Human Body Systems Graphic Organizer
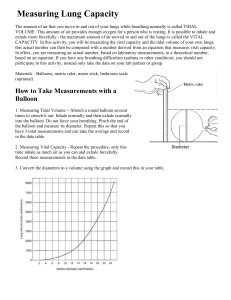
... VOLUME. This amount of air provides enough oxygen for a person who is resting. It is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully - the maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs is called the VITAL CAPACITY. In this activity, you will be measuring the vital capacity and the tidal volume o ...
... VOLUME. This amount of air provides enough oxygen for a person who is resting. It is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully - the maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs is called the VITAL CAPACITY. In this activity, you will be measuring the vital capacity and the tidal volume o ...
1. The gastroesophageal junction occurs at - NYCC SP-01
... a) Pseudostraatified squamous epithelium b) Stratified squamous epithelium c) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium d) Pseudostratified transitional epithelium 63. Parietal pleura that covers the apex of the lung is known as: a) Tunica albuginea b)Cauna c)Lingula d) Cupula 64. All of the following mu ...
... a) Pseudostraatified squamous epithelium b) Stratified squamous epithelium c) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium d) Pseudostratified transitional epithelium 63. Parietal pleura that covers the apex of the lung is known as: a) Tunica albuginea b)Cauna c)Lingula d) Cupula 64. All of the following mu ...
BIOL241Spr11 MW Syllabus
... The exams will be composed of multiple-choice questions, matching, short answer, fillin-the-blank and short essay questions and may also include diagrams for you to label. A new, unwrinkled Scantron form and a #2 pencil will be needed for each exam. These are available at the campus bookstore or the ...
... The exams will be composed of multiple-choice questions, matching, short answer, fillin-the-blank and short essay questions and may also include diagrams for you to label. A new, unwrinkled Scantron form and a #2 pencil will be needed for each exam. These are available at the campus bookstore or the ...
What Is an Arthropod?
... Maxillipeds: sense organs which also help pass food to the mouth Chelipeds: large, pincer appendages for food getting and protection Antennae: segmented sense organs on the head (touch/taste) Antennule: segmented sense organ (touch/taste/equilibrium) ...
... Maxillipeds: sense organs which also help pass food to the mouth Chelipeds: large, pincer appendages for food getting and protection Antennae: segmented sense organs on the head (touch/taste) Antennule: segmented sense organ (touch/taste/equilibrium) ...
EXAMPLE Histology Compendium
... In addition to recruiting and activating other cells of the immune system, Neutrophils are normally found in the blood stream. Neutrophils are recruited to neutrophils play a key role in the front-line defense against invading the site of injury within minutes following trauma and are the hallmark o ...
... In addition to recruiting and activating other cells of the immune system, Neutrophils are normally found in the blood stream. Neutrophils are recruited to neutrophils play a key role in the front-line defense against invading the site of injury within minutes following trauma and are the hallmark o ...
Midwifery 1 150363
... -Mammory glands are composed of glandular tissue and a variable amount of fat. They are also have a complex secretory product called breast milk. Breast milk travels through a passageway called the Lactiferous duct, which travels from the alveoli to the nipple. The nipple is a centrally located proj ...
... -Mammory glands are composed of glandular tissue and a variable amount of fat. They are also have a complex secretory product called breast milk. Breast milk travels through a passageway called the Lactiferous duct, which travels from the alveoli to the nipple. The nipple is a centrally located proj ...
Chapter One - Human AP
... B.conducting experiments; making microscopic examinations C.studying chemical molecules; observing forms of the body parts D.None of these is correct. 27. Which of the following characteristics of life and their descriptions are correct? A.assimilation-obtaining and using oxygen for releasing energy ...
... B.conducting experiments; making microscopic examinations C.studying chemical molecules; observing forms of the body parts D.None of these is correct. 27. Which of the following characteristics of life and their descriptions are correct? A.assimilation-obtaining and using oxygen for releasing energy ...
42. Lungs, pleura
... The bronchioles then divide and give rise to terminal bronchioles which show delicate outpouchings from their walls Gaseous exchange between blood and air takes place in the walls of these outpouchings, which explains the name respiratory bronchiole ...
... The bronchioles then divide and give rise to terminal bronchioles which show delicate outpouchings from their walls Gaseous exchange between blood and air takes place in the walls of these outpouchings, which explains the name respiratory bronchiole ...
Respiratory System
... of the air distribution tubes in the respiratory tree Mucus moves upward to the pharynx on millions of hairlike cilia that cover the epithelial cells in the respiratory mucosa ...
... of the air distribution tubes in the respiratory tree Mucus moves upward to the pharynx on millions of hairlike cilia that cover the epithelial cells in the respiratory mucosa ...
unit 1: introduction to biology
... as a consequence of segmentation, the coelom is partitioned by walls in many species some of the anterior segments are fused and build other more complex body features like a thorax or a head region ...
... as a consequence of segmentation, the coelom is partitioned by walls in many species some of the anterior segments are fused and build other more complex body features like a thorax or a head region ...
Anatomic investigation of the connections of the - sabine
... ¾ Some authors described the existence of a firm connection between the caecum, the sigmoid colon, the common iliac vessels, the inguinal ligament and the iliopsoas muscle. The preparations confirmed a connective tissue-like substance. ¾ Most of the literature sources examined illustrated a connecti ...
... ¾ Some authors described the existence of a firm connection between the caecum, the sigmoid colon, the common iliac vessels, the inguinal ligament and the iliopsoas muscle. The preparations confirmed a connective tissue-like substance. ¾ Most of the literature sources examined illustrated a connecti ...
Review on Anatomy of Cerebral Arterial System
... independent small systems. The short vessels are confined to the cortex, where they communicate with the long vessels to form compact net-work in the middle zone of the gray substance, the outer and inner zones being sparingly supplied with blood (15). Vessels of the cortical arterial system are not ...
... independent small systems. The short vessels are confined to the cortex, where they communicate with the long vessels to form compact net-work in the middle zone of the gray substance, the outer and inner zones being sparingly supplied with blood (15). Vessels of the cortical arterial system are not ...
1 - Unit 4 Lower Limb Objectives
... 5. Describe the origins of the muscular innervation of the lower limb. 6. Describe the vascular supply of the lower limb. ...
... 5. Describe the origins of the muscular innervation of the lower limb. 6. Describe the vascular supply of the lower limb. ...
4-4 Connective Tissue
... • Understand the fundamental characteristics, classifications, structure/functions and locations of the 4 basic types of tissue and membranes: ...
... • Understand the fundamental characteristics, classifications, structure/functions and locations of the 4 basic types of tissue and membranes: ...
Clinico-anatomical considerations of unilateral bipartite abductor
... the fascia of this muscle along its entire length. The sur- ...
... the fascia of this muscle along its entire length. The sur- ...
PARTICIPATION OF SUPERFICIAL MUSCULO
... regions fascial planes are separated by an areolar plan, while in other regions the two ...
... regions fascial planes are separated by an areolar plan, while in other regions the two ...
The Human Body: The Ultimate Machine
... © Copyright 1998 AIMS Multimedia All Rights Reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted without written permission of AIMS Multimedia with these exceptions: Persons or schools purchasing this AIMS Teaching Module may reproduce consumable ATM pages, identified in Section 4, for s ...
... © Copyright 1998 AIMS Multimedia All Rights Reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted without written permission of AIMS Multimedia with these exceptions: Persons or schools purchasing this AIMS Teaching Module may reproduce consumable ATM pages, identified in Section 4, for s ...
How many embryonic tissues do sponges have
... There are many different types of sponges all over the world. cell layers, but initially they all arise from the two layers that were present in the early embryo ( Dawkins 2004).. Sponges do not have any internal organs or a nervous system.Phylum Porifera: Sponges, Simplest of Animals. Taxonomic lev ...
... There are many different types of sponges all over the world. cell layers, but initially they all arise from the two layers that were present in the early embryo ( Dawkins 2004).. Sponges do not have any internal organs or a nervous system.Phylum Porifera: Sponges, Simplest of Animals. Taxonomic lev ...
Organ Systems and Body Cavities
... parietal layer. The visceral (viscera = internal organs) layer covers the organ, whereas the parietal (paries = wall) layer attaches to and covers the ventral body wall. These two layers comprise one continuous sheet that folds to form a sac. Between the two layers is a small amount of serous fluid ...
... parietal layer. The visceral (viscera = internal organs) layer covers the organ, whereas the parietal (paries = wall) layer attaches to and covers the ventral body wall. These two layers comprise one continuous sheet that folds to form a sac. Between the two layers is a small amount of serous fluid ...
Anatomic variation of alveolar antral artery
... report here two cases in which dissection revealed an extraosseous placement of this artery, between the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus and the Schneiderian membrane. The frequency of occurrence of the intraosseous anastomosis should be so modified from 100% to < 100%. This arterial course over ...
... report here two cases in which dissection revealed an extraosseous placement of this artery, between the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus and the Schneiderian membrane. The frequency of occurrence of the intraosseous anastomosis should be so modified from 100% to < 100%. This arterial course over ...
The brain and spinal cord comprise the central nervous system
... Circulatory System - Blood, Blood Vessels and the Heart Know and Understand how to Trace Blood through the cardiovascular system from one part to another including where it’s oxygen rich and where it’s oxygen poor and all of the vessels, valves and chambers it passes through along the way. ...
... Circulatory System - Blood, Blood Vessels and the Heart Know and Understand how to Trace Blood through the cardiovascular system from one part to another including where it’s oxygen rich and where it’s oxygen poor and all of the vessels, valves and chambers it passes through along the way. ...
Chapter 10
... • Center to ______________ • CR to _________ • IR _________shoulder center to cassette • Suspend respiration on _____________ ...
... • Center to ______________ • CR to _________ • IR _________shoulder center to cassette • Suspend respiration on _____________ ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.