sample - Create Training
... vertebra superior to it Joins head with body of rib • Articulates with transverse process of vertebra of same number • Located at junction of neck and body • Bears pronounced angle • Inferior internal border has costal groove for intercostal neurovascular elements • The heads of the first 2 ribs onl ...
... vertebra superior to it Joins head with body of rib • Articulates with transverse process of vertebra of same number • Located at junction of neck and body • Bears pronounced angle • Inferior internal border has costal groove for intercostal neurovascular elements • The heads of the first 2 ribs onl ...
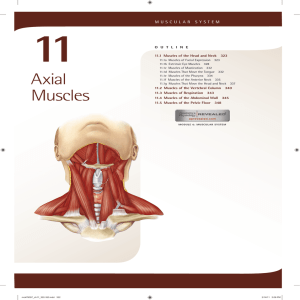
11. Axial Muscles
... the orbit and insert onto the white outer surface of the eye, called the sclera. There are six extrinsic eye muscles: the rectus muscles (medial, lateral, inferior, and superior) and the oblique muscles (inferior and superior) (figure 11.4). The rectus eye muscles have their origin from a common ten ...
... the orbit and insert onto the white outer surface of the eye, called the sclera. There are six extrinsic eye muscles: the rectus muscles (medial, lateral, inferior, and superior) and the oblique muscles (inferior and superior) (figure 11.4). The rectus eye muscles have their origin from a common ten ...
File
... vastus medialis. The antagonist muscles during extension include the hamstring muscles and the popliteus. During both flexion and extension, the muscles involved are occurring in the sagittal plane. ...
... vastus medialis. The antagonist muscles during extension include the hamstring muscles and the popliteus. During both flexion and extension, the muscles involved are occurring in the sagittal plane. ...
The development of the orbital region of Caretta caretta (Chelonia
... Chelydra: Rieppel, 1976). Specifically, the formation of the subiculum infundibuli and the cartilago hypochiasmatica are shown in these forms. The anteromedial process of the former stage, the subiculum infundibuli, has united with its counterpart on the opposite side, and united anteriorly with the ...
... Chelydra: Rieppel, 1976). Specifically, the formation of the subiculum infundibuli and the cartilago hypochiasmatica are shown in these forms. The anteromedial process of the former stage, the subiculum infundibuli, has united with its counterpart on the opposite side, and united anteriorly with the ...
- Free Documents
... it forms the medial border of the anatomical snuffbox. works with the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis mm. and opponens digiti minimi are in the hypothenar . hook flexes wrist. in which the radial arterial pulse can be felt base of the second and third metacarpals flexes the wrist. adducts ...
... it forms the medial border of the anatomical snuffbox. works with the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis mm. and opponens digiti minimi are in the hypothenar . hook flexes wrist. in which the radial arterial pulse can be felt base of the second and third metacarpals flexes the wrist. adducts ...
Variable space distribution of the structures forming the muscle and
... between the classical descriptions [11, 14] and the reality of dissections. This enabled us to make some assessments regarding the structure of the lumbosacral muscle mass and the associated fascial system.During the stratigraphic dissection of the thoracolumbosacral region, after removing the fasci ...
... between the classical descriptions [11, 14] and the reality of dissections. This enabled us to make some assessments regarding the structure of the lumbosacral muscle mass and the associated fascial system.During the stratigraphic dissection of the thoracolumbosacral region, after removing the fasci ...
Anatomical Relationship of the Axillary Nerve to the Pectoralis Major
... Axillary nerve injury is a risk of the deltopectoral approach to the proximal humerus. The anterior motor branch is potentially vulnerable during subdeltoid dissection. Insertion of the pectoralis major tendon is an easily identifiable landmark on the humerus. This anatomical study explored whether ...
... Axillary nerve injury is a risk of the deltopectoral approach to the proximal humerus. The anterior motor branch is potentially vulnerable during subdeltoid dissection. Insertion of the pectoralis major tendon is an easily identifiable landmark on the humerus. This anatomical study explored whether ...
15. - Geometrical Anatomy
... Superior and Inferior Surfaces of the Vertebral Body The superior face of the vertebral body is generally flat and it may be tilted up as much as 20°, i.e. the posterior margin more rostral than the anterior margin. The lateral margins in a mature spine have substantial flanges, called uncinate proc ...
... Superior and Inferior Surfaces of the Vertebral Body The superior face of the vertebral body is generally flat and it may be tilted up as much as 20°, i.e. the posterior margin more rostral than the anterior margin. The lateral margins in a mature spine have substantial flanges, called uncinate proc ...
Lungs and Pleura – Lecture Two
... Diaphragmatic Pleura – this is parietal pleura as it passes superior to the diaphragm muscle. Once again there is a thin layer of connective tissue called: phrenicopleural fascia that separates the pleura from the muscle fibres. Cervical Pleura – this is parietal pleura that is continuous with the ...
... Diaphragmatic Pleura – this is parietal pleura as it passes superior to the diaphragm muscle. Once again there is a thin layer of connective tissue called: phrenicopleural fascia that separates the pleura from the muscle fibres. Cervical Pleura – this is parietal pleura that is continuous with the ...
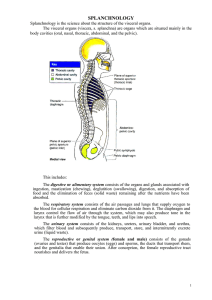
2. Splanchnology
... descends in the posterior mediastinum along the right side of the descending aorta, then runs in front and a little to the left of the aorta, and enters the abdomen through the diaphragm at the level of the tenth thoracic vertebra. Just before it perforates the diaphragm it presents a distinct dilat ...
... descends in the posterior mediastinum along the right side of the descending aorta, then runs in front and a little to the left of the aorta, and enters the abdomen through the diaphragm at the level of the tenth thoracic vertebra. Just before it perforates the diaphragm it presents a distinct dilat ...
Bones and Muscles - An Illustrated Anatomy
... mourning.(The lacrimal bone forms half of the receptacle, which holds the lacrimal sac, a structure that receives the tears and directs them into the nasal cavity. That explains why we blow our noses in cold weather, or when we cry, we are blowing out the tears that have drained into the cavity. The ...
... mourning.(The lacrimal bone forms half of the receptacle, which holds the lacrimal sac, a structure that receives the tears and directs them into the nasal cavity. That explains why we blow our noses in cold weather, or when we cry, we are blowing out the tears that have drained into the cavity. The ...
Movements of the Upper Cervical Assembly and Strain in the
... Superior and Inferior Surfaces of the Vertebral Body The superior face of the vertebral body is generally flat and it may be tilted up as much as 20°, i.e. the posterior margin more rostral than the anterior margin. ...
... Superior and Inferior Surfaces of the Vertebral Body The superior face of the vertebral body is generally flat and it may be tilted up as much as 20°, i.e. the posterior margin more rostral than the anterior margin. ...
The ossification of the middle and internal ear of the golden hamster
... or only into ligaments at the narrowest point thereby leaving part of the malleus (the prearticular portion) attached to the ectotynipanic. ...
... or only into ligaments at the narrowest point thereby leaving part of the malleus (the prearticular portion) attached to the ectotynipanic. ...
Anatomic considerations and the relationship between the piriformis
... stretch test. Only Parameter 11 was significant statistically (P \ 0.05; Table 4). ...
... stretch test. Only Parameter 11 was significant statistically (P \ 0.05; Table 4). ...
15-Gluteal Region and Back of Thigh2017-01
... Greater sciatic notch of hip bone is transformed into foramen by: sacrotuberous (between the sacrum to ischial tuberosity) & sacrospinous (between the sacrum to ischial spine ) Structures passing through Greater sciatic foramen : ...
... Greater sciatic notch of hip bone is transformed into foramen by: sacrotuberous (between the sacrum to ischial tuberosity) & sacrospinous (between the sacrum to ischial spine ) Structures passing through Greater sciatic foramen : ...
Tibialis anterior (7
... Tibialis anterior is the primary dorsi flexor of the ankle and an adequate knowledge of its normal anatomy and variations in attachments and course is required for clinicians. Ebraheim et al. (2003) found the muscle to be a relatively easy flap to use for covering anterior tibial open wounds. It is ...
... Tibialis anterior is the primary dorsi flexor of the ankle and an adequate knowledge of its normal anatomy and variations in attachments and course is required for clinicians. Ebraheim et al. (2003) found the muscle to be a relatively easy flap to use for covering anterior tibial open wounds. It is ...
The Thorax (Chest)
... capable to expand & reduce its size which will change the intrathoracic pressure & permits air to flow in & out the lungs through the respiratory airways * The bones of the thoracic wall are: - The sternum - The thoracic vertebrae & their discs - The ribs & their costal cartilages The Sternum: - Thi ...
... capable to expand & reduce its size which will change the intrathoracic pressure & permits air to flow in & out the lungs through the respiratory airways * The bones of the thoracic wall are: - The sternum - The thoracic vertebrae & their discs - The ribs & their costal cartilages The Sternum: - Thi ...
Axillary Space Exploration and Resections
... greatly improved our ability to perform limb-sparing resections in this location. The key to adequate and safe surgical resection of axillary tumors is the complete visualization and mobilization of the infraclavicular portion of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery and vein and the cords tha ...
... greatly improved our ability to perform limb-sparing resections in this location. The key to adequate and safe surgical resection of axillary tumors is the complete visualization and mobilization of the infraclavicular portion of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery and vein and the cords tha ...
The Vertebral column, including the thoracic cage
... The Occiput, Atlas and Axis............................................................................................... 4 The Occiput, Atlas and Axis ........................................................................................... 4 The atlas and axis: C1 and C2 ....................... ...
... The Occiput, Atlas and Axis............................................................................................... 4 The Occiput, Atlas and Axis ........................................................................................... 4 The atlas and axis: C1 and C2 ....................... ...
1 Anatomy, Kinesiology and Pathology of the Thoracic Spine
... Most common sites are T7, T8, T11 and L1 Estimated 2/3 of fractures are undiagnosed ...
... Most common sites are T7, T8, T11 and L1 Estimated 2/3 of fractures are undiagnosed ...
bio-mechanics of hip joint
... • The inferior aspect of the lunate surface (the base of the horseshoe) is interrupted by a deep notch called the acetabular notch. The acetabular notch is spanned by a fibrous band, the transverse acetabular ligament, that connects the two ends of the horseshoe. • The transverse acetabular ligame ...
... • The inferior aspect of the lunate surface (the base of the horseshoe) is interrupted by a deep notch called the acetabular notch. The acetabular notch is spanned by a fibrous band, the transverse acetabular ligament, that connects the two ends of the horseshoe. • The transverse acetabular ligame ...
Anatomy and Functional Architecture of the Anconeus Muscle
... SUMMARY: The anconeus is a small muscle situated at the elbow. Although the anconeus is active during elbow extension its importance for the movement is probably small. It could work as an elbow stabilizer. The object of this study was to investigate some anatomic and architectural characteristics o ...
... SUMMARY: The anconeus is a small muscle situated at the elbow. Although the anconeus is active during elbow extension its importance for the movement is probably small. It could work as an elbow stabilizer. The object of this study was to investigate some anatomic and architectural characteristics o ...
The Primitive Cynodont Procynosuchus: Functional Anatomy of the
... of replacement teeth (figure 4). The tooth which is apparently completely missing on the left side is probably the first postcanine which has been shed but not replaced, as discussed below. The form of the lower incisors is shown by the perfectly preserved second right tooth. The base of the crown i ...
... of replacement teeth (figure 4). The tooth which is apparently completely missing on the left side is probably the first postcanine which has been shed but not replaced, as discussed below. The form of the lower incisors is shown by the perfectly preserved second right tooth. The base of the crown i ...
Module 1. Which of the following nerves lies on spermatic cord
... 62. The facial artery gives rise to branches that supply each of the regions listed below EXCEPT for the: A. medial angle of the orbit B. lateral nose C. region of the eyebrow D. upper lip E. lower lip 63. The pterygomandibular raphe serves as a point of attachment for two important muscles. They ar ...
... 62. The facial artery gives rise to branches that supply each of the regions listed below EXCEPT for the: A. medial angle of the orbit B. lateral nose C. region of the eyebrow D. upper lip E. lower lip 63. The pterygomandibular raphe serves as a point of attachment for two important muscles. They ar ...
Chapter 2 Implants and oral anatomy Read Now
... expands into an egg shape, is referred to as the condylar process of the mandible. This swelling at the tip is referred to as the head of the mandible, which fits into the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone, constituting the temporomandibular joint. The constricted section directly beneath the he ...
... expands into an egg shape, is referred to as the condylar process of the mandible. This swelling at the tip is referred to as the head of the mandible, which fits into the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone, constituting the temporomandibular joint. The constricted section directly beneath the he ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.