wall of the inguinal canal? A. obliquus abdominis internus and transversus muscles B. fascia transversalis C. inguinal ligament D. aponeurosis of m. obliquus abdominis externus E. obliquus abdominis i ...
... The inguinal canal in patient is so wide that the internal organs extend from it. What is the upper wall of the inguinal canal? A. obliquus abdominis internus and transversus muscles B. fascia transversalis C. inguinal ligament D. aponeurosis of m. obliquus abdominis externus E. obliquus abdominis i ...
PowerPoint Sunusu - Yeditepe University Pharma Anatomy
... Coracohumeral ligament Transverse humeral ligament Coracoacromial ligament ...
... Coracohumeral ligament Transverse humeral ligament Coracoacromial ligament ...
17 Loukas.p65
... anterior belly of the digastric muscle [1, 4, 6, 11, 15, 20, 21, 24]. Norton [11], in 2000, reported a case of bilateral occurrence of accessory digastric muscles, which inserted upon the midline raphe, decussated, and continued to rejoin the contralateral anterior bellies of the digastric muscles b ...
... anterior belly of the digastric muscle [1, 4, 6, 11, 15, 20, 21, 24]. Norton [11], in 2000, reported a case of bilateral occurrence of accessory digastric muscles, which inserted upon the midline raphe, decussated, and continued to rejoin the contralateral anterior bellies of the digastric muscles b ...
The Ankle Joint HO
... malleolus to the neck of the talus. It is a flat band. The calcaneofibular ligament is a rounded cord extending from the front of the tip of the malleolus down and back to the lateral surface of the calcaneus. The strong posterior talofibular ligament lies horizontally between the malleolar fossa an ...
... malleolus to the neck of the talus. It is a flat band. The calcaneofibular ligament is a rounded cord extending from the front of the tip of the malleolus down and back to the lateral surface of the calcaneus. The strong posterior talofibular ligament lies horizontally between the malleolar fossa an ...
3 Summary of the Gross Anatomy of the Extraocular Muscles
... insertion forms a curved concave line toward the origin of the muscle. Its anterior margin is about 10 mm behind the lower edge of the insertion of the lateral rectus muscle; its posterior end is 1 mm below and 1 to 2 mm in front of the macula (Fig. 3–7). Near its insertion the posterior border of t ...
... insertion forms a curved concave line toward the origin of the muscle. Its anterior margin is about 10 mm behind the lower edge of the insertion of the lateral rectus muscle; its posterior end is 1 mm below and 1 to 2 mm in front of the macula (Fig. 3–7). Near its insertion the posterior border of t ...
THE ANKLE AND FOOT
... • Origin: head and upper 2/3 of the outer surface of the fibula • Insertion: undersurfaces of the 1st cuneiform and first metatarsal bones • Note: passes posterior to lateral malleolus. • Actions: – Eversion – Plantar flexion • The tendon goes under the foot from the lateral to the medial surface, t ...
... • Origin: head and upper 2/3 of the outer surface of the fibula • Insertion: undersurfaces of the 1st cuneiform and first metatarsal bones • Note: passes posterior to lateral malleolus. • Actions: – Eversion – Plantar flexion • The tendon goes under the foot from the lateral to the medial surface, t ...
Spine - Amazon Web Services
... vertebra to form the odontoid peg (Fig. 3.5), which sits within the ring of bone anteriorly where the vertebral body of C1 should be located. Superiorly the laminae have an impression due to the vertebral artery passing across their cranial surface before entering the cranial cavity. The spinous pro ...
... vertebra to form the odontoid peg (Fig. 3.5), which sits within the ring of bone anteriorly where the vertebral body of C1 should be located. Superiorly the laminae have an impression due to the vertebral artery passing across their cranial surface before entering the cranial cavity. The spinous pro ...
Muscles of the Knee
... Medial (Tibial) collateral ligament: broad flat ligament on the medial surface of the knee joint extending from the medial femoral condyle to the medial tibial condyle Lateral (Fibular) collateral ligament: strong rounded ligament on the lateral surface of the knee joint extending from the lateral f ...
... Medial (Tibial) collateral ligament: broad flat ligament on the medial surface of the knee joint extending from the medial femoral condyle to the medial tibial condyle Lateral (Fibular) collateral ligament: strong rounded ligament on the lateral surface of the knee joint extending from the lateral f ...
Process
... • Characteristic external and internal features related to particular functions called surface ...
... • Characteristic external and internal features related to particular functions called surface ...
6.Sacrum and Pelvis 2014-12-23 07:012.5 MB
... in correct position of bony pelvis: 1- the superior anterior iliac spine and pubic tubercle are in same line in sagittal cut. 2- axis between central points of inlet and outlet is parallel to sacrum curvature. in this correct position the sacrum is facing downward and forward and the pelvic surface ...
... in correct position of bony pelvis: 1- the superior anterior iliac spine and pubic tubercle are in same line in sagittal cut. 2- axis between central points of inlet and outlet is parallel to sacrum curvature. in this correct position the sacrum is facing downward and forward and the pelvic surface ...
Gluteal - Faculty
... Sciatic nerve (L4 - S3) Posterior thigh and all leg and foot compartments Tibial nerve (L4 - S3) Posterior leg and plantar foot Common fibular nerve (L4 - S2) Lateral/anterior leg and dorsal foot Pudendal nerve (S2 - S4) Pelvic perineum Identify the nerves from the entire lumbrosacral plexus (Nerve ...
... Sciatic nerve (L4 - S3) Posterior thigh and all leg and foot compartments Tibial nerve (L4 - S3) Posterior leg and plantar foot Common fibular nerve (L4 - S2) Lateral/anterior leg and dorsal foot Pudendal nerve (S2 - S4) Pelvic perineum Identify the nerves from the entire lumbrosacral plexus (Nerve ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy.org Thoracic Wall THORACIC
... The innermost intercostal muscles are the least distinct of the intercostal muscles, and the fibers have the same orientation as the internal intercostals. The neurovascular bundles associated with the intercostal spaces pass around the thoracic wall in the costal grooves in a plane between the inne ...
... The innermost intercostal muscles are the least distinct of the intercostal muscles, and the fibers have the same orientation as the internal intercostals. The neurovascular bundles associated with the intercostal spaces pass around the thoracic wall in the costal grooves in a plane between the inne ...
thorax - bones joints muscles
... The external intercostal muscles are con>nuous inferiorly with the external oblique muscles in the anterolateral abdominal wall. The internal intercostal muscles (11 pairs) run deep to and at right angles to the external intercostals. Between the ribs posteriorly, medial to the angles, the inter ...
... The external intercostal muscles are con>nuous inferiorly with the external oblique muscles in the anterolateral abdominal wall. The internal intercostal muscles (11 pairs) run deep to and at right angles to the external intercostals. Between the ribs posteriorly, medial to the angles, the inter ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.