* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download thorax - bones joints muscles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
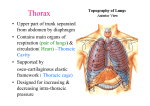
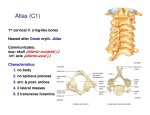
THETHORAX THORACICWALL BREAST THETHORAX • THORACICWALL • BREAST THETHORAX THORACICWALL THETHORAX THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Thepartofthebodybetweentheneckandabdomen. Thethoraciccage(ribcage),withthehorizontalbarsformedbyribs andcostalcar;lages,isalsosupportedbythever>calsternum (breastbone)andthoracicvertebrae Thethoracicskeletonincludes: • 12pairsofribsandassociatedcostalcar>lages, • 12thoracicvertebraeandtheintervertebral(IV)discsinterposed betweenthem, • andthesternum. THERIBS THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Ribsarecurved,flatbonesthatformmostofthethoraciccage Therearethreetypesofribsthatcanbeclassifiedastypicalor atypical: • true(vertebrosternal)ribs(1st–7thribs) • false(vertebrochondral)ribs(8th,9th,andusually10thribs) • floa;ng(vertebral,free)ribs(11th,12th,andsome>mes10thribs) THERIBS THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Therearethreetypesofribsthatcanbeclassifiedastypicalor atypical: • true(vertebrosternal)ribs(1st–7thribs): theyaWachdirectlytothesternumthroughtheirowncostalcar>lages. • false(vertebrochondral)ribs(8th,9th,andusually10thribs): theircar>lagesareconnectedtothecar>lageoftheribabovethem; thustheirconnec>onwiththesternumisindirect. • floa;ng(vertebral,free)ribs(11th,12th,andsome;mes10thribs): therudimentarycar>lagesoftheseribsdonotconnectevenindirectly withthesternum;insteadtheyendintheposteriorabdominal musculature. THERIBS THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Typicalribs(3rd–9th)havethefollowingcomponents: •Head •Neck •Tubercle •Body Typicalribs(3rd–9th)havethefollowingcomponents: •Head:hastwofacets,oneforar>cula>onwiththenumerically correspondingvertebraandonefacetforthevertebrasuperiortoit. •Neck:connectstheheadoftheribwiththebodyatthe levelofthetubercle. •Tubercle:ar>culateswiththecorrespondingtransverseprocessof thevertebra, •Body(sha[):thin,flat,andcurved. THERIBS THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS ATYPICALRIBS(1st,2nd,and10th–12th)aredissimilar: • the1stribisthebroadest(i.e.,itsbodyiswidestandnearly horizontal),shortest,andmostsharplycurved • the1stribhasasinglefacetonitsheadforar>cula>onwiththeT1 vertebraonly • the1stribhastwotransverselydirectedgroovescrossingits superiorsurfaceforthesubclavianvessels • the1stribhasthegroovesseparatedbyascalenetubercleand ridge,towhichtheanteriorscalenemuscleisaWached. THERIBS THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Atypicalribs(1st,2nd,and10th–12th)aredissimilar: • the2ndribishasathinner,lesscurvedbody • hastwofacetsforar>cula>onwiththebodiesoftheT1andT2 vertebrae Atypicalribs(1st,2nd,and10th–12th)aredissimilar: • The10th–12thribs,likethe1strib,haveonlyonefaceton theirheadsandar;culatewithasinglevertebra. Atypicalribs(1st,2nd,and10th–12th)aredissimilar: •The11thand12thribsareshortandhavenoneckor tubercle. THECOSTALCARTILAGES THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Costalcar;lagesprolongtheribsanteriorlyandcontributetothe elas>cityofthethoracicwall,providingaflexibleaWachment fortheiranteriorends(>ps). Intercostalspacesseparatetheribsandtheircostalcar>lagesfromone another THETHORACICVERTEBRAE THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Characteris>cfeaturesofthoracicvertebraeinclude: • Bilateralcostalfacets(demifacets)onthevertebralbodies,usually occurringininferiorandsuperiorpairs,forar>cula>onwiththe headsofribs. • Costalfacetsonthetransverseprocessesforar>cula>onwiththe tuberclesofribs,exceptfortheinferiortwoorthreethoracic vertebrae. • Long,inferiorlyslan>ngspinousprocesses. THETHORACICVERTEBRAE THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Superiorandinferiorcostalfacetsoccurasbilaterallypaired,planar surfacesonthesuperiorandinferiorposterolateralmarginsofthe bodiesoftypicalthoracicvertebrae(T2–T9). Atypicalthoracicvertebrae: • ThesuperiorcostalfacetsofvertebraT1arenotdemifacetsbecause therearenodemifacetsontheC7vertebraabove,andrib1 ar;culatesonlywithvertebraT1.T1hasatypicalinferiorcostal facet. • T10hasonlyonebilateralpairof(whole)costalfacets,located partlyonitsbodyandpartlyonitspedicle. • T11andT12alsohaveonlyasinglepairof(whole)costalfacets, locatedontheirpedicles. THESTERNUM THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Thesternumistheflat,elongatedbonethatformsthemiddleofthe anteriorpartofthethoraciccage. Thesternumconsistsofthreeparts: • manubrium, • body,and • xiphoidprocess THESTERNUM THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Theeasilypalpatedconcavecenterofthesuperiorborderofthe manubriumisthejugularnotch(suprasternalnotch). Thejugularnotchliesattheleveloftheinferiorborderofthebodyof T2vertebraandthespacebetweenthe1stand2ndthoracicspinous processes. Themanubriumandbodyofthesternumlieinslightlydifferentplanes superiorandinferiortotheirjunc>on, themanubriosternaljoint; hence,theirjunc>onformsaprojec>ngsternalangle(ofLouis). Inferolateraltotheclavicularnotch,thecostalcar>lageofthe1stribis >ghtlyaWachedtothelateralborderofthemanubrium– -thesynchondrosisofthefirstrib THESTERNUM THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Thebodyofthesternum,islonger,narrower,andthinnerthanthe manubrium,andislocatedattheleveloftheT5–T9vertebrae Thexiphoidprocess,thesmallestandmostvariablepartofthe sternum,isthinandelongated.ItsinferiorendliesatthelevelofT10 vertebra. THESTERNUM THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Thexiphisternaljointisamidlinemarkerforthesuperiorlimitofthe liver,thecentraltendonofthediaphragm,andtheinferiorborderof theheart. JOINTSOFTHORACICWALL • Intervertebral(ofvertebraeT1–T12) • Costovertebral(jointsofheadofrib) • Costochondral • Interchondral • Sternocostal • Sternoclavicular • Manubriosternal • Xiphisternal THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS JOINTSOFTHORACICWALL THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS JOINTSOFTHORACICWALL THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS THETHORACICAPERTURES THETHORACICAPERTURES THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Whilethethoraciccageprovidesacompletewallperipherally,itis opensuperiorlyandinferiorly. Themuchsmallersuperioropening(aperture)isapassagewaythat allowscommunica>onwiththeneckandupperlimbs. Thelargerinferioropeningprovidesthering-likeoriginofthe diaphragm,whichcompletelyoccludestheopening. THETHORACICAPERTURES THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS TheSUPERIORTHORACICAPERTUREisbounded: •Posteriorly,byvertebraT1,thebodyofwhichprotrudes anteriorlyintotheopening. •Laterally,bythe1stpairofribsandtheircostalcar>lages. •Anteriorly,bythesuperiorborderofthemanubrium. THETHORACICAPERTURES THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS THETHORACICINLET Space-occupyingtumoursinthisloca>onmaycompressadjacent structures,leadingtotheclinicalcondi>oncalledthoracicoutlet syndrome. THETHORACICAPERTURES THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS Inferiorlythecavityofthethoraxisseparatedfromtheabdominal contentsbyafibromuscularsheetcalledthediaphragm. Thefloorofthethoraciccavity(thoracicdiaphragm)isdeeply invaginatedinferiorly(i.e.,ispushedupward)byvisceraofthe abdominalcavity. THETHORAX-BONES&JOINTS THETHORACICAPERTURES TheINFERIORTHORACICAPERTUREisboundedasfollows: •Posteriorly,bythe12ththoracicvertebra,thebodyofwhich protrudesanteriorlyintotheopening. •Posterolaterally,bythe11thand12thpairsofribs. •Anterolaterally,bythejoinedcostalcar>lagesofribs7–10,forming thecostalmargins. •Anteriorly,bythexiphisternaljoint. THEMUSCLESOFTHETHORAX MUSCLESOFTHORACICWALL THETHORAX THEMUSCLESOFTHETHORAX MUSCLESOFTHEPECTORALREGION: • Lateralandmedialpectoralnerves • Pectoralismajor • Subclavius • Nervetosubclavius • Pectoralisminor • Medialpectoralnerve Thepectoralismajormuscleisthelargestandmostsuperficialofthe pectoralregionmuscles. Thesubclaviusandpectoralisminormusclesunderliepectoralis major: • subclaviusissmallandpasseslaterallyfromtheanteriorand medialpartofribItotheinferiorsurfaceoftheclavicle; • pectoralisminorpassesfromtheanteriorsurfacesofribsIIItoVto thecoracoidprocessofthescapula. THETHORAX THEMUSCLESOFTHETHORAX Themusclesofthepectoralregionformtheanteriorwalloftheaxilla, aregionbetweentheupperlimbandtheneckthroughwhichallmajor structurespass. Nerves,vessels,andlympha>csthatpassbetweenthepectoral regionandtheaxillapassthroughtheclavipectoralfasciabetween subclaviusandpectoralisminororpassundertheinferiormarginsof pectoralismajorandminor. THEMUSCLESOFTHETHORAX THEMUSCLES Thetruemusclesofthethoracicwallarethe: serratusposterior,levatorescostarum,intercostal,subcostal, andtransversusthoracis. THEMUSCLESOFTHETHORAX THEMUSCLES Thelevatorescostarummusclesare12fan-shapedmusclesthat elevatetheribs,buttheirrole,ifany,innormalinspira>onis uncertain. Theintercostalmusclesoccupytheintercostalspaces Thesuperficiallayer-theexternalintercostals,theinnerlayer-the internalintercostals.Thedeepestfibers-theinnermostintercostals. Theexternalintercostalmuscles(11pairs)occupytheintercostal spacesfromthetuberclesoftheribsposteriorlytothecostochondral junc>onsanteriorly. THEMUSCLESOFTHETHORAX THEMUSCLES Theexternalintercostalmusclesarecon>nuousinferiorlywiththe externalobliquemusclesintheanterolateralabdominalwall. Theinternalintercostalmuscles(11pairs)rundeeptoandatright anglestotheexternalintercostals. Betweentheribsposteriorly,medialtotheangles,theinternal intercostalsarereplacedbytheinternalintercostalmembranes. Theinferiorinternalintercostalmusclesarecon>nuouswiththe internalobliquemusclesintheanterolateralabdominalwall. Theinnermostintercostalmusclesaresimilartotheinternal intercostalsandareessen>allytheirdeeperparts. Theinnermostintercostalsareseparatedfromtheinternal intercostalsbyintercostalnervesandvessels THEMUSCLESOFTHETHORAX THEMUSCLES Thesubcostalmusclesarevariableinsizeandshape,usuallybeing welldevelopedonlyinthelowerthoracicwall. Thetransversusthoracismusclesconsistoffourorfive slipsthatradiatesuperolaterallyfromtheposterioraspect oftheinferiorsternum. Theexternalandinternalintercostalsareac>veduringinspira;on andexpira;on.Theroleofthesemusclesinproducingmovementof theribsappearstoberelatedmainlytoforcedrespira;on. Theprimaryroleoftheintercostalmusclesinrespira>onistosupport (increasethetonusorrigidityof)theintercostalspace. Thediaphragmistheprimarymuscleofinspira>on. THERESPIRATORYSYSTEM NERVESOFTHETHORACICWALL The12pairsof thoracicspinal nervessupplythe thoracic wall. AssoonastheyleavetheIVforaminain whichtheyareformed,themixed thoracicspinalnervesdivideinto anteriorandposterior(primary)ramior branches Theanteriorramiof nervesT1–T11form theintercostalnerves thatrunalongtheextent oftheintercostalspaces. THERESPIRATORYSYSTEM NERVESOFTHETHORACICWALL Neartheanglesoftheribs,thenervespassbetweentheinternal intercostalandtheinnermostintercostalmuscles. Atthispoint,theintercostalnervespasstoandthencon>nueto courseinorjustinferiortothecostalgrooves,runninginferiortothe intercostalarteries. THERESPIRATORYSYSTEM NERVESOFTHETHORACICWALL Thebranchesofatypicalintercostalnerveare: • Ramicommunicantes,orcommunica>ngbranches,thatconnect eachintercostalnervetotheipsilateralsympathe>ctrunk. • Collateralbranchesthatariseneartheanglesoftheribs • LateralcutaneousbranchesthatariseneartheMAL • Anteriorcutaneousbranchespiercethemusclesandmembranes oftheintercostalspace • Muscularbranchesthatsupplytheintercostal,subcostal, transversusthoracis,levatorescostarum,andserratusposterior muscles ARTERIESOFTHORACICWALL THERESPIRATORYSYSTEM Thearterialsupplytothethoracicwallderivesfromthe: • Thoracicaorta,throughtheposteriorintercostalandsubcostal arteries. • Subclavianartery,throughtheinternalthoracicandsupreme intercostalarteries. • Axillaryartery,throughthesuperiorandlateralthoracicarteries. Theintercostalarteriescoursethroughthethoracicwall betweentheribs. Eachintercostalspaceissuppliedbythreearteries:alarge posteriorintercostalartery(anditscollateralbranch)anda smallpairofanteriorintercostalarteries. VEINSOFTHORACICWALL THERESPIRATORYSYSTEM Thereare11posteriorintercostalveinsandonesubcostalveinon eachside.Theposteriorintercostalveinsanastomosewiththe anteriorintercostalveins(tributariesofinternalthoracicveins). Mostposteriorintercostalveins(4–11)endintheazygos/hemiazygosvenoussystem,whichconveysvenousbloodtothesuperior venacava(SVC). Theposteriorintercostalveinsofthe1stintercostalspaceusually enterdirectlyintotherightandle[brachiocephalicveins. THERESPIRATORYSYSTEM THEBREASTS BREASTS THEBREASTS Thebreastsconsistofglandularandsuppor>ngfibrous ;ssueembeddedwithinafaWymatrix,togetherwithblood vessels,lympha>cs,andnerves. Themammaryglandsareinthesubcutaneous>ssueoverlyingthe pectoralismajorandminormuscles. Atthegreatestprominenceofthebreastisthenipple,surrounded byacircularpigmentedareaofskin,theareola Theroughlycircularbodyofthefemalebreastrestsonabedofthe breastthatextendstransverselyfromthelateralborderofthe sternumtothemidaxillarylineandver>callyfromthe2ndthrough 6thribs. FEMALEBREASTS THEBREASTS Twothirdsofthebedareformedbythepectoralfasciaoverlying thepectoralismajor;theotherthird,bythefasciacoveringthe serratusanterior. Betweenthebreastandthepectoralfasciaisaloosesubcutaneous >ssueplaneorpoten>alspace– -theretromammaryspace. Asmallpartofthemammaryglandmayextendalongthe inferolateraledgeofthepectoralismajortowardtheaxillaryfossa (armpit),forminganaxillaryprocessortail(ofSpence). ThemammaryglandsarefirmlyaWachedtothedermisofthe overlyingskin,especiallybysubstan>alskinligaments, thesuspensoryligamentsofCooper. FEMALEBREASTS THEBREASTS Thesecondensa>onsoffibrousconnec>ve>ssue,par>cularlywell developedinthesuperiorpartofthegland,helpsupportthelobes andlobulesofthemammarygland. Thelac;ferousductsgiverisetobudsthatdevelopinto15–20 lobulesofthemammarygland,whichcons>tutetheparenchyma (func>onalsubstance)ofthemammarygland. Thuseachlobuleisdrainedbyalac;ferousduct. Eachducthasadilatedpor>ondeeptotheareola,thelac;ferous sinus,inwhichasmalldropletofmilkaccumulates orremainsinthenursingmother. Theareolaecontainnumeroussebaceousglands,whichenlarge duringpregnancyandsecreteanoilysubstance FEMALEBREASTS THEBREASTS Thenipplesareconicalorcylindricalprominencesinthecentersof theareolae. Themammaryglandsaremodifiedsweatglands;therefore,they havenocapsuleorsheath. Inmostwomen,thebreastsenlargeslightlyduringthemenstrual periodfromincreasedreleaseofgonadotropichormones:follicles;mula;nghormone(FSH)andluteinizinghormone(LH)-onthe glandular>ssue. VASCULATUREOFBREASTS THEBREASTS Thearterialsupplyofthebreastderivesfromthe: • Medialmammarybranchesofperfora>ngbranchesandanterior intercostalbranchesoftheinternalthoracicartery,origina>ng fromthesubclavianartery. • Lateralthoracicandthoraco-acromialarteries,branchesofthe axillaryartery. • Posteriorintercostalarteries,branchesofthethoracicaortainthe 2nd,3rd,and4thintercostalspaces. Thevenousdrainageofthebreastismainlytotheaxillaryvein,but thereissomedrainagetotheinternalthoracicvein. VASCULATUREOFBREASTS THEBREASTS Thelympha;cdrainageofthebreastisimportantbecauseofitsrole inthemetastasisofcancercells. Lymphpassesfromthenipple,areola,andlobulesoftheglandtothe subareolarlympha;cplexus. VASCULATUREOFBREASTS THEBREASTS Fromthesubareolarlympha;cplexus: • mostlymph(>75%),especiallyfromthelateralbreastquadrants, drainstotheaxillarylymphnodes,ini>allytotheanterioror pectoralnodesforthemostpart. • mostoftheremaininglymph,par>cularlyfromthemedialbreast quadrants,drainstotheparasternallymphnodesortothe oppositebreast. • lymphfromtheinferiorquadrantsmaypassdeeplytoabdominal lymphnodes(subdiaphragma>cinferiorphreniclymphnodes). VASCULATUREOFBREASTS THEBREASTS Lymphfromtheaxillarynodesdrainsintoclavicular(infraclavicular andsupraclavicular)lymphnodesandfromthemintothesubclavian lympha;ctrunk,whichalsodrainslymphfromtheupperlimb. Lymphfromtheparasternalnodesentersthebronchomedias>nal lympha>ctrunks,whichalsodrainlymphfromthethoracicviscera. Thetermina>onofthelympha>ctrunksvaries. Thesetrunksaredescribedasmergingwitheachotherandwiththe jugularlympha;ctrunk,drainingtheheadandnecktoformashort rightlympha;cductontherightsideorenteringthetermina>onat thethoracicductonthele[side. VASCULATUREOFBREASTS THEBREASTS Thetrunksopenindependentlyintothejunc>onoftheinternal jugularandsubclavianveins,therightorledvenousangles,that formtherightandle[brachiocephalicveins. NERVESOFBREASTS THEBREASTS Thenervesofthebreastderivefromanteriorandlateralcutaneous branchesofthe4th-6thintercostalnerves. Thebranchesoftheintercostalnervesconvey: • sensoryfibersfromtheskinofthebreast • sympathe;cfiberstothebloodvesselsinthebreastsandsmooth muscleintheoverlyingskinandnipple.