Lower limb
... Lower arm - blends with the deep fascia Contents: tendons of the anterior leg muscles pass deep to it as they enter the foot Function: holds the tendons of the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg in position at the ankle; prevents bowstringing during muscular contraction *Flexor retinac ...
... Lower arm - blends with the deep fascia Contents: tendons of the anterior leg muscles pass deep to it as they enter the foot Function: holds the tendons of the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg in position at the ankle; prevents bowstringing during muscular contraction *Flexor retinac ...
The Vertebral Column
... the fifth lumbar vertebra 2-The narrow inferior border articulates with the coccyx. 3-Laterally, the sacrum articulates with the two iliac bones to form the sacroiliac joints The anterior and upper margin of the first sacral vertebra bulges forward and is known as the sacral promontory The sacral p ...
... the fifth lumbar vertebra 2-The narrow inferior border articulates with the coccyx. 3-Laterally, the sacrum articulates with the two iliac bones to form the sacroiliac joints The anterior and upper margin of the first sacral vertebra bulges forward and is known as the sacral promontory The sacral p ...
Pelvis - Lectures - gblnetto
... The anterior parts of space in the male contains the urinaÂry bladder, the prostate, the seminal vesicle and ampulla of vas deferens. The anterior part of space in the female contains the urinary bladder and vagina. The posterior part of space contains the rectum in the male and female. The perito ...
... The anterior parts of space in the male contains the urinaÂry bladder, the prostate, the seminal vesicle and ampulla of vas deferens. The anterior part of space in the female contains the urinary bladder and vagina. The posterior part of space contains the rectum in the male and female. The perito ...
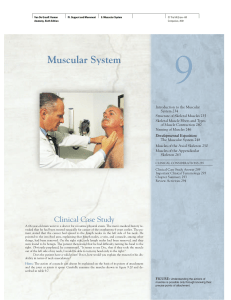
Muscular System - Atypically Relevant
... thin. Deep fascia is an inward extension of the superficial fascia. It lacks adipose tissue and blends with the epimysium of muscle. Deep fascia surrounds adjacent muscles, compartmentalizing and binding them into functional groups. Subserous fascia extends between the deep fascia and serous membran ...
... thin. Deep fascia is an inward extension of the superficial fascia. It lacks adipose tissue and blends with the epimysium of muscle. Deep fascia surrounds adjacent muscles, compartmentalizing and binding them into functional groups. Subserous fascia extends between the deep fascia and serous membran ...
View PDF
... the time. The same vascular arrangement described in the current case (with the suprascapular vein crossing over the transverse scapular ligament and the artery running under) occurred in 10.9% of their cadaveric specimens.22 Although venous compression at the suprascapular notch has not been report ...
... the time. The same vascular arrangement described in the current case (with the suprascapular vein crossing over the transverse scapular ligament and the artery running under) occurred in 10.9% of their cadaveric specimens.22 Although venous compression at the suprascapular notch has not been report ...
View/Open - SUST Repository
... symphysis, where the bone is formed by the fusion of right and left processes during mandibular development. Like other symphysis in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood. )wikipedia.org/wiki/man ...
... symphysis, where the bone is formed by the fusion of right and left processes during mandibular development. Like other symphysis in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood. )wikipedia.org/wiki/man ...
Outline
... 7.1a Views of the Skull and Landmark Features The skull is composed of multiple bones that exhibit complex shapes, and each bone articulates with at least one other. To best understand the complex nature of the skull, we first examine the skull as a whole and learn which bones are best seen from a ...
... 7.1a Views of the Skull and Landmark Features The skull is composed of multiple bones that exhibit complex shapes, and each bone articulates with at least one other. To best understand the complex nature of the skull, we first examine the skull as a whole and learn which bones are best seen from a ...
SUMMARY TERMS-HEAD AND NECK
... Location: medial and deep to the thyrocervical trunk. It passes superiorly in the triangular-shaped region between the longus colli muscle medially and the scalenus anterior muscle laterally. The transverse process of the C6 vertebra is at the apex of this triangle. The vertebral artery enters the f ...
... Location: medial and deep to the thyrocervical trunk. It passes superiorly in the triangular-shaped region between the longus colli muscle medially and the scalenus anterior muscle laterally. The transverse process of the C6 vertebra is at the apex of this triangle. The vertebral artery enters the f ...
PTA Hip presentation
... O: Inferior ramus of pubis and ischium to ischial tuberosity I: Linea aspera of femur, medial supracondylar line & adductor ...
... O: Inferior ramus of pubis and ischium to ischial tuberosity I: Linea aspera of femur, medial supracondylar line & adductor ...
Cook, Orthopedic Manual Therapy: An Evidence
... upward into the anterior lower third of the vertebral lamina at the level above and originate on the posterior upper third of the lamina below. The elastic, yellow-colored ligament forms the posterior wall of the vertebral canal and assists in preventing the synovial capsule and menisci from entrapm ...
... upward into the anterior lower third of the vertebral lamina at the level above and originate on the posterior upper third of the lamina below. The elastic, yellow-colored ligament forms the posterior wall of the vertebral canal and assists in preventing the synovial capsule and menisci from entrapm ...
Bilateral anomalous suprascapular arteries
... Institute of Medical Sciences, Indore, India. These arteries originated from the supro-dorsal aspect of the axillary arteries opposite to the origin of the subscapular arteries on both the sides. These vessels ascended upwards between the lateral cord of the brachial plexus anteriorly and the poster ...
... Institute of Medical Sciences, Indore, India. These arteries originated from the supro-dorsal aspect of the axillary arteries opposite to the origin of the subscapular arteries on both the sides. These vessels ascended upwards between the lateral cord of the brachial plexus anteriorly and the poster ...
7. Axial Skeleton
... (figure 7.2). Cranial bones form the rounded cranium (krā n ́ ēum; kranion = skull), which completely surrounds and encloses the brain.1 Eight bones make up the cranium: the unpaired ethmoid, frontal, occipital, and sphenoid bones, and the paired parietal and temporal bones. These bones also prov ...
... (figure 7.2). Cranial bones form the rounded cranium (krā n ́ ēum; kranion = skull), which completely surrounds and encloses the brain.1 Eight bones make up the cranium: the unpaired ethmoid, frontal, occipital, and sphenoid bones, and the paired parietal and temporal bones. These bones also prov ...
Anatomy - Beck-Shop
... White males had the thickest laminae, while white females had the thinnest. Laminar thickness was 0.46 mm (8.3 %) less in females than in males. There was no statistical effect of patient race, height, or weight on any of the measurements [14]. Several other studies examining the LT came to similar ...
... White males had the thickest laminae, while white females had the thinnest. Laminar thickness was 0.46 mm (8.3 %) less in females than in males. There was no statistical effect of patient race, height, or weight on any of the measurements [14]. Several other studies examining the LT came to similar ...
Functional Anatomy
... The articular part of each tubercle connects with the costal facet of each thoracic transverse process. The rounded angle forms the most lateral portion of the ribs. ...
... The articular part of each tubercle connects with the costal facet of each thoracic transverse process. The rounded angle forms the most lateral portion of the ribs. ...
ch_07_lecture_presentation
... • Thick, flattened area • Articulates with pelvic girdle (forming sacroiliac joint) ...
... • Thick, flattened area • Articulates with pelvic girdle (forming sacroiliac joint) ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... White males had the thickest laminae, while white females had the thinnest. Laminar thickness was 0.46 mm (8.3 %) less in females than in males. There was no statistical effect of patient race, height, or weight on any of the measurements [14]. Several other studies examining the LT came to similar ...
... White males had the thickest laminae, while white females had the thinnest. Laminar thickness was 0.46 mm (8.3 %) less in females than in males. There was no statistical effect of patient race, height, or weight on any of the measurements [14]. Several other studies examining the LT came to similar ...
Anatomy of the Head, Neck, Face, and Jaws.
... fingerlike projection, the zygomatic process, which joins with the zygoma anteriorly to form the zygomatic arch. Immediately posterior to the root of the zygomatic process is a large opening into the depth of the bone. This opening is the entrance to the middle ear and is known as the external audit ...
... fingerlike projection, the zygomatic process, which joins with the zygoma anteriorly to form the zygomatic arch. Immediately posterior to the root of the zygomatic process is a large opening into the depth of the bone. This opening is the entrance to the middle ear and is known as the external audit ...
Concise Guide to HUMAN ANATOMY 2
... Face and eyes are directed forward . Hands are by both sides with palms directed forwards . Feet are pointed forwards so that the hells and greater toes together . 2. The terms Anterior-------- front or belly side Posterior-------- back side Superior-------- upper part Inferior-------- lower part La ...
... Face and eyes are directed forward . Hands are by both sides with palms directed forwards . Feet are pointed forwards so that the hells and greater toes together . 2. The terms Anterior-------- front or belly side Posterior-------- back side Superior-------- upper part Inferior-------- lower part La ...
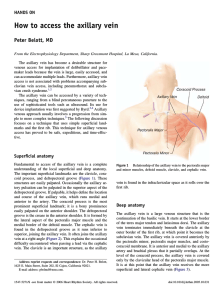
How to access the axillary vein Peter Belott, MD HANDS ON
... defined by the pectoralis major– clavicular junction. The surface of the pectoralis major muscle is clearly visualized superiorly under the edge of the incision. The incision is held open with a Weitlaner retractor, which is continuously repositioned for optimal exposure. The purpose of this dissect ...
... defined by the pectoralis major– clavicular junction. The surface of the pectoralis major muscle is clearly visualized superiorly under the edge of the incision. The incision is held open with a Weitlaner retractor, which is continuously repositioned for optimal exposure. The purpose of this dissect ...
Practice Mink Practical
... look at the deeper abdominal muscle, which abdominal muscle would you find moving laterally? • External abdominal oblique • Transverse abdominus ...
... look at the deeper abdominal muscle, which abdominal muscle would you find moving laterally? • External abdominal oblique • Transverse abdominus ...
Dr. Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.wordpress.com Yeditepe
... Greek mythology bore the weight of the world on his shoulders. The transverse processes of the atlas arise from the lateral masses, causing them to be more laterally placed than those of the inferior vertebrae. This feature makes the atlas the widest of the cervical vertebrae, thus providing increas ...
... Greek mythology bore the weight of the world on his shoulders. The transverse processes of the atlas arise from the lateral masses, causing them to be more laterally placed than those of the inferior vertebrae. This feature makes the atlas the widest of the cervical vertebrae, thus providing increas ...
Chapter 35: Nose
... nasolacrimal duct's drainage. The opening of the nasolacrimal duct is located in the anterosuperior portion of the meatus at the point that the inferior concha contacts the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. Because the inferior meatus is a common point of entry when placing a troacar during irrigati ...
... nasolacrimal duct's drainage. The opening of the nasolacrimal duct is located in the anterosuperior portion of the meatus at the point that the inferior concha contacts the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. Because the inferior meatus is a common point of entry when placing a troacar during irrigati ...
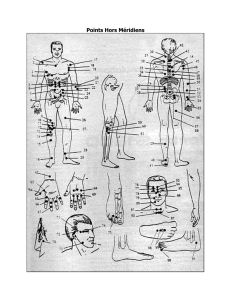
Points Hors Méridiens
... Yuchien : One Tsun lateral to LI 15 (shoulder pain, frozen shoulder) Chihhsueh : One Tsun lateral to CV 21 (asthma, cough, intercostal neuralgia) Tanchuan : 1.8 Tsun lateral to ST 16 (chronic bronchitis, asthma, emphysema) Tsuoyi : One Tsun L & R of ST 18 (mastitis, pleurisy) Shihtsang : 3 Tsun late ...
... Yuchien : One Tsun lateral to LI 15 (shoulder pain, frozen shoulder) Chihhsueh : One Tsun lateral to CV 21 (asthma, cough, intercostal neuralgia) Tanchuan : 1.8 Tsun lateral to ST 16 (chronic bronchitis, asthma, emphysema) Tsuoyi : One Tsun L & R of ST 18 (mastitis, pleurisy) Shihtsang : 3 Tsun late ...
Musculoskeletal System
... – Closed means the fracture site is not surgically exposed – Three methods • Without manipulation • With manipulation • With or without traction ...
... – Closed means the fracture site is not surgically exposed – Three methods • Without manipulation • With manipulation • With or without traction ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.