Muscles, Innervation and the Compartments of the Upper Limb
... The lateral head. Originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of the glenoid fossa The biceps inserts into the tuberosity of radius; and it also inserts into the antebrachial fascia by virtue of the bicipital aponeurosis. It does very different things depending on what position the arm is in: o It sup ...
... The lateral head. Originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of the glenoid fossa The biceps inserts into the tuberosity of radius; and it also inserts into the antebrachial fascia by virtue of the bicipital aponeurosis. It does very different things depending on what position the arm is in: o It sup ...
Fascia 1. Investing layer 2. Prevertebral layer 3. Pretracheal layer
... 3. Transverse cervical and suprascapular arteries (Fig. 8.182, p.1026) brr. of thyrocervical trunk (from 1st part of subcalvian a.), Transverse cervical a. divides into: Superficial br. – on deep surface of trapezius m. Deep br. (dorsal scapular artery) – deep surface of rhomboid mm. Suprascapular a ...
... 3. Transverse cervical and suprascapular arteries (Fig. 8.182, p.1026) brr. of thyrocervical trunk (from 1st part of subcalvian a.), Transverse cervical a. divides into: Superficial br. – on deep surface of trapezius m. Deep br. (dorsal scapular artery) – deep surface of rhomboid mm. Suprascapular a ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Joints of the upper limb
... Movement of the pectoral girdle involves the sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, and glenohumeral joints, usually all moving simultaneously. Functional defects in any of the joints impair movements of the pectoral girdle. Mobility of the scapula is essential for free movement of the upper limb. The ...
... Movement of the pectoral girdle involves the sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, and glenohumeral joints, usually all moving simultaneously. Functional defects in any of the joints impair movements of the pectoral girdle. Mobility of the scapula is essential for free movement of the upper limb. The ...
Bilateral Costoclavicular Compression in a Patient With Thoracic
... 536 JOURNAL OF THE NATIONAL MEDICAL ASSOCIATION ...
... 536 JOURNAL OF THE NATIONAL MEDICAL ASSOCIATION ...
Parasympathetic: "Sex, Sandwiche
... Vagal nerve: path into thorax Vagus nerve, unlike phrenic, continues through diaphragm with esophagus--it is "Not Left Behind": · The left vagus is anterior, right is posterior [behind]. ...
... Vagal nerve: path into thorax Vagus nerve, unlike phrenic, continues through diaphragm with esophagus--it is "Not Left Behind": · The left vagus is anterior, right is posterior [behind]. ...
Figure S1: Distal Humerus
... convex proximal edge that does not extend to either the plantar or the dorsal edge of the lateral face of the bone. The proximo-plantar projection of the medial articular ridge of the trochlea is smaller and flatter and may be more pointed. When viewed from the plantar aspect, the medial articular r ...
... convex proximal edge that does not extend to either the plantar or the dorsal edge of the lateral face of the bone. The proximo-plantar projection of the medial articular ridge of the trochlea is smaller and flatter and may be more pointed. When viewed from the plantar aspect, the medial articular r ...
Diapositive 1
... Muscle divided at midway along its length Muscle mobilized from above toward distal pedicle ...
... Muscle divided at midway along its length Muscle mobilized from above toward distal pedicle ...
The Skull - OpenStax CNX
... Within the nasal cavity, the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone forms the upper portion of the nasal septum. The ethmoid bone also forms the lateral walls of the upper nasal cavity. Extending from each lateral wall are the superior nasal concha and middle nasal concha, which are thin, curved pr ...
... Within the nasal cavity, the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone forms the upper portion of the nasal septum. The ethmoid bone also forms the lateral walls of the upper nasal cavity. Extending from each lateral wall are the superior nasal concha and middle nasal concha, which are thin, curved pr ...
Bones of the Lower Limb
... When the foot comes into contact with the ground during walking, running, or jumping activities, the impact of the body weight puts a tremendous amount of pressure and force on the foot. During running, the force applied to each foot as it contacts the ground can be up to 2.5 times your body weight. ...
... When the foot comes into contact with the ground during walking, running, or jumping activities, the impact of the body weight puts a tremendous amount of pressure and force on the foot. During running, the force applied to each foot as it contacts the ground can be up to 2.5 times your body weight. ...
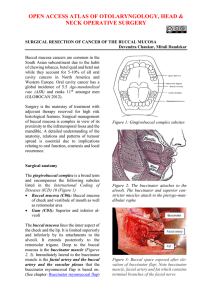
Surgical resection of cancer of the buccal mucosa - Vula
... the presence of trismus, the surgical team must be present during induction of anaesthesia. If a difficult intubation is anticipated, then one should infiltrate the skin and trachea with local anaesthesia and a vasoconstrictor prior to induction, and the tracheostomy team must be ready to proceed if ...
... the presence of trismus, the surgical team must be present during induction of anaesthesia. If a difficult intubation is anticipated, then one should infiltrate the skin and trachea with local anaesthesia and a vasoconstrictor prior to induction, and the tracheostomy team must be ready to proceed if ...
Calcaneal fracture
... indicated deformation of the calcaneus in comminuted fractures. For reduction Lorenz Böhler used a traction device with a Kirschner wire driven through the calcaneus and the Phelps-Gocht apparatus for lateral compression and reduction of the displaced fragments. He also accepted reduction of the cal ...
... indicated deformation of the calcaneus in comminuted fractures. For reduction Lorenz Böhler used a traction device with a Kirschner wire driven through the calcaneus and the Phelps-Gocht apparatus for lateral compression and reduction of the displaced fragments. He also accepted reduction of the cal ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... ossicles are stabilized by numerous suspensory ligaments (Figs. 7, 9), joint capsules, and two tendons: the tensor tympani tendon, which attaches to the upper part of the manubrium of the malleus, and the stapedial tendon, which attaches to the neck of the stapes. The incus has the least number of s ...
... ossicles are stabilized by numerous suspensory ligaments (Figs. 7, 9), joint capsules, and two tendons: the tensor tympani tendon, which attaches to the upper part of the manubrium of the malleus, and the stapedial tendon, which attaches to the neck of the stapes. The incus has the least number of s ...
Anatomy of the Cervical Spine - All About Back and Neck Pain
... occurs at occiput-C1 • Approximately 50% of rotation occurs at C1-C2 • Lesser amounts of flexionextension, rotation, and lateral bending occur segmentally between C2-C7 ...
... occurs at occiput-C1 • Approximately 50% of rotation occurs at C1-C2 • Lesser amounts of flexionextension, rotation, and lateral bending occur segmentally between C2-C7 ...
four heads of sternocleidomastoid: a case report
... Sternocleidomastoid is a key landmark because it divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles. Sternocleidomastoid descends obliquely across the side of the neck and forms a prominent surface landmark, especially when contracted. It is thick and narrow centrally, and broader and thinner at ...
... Sternocleidomastoid is a key landmark because it divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles. Sternocleidomastoid descends obliquely across the side of the neck and forms a prominent surface landmark, especially when contracted. It is thick and narrow centrally, and broader and thinner at ...
Robert J - Anthropology - Smithsonian Institution
... During the production of this present database, there needed to be verification of the osteometric measurements between observers. Metric values for each element that had comparable data were evaluated. All measurements differing greater than 7mm between observers and between the left and right side ...
... During the production of this present database, there needed to be verification of the osteometric measurements between observers. Metric values for each element that had comparable data were evaluated. All measurements differing greater than 7mm between observers and between the left and right side ...
Location
... Location: small l.n found at or near the caudal border of the infraspinatus m. near the proximal end of the long head of the triceps m. Afferent: from the latissimus dorsi m. Efferent: go to the proper axillary l.n. Lymphocenters of the thoracic cavity: 1- Dorsa thoracic lymphocenter: consists of: A ...
... Location: small l.n found at or near the caudal border of the infraspinatus m. near the proximal end of the long head of the triceps m. Afferent: from the latissimus dorsi m. Efferent: go to the proper axillary l.n. Lymphocenters of the thoracic cavity: 1- Dorsa thoracic lymphocenter: consists of: A ...
THORACIC CAGE AND THORACIC INLET NOTE
... articulated skeleton (and in life) by the medial (sternal) ends of the clavicles, which are much larger than the relatively small clavicular notches in the manubrium that receive them, forming the sternoclavicular (SC) joints. Inferolateral to the clavicular notch, the costal cartilage of the 1st ri ...
... articulated skeleton (and in life) by the medial (sternal) ends of the clavicles, which are much larger than the relatively small clavicular notches in the manubrium that receive them, forming the sternoclavicular (SC) joints. Inferolateral to the clavicular notch, the costal cartilage of the 1st ri ...
dıgestıve System - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... into two types: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic muscles are confined to the tongue and are not attached to bone and alter the shape of the tongue. The extrinsic muscles are attached to bones and the soft palate. Intrinsic muscles The intrinsic muscles of the tongue originate and insert within the ...
... into two types: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic muscles are confined to the tongue and are not attached to bone and alter the shape of the tongue. The extrinsic muscles are attached to bones and the soft palate. Intrinsic muscles The intrinsic muscles of the tongue originate and insert within the ...
18 The muscles of lower limb.
... The external group of the muscles of the hip region consists of the following muscles: +the gluteus maximus, medius, minimus; the tensor fasciae latae; the quadratus femoris; the obturator externus; the superior and inferior gemellus -the gluteus maximus, medius, minimus; the obturator externus and ...
... The external group of the muscles of the hip region consists of the following muscles: +the gluteus maximus, medius, minimus; the tensor fasciae latae; the quadratus femoris; the obturator externus; the superior and inferior gemellus -the gluteus maximus, medius, minimus; the obturator externus and ...
nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
... • They are two in number • They lie within the body of the sphenoid bone. • Each sinus opens into the sphenoethmoidal recess above the superior concha. • The mucous membrane is supplied by the posterior ethmoidal nerves. Dr. Vohra ...
... • They are two in number • They lie within the body of the sphenoid bone. • Each sinus opens into the sphenoethmoidal recess above the superior concha. • The mucous membrane is supplied by the posterior ethmoidal nerves. Dr. Vohra ...
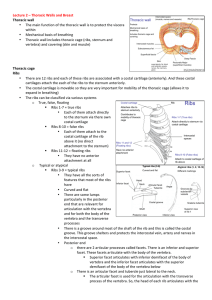
Thoracic Walls and Breast Thoracic wall • The main function of the
... • Posterior intercostal arteries are just segmental branches of the thoracic aorta • Anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic arteries. The internal thoracic arteries are branches of the subclavian artery and they descend posterior and lateral to the sternum all the ...
... • Posterior intercostal arteries are just segmental branches of the thoracic aorta • Anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic arteries. The internal thoracic arteries are branches of the subclavian artery and they descend posterior and lateral to the sternum all the ...
how I do it
... aspect or the inferior meatus. At this stage some surgeons use a straight artery clip, placed along the length of the inferior turbinate to crush the hypertrophied and vascular mucosa – but the authors feel this is unnecessary if the nose is adequately prepared. Turbinectomy scissors are then used t ...
... aspect or the inferior meatus. At this stage some surgeons use a straight artery clip, placed along the length of the inferior turbinate to crush the hypertrophied and vascular mucosa – but the authors feel this is unnecessary if the nose is adequately prepared. Turbinectomy scissors are then used t ...
Supernumerary Peronei in the Leg Musculature
... tion from the PL.(8) The current study reports supernumerary peroneal muscles from both the PL and PB gaining attachment to the lateral calcaneal surface. A bifid PB muscle leading to chronic subluxation of the peroneal tendons has been described. (9) Another MRI study confirmed that tears in the PB ...
... tion from the PL.(8) The current study reports supernumerary peroneal muscles from both the PL and PB gaining attachment to the lateral calcaneal surface. A bifid PB muscle leading to chronic subluxation of the peroneal tendons has been described. (9) Another MRI study confirmed that tears in the PB ...
Physio pages use this.indd - Physiotherapy New Zealand
... seen in situ (Figure 2). Immediately underneath the clavicular head of SCM the fat pad described by Mattson (2004) amounted to a signicant layer of tissue that took some time to remove cleanly. The superior aspect of scalenus anterior tapered, diverged and became tendinous before inserting into the ...
... seen in situ (Figure 2). Immediately underneath the clavicular head of SCM the fat pad described by Mattson (2004) amounted to a signicant layer of tissue that took some time to remove cleanly. The superior aspect of scalenus anterior tapered, diverged and became tendinous before inserting into the ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.