Circulatory System Part 3
... Fenestrated capillaries – (fenestra = windows) abundant in small intestine, kidneys, endocrine glands – allows slightly larger things to pass through Endothelial cells (lining) have oval pores called fenestra ...
... Fenestrated capillaries – (fenestra = windows) abundant in small intestine, kidneys, endocrine glands – allows slightly larger things to pass through Endothelial cells (lining) have oval pores called fenestra ...
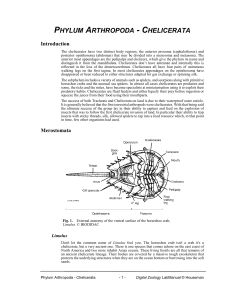
phylum arthropoda - chelicerata
... some, the ticks and the mites, have become specialists at miniaturisation using it to exploit their predatory habits. Chelicerates are fluid feeders and either liquefy their prey before ingestion or squeeze the juices from their food using their mouthparts. The success of both Tracheata and Chelicer ...
... some, the ticks and the mites, have become specialists at miniaturisation using it to exploit their predatory habits. Chelicerates are fluid feeders and either liquefy their prey before ingestion or squeeze the juices from their food using their mouthparts. The success of both Tracheata and Chelicer ...
Chapter 31
... are organized in layers, called germ layers. In diploblasts these germ layers are called ectoderm and endoderm; the third layer in triploblasts is found between these two and is called mesoderm. The Greek roots ecto, meso, and endo refer to outer, middle, and inner, respectively; the root derm means ...
... are organized in layers, called germ layers. In diploblasts these germ layers are called ectoderm and endoderm; the third layer in triploblasts is found between these two and is called mesoderm. The Greek roots ecto, meso, and endo refer to outer, middle, and inner, respectively; the root derm means ...
Upper limb - Wikispaces
... m. laterally, Pronator teres medially and Brachialis which forms the floor of the fossa. ...
... m. laterally, Pronator teres medially and Brachialis which forms the floor of the fossa. ...
Dissection of the Rat
... The rat's body is divided into six anatomical regions: cranial region - head cervical region - neck pectoral region - area where front legs attach thoracic region - chest area abdomen - belly pelvic region - area where the back legs attach 1. Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory h ...
... The rat's body is divided into six anatomical regions: cranial region - head cervical region - neck pectoral region - area where front legs attach thoracic region - chest area abdomen - belly pelvic region - area where the back legs attach 1. Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory h ...
What Is a Flatworm?
... • Most live in marine or fresh water • Most species are bottom dwellers, living in the sand or mud under stones and shells • The most familiar flatworms of this group are the planarians, the “cross-eyed” freshwater worms • Turbellarians can vary greatly in color, form, and ...
... • Most live in marine or fresh water • Most species are bottom dwellers, living in the sand or mud under stones and shells • The most familiar flatworms of this group are the planarians, the “cross-eyed” freshwater worms • Turbellarians can vary greatly in color, form, and ...
What is an animal?
... and anus in deuterostomes – Some cells on the surface of the embryo may migrate into the blastopore to form a new cavity called the archenteron or “primitive gut” – As a result of this cell movement, a threelayered embryo called a gastrula is formed Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishin ...
... and anus in deuterostomes – Some cells on the surface of the embryo may migrate into the blastopore to form a new cavity called the archenteron or “primitive gut” – As a result of this cell movement, a threelayered embryo called a gastrula is formed Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishin ...
Porifera - Perth Beachcombers Education Kit
... microscopic holes or pores, as well as one or more larger round openings or vents. Because they are sedentary (fixed in one place), colourful and simple in structure, sponges are often mistaken for plants. Sponges are in fact the simplest form of multicellular animal. They have no mouth, internal or ...
... microscopic holes or pores, as well as one or more larger round openings or vents. Because they are sedentary (fixed in one place), colourful and simple in structure, sponges are often mistaken for plants. Sponges are in fact the simplest form of multicellular animal. They have no mouth, internal or ...
Taxonomy - Brief facts
... tunic serves as exoskeleton that grows as the animal grows and does not require molting; it consists of a matrix cellulose (tunicin), protein fibers, cells, and proteoglycan ground substance ...
... tunic serves as exoskeleton that grows as the animal grows and does not require molting; it consists of a matrix cellulose (tunicin), protein fibers, cells, and proteoglycan ground substance ...
Chapter 29: Mollusks and Annelids
... Important Features : Mollusks organ systems for excretion circulation, respiration, reproduction, two ends to digestive tract, radula for feeding ...
... Important Features : Mollusks organ systems for excretion circulation, respiration, reproduction, two ends to digestive tract, radula for feeding ...
Homeostasis
... UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS Move materials in and out using the cell membrane. In direct contact with external environment unlike multicellular organisms Just move wastes out of the cell and be done with them Do not have tissues, so all homeostasis is controlled by the cell membrane moving material ...
... UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS Move materials in and out using the cell membrane. In direct contact with external environment unlike multicellular organisms Just move wastes out of the cell and be done with them Do not have tissues, so all homeostasis is controlled by the cell membrane moving material ...
UPPER LIMB AND BACK 3
... Always read the relevant clinical blue boxes to have an idea about clinical significance of structures you learn about. Attend the lectures for more clinical anatomy and supplementary anatomical data. In the dissection room, you are supposed to recognize: 1. Bones of the forearm, elbow joint (repeti ...
... Always read the relevant clinical blue boxes to have an idea about clinical significance of structures you learn about. Attend the lectures for more clinical anatomy and supplementary anatomical data. In the dissection room, you are supposed to recognize: 1. Bones of the forearm, elbow joint (repeti ...
GROSS ANATOMY OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Marieb, Human
... RAMUS - A round or flattened extension from the body, usually for articulation SINUS - An air-filled cavity within a bone, lined by mucous membrane SPINE - A sharp, slender projection for muscle attachment TROCHANTER - A large, irregularly shaped projection TUBERCLE - A small rounded projection TUBE ...
... RAMUS - A round or flattened extension from the body, usually for articulation SINUS - An air-filled cavity within a bone, lined by mucous membrane SPINE - A sharp, slender projection for muscle attachment TROCHANTER - A large, irregularly shaped projection TUBERCLE - A small rounded projection TUBE ...
Handout for Skeletal System
... The skull really consists of two separate sets of bones: the bones of the cranium surround and protect the brain, while the bones of the face support the eyes, nose, and mouth and provide attachment for what we call the muscles of facial expression. Of course, these two sets of bones must attach to ...
... The skull really consists of two separate sets of bones: the bones of the cranium surround and protect the brain, while the bones of the face support the eyes, nose, and mouth and provide attachment for what we call the muscles of facial expression. Of course, these two sets of bones must attach to ...
Respiratory
... Provides an airway for respiration Moistens and warms air Filters inhaled air Resonating chamber for speech Houses olfactory receptors Skin is thin – contains many sebaceous glands ...
... Provides an airway for respiration Moistens and warms air Filters inhaled air Resonating chamber for speech Houses olfactory receptors Skin is thin – contains many sebaceous glands ...
Reptiles Which one is a reptile which one an amphibian?
... 3. Reptiles that live in the water such as crocodiles and alligators have ammonia as liquid waste because they drink lots of water. ...
... 3. Reptiles that live in the water such as crocodiles and alligators have ammonia as liquid waste because they drink lots of water. ...
bones of the appendicular skeleton
... Although bones of males are usually larger and heavier and have more prominent bone markings, the bones of the male and female skeletons are very similar. The outstanding exception is the pelvic structure. The female pelvis reflects modifications for child-bearing. Generally speaking, the female pel ...
... Although bones of males are usually larger and heavier and have more prominent bone markings, the bones of the male and female skeletons are very similar. The outstanding exception is the pelvic structure. The female pelvis reflects modifications for child-bearing. Generally speaking, the female pel ...
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye
... The blood supply of the globe is derived from three sources: the central retinal artery, the anterior ciliary arteries and the posterior ciliary arteries. All these are derived from the ophthalmic artery, which is a branch of the internal carotid. The central retinal artery runs in the optic nerve t ...
... The blood supply of the globe is derived from three sources: the central retinal artery, the anterior ciliary arteries and the posterior ciliary arteries. All these are derived from the ophthalmic artery, which is a branch of the internal carotid. The central retinal artery runs in the optic nerve t ...
beauty and facial esthetic treatments
... due to the platelets effect on stem cell activity. It takes about 3-4 weeks for this process to occur. You have the immediate improvement in appearance from the dermal fillers coupled with a more lasting effect from the regenerative approach using prp. Obviously, the combined procedures is more cost ...
... due to the platelets effect on stem cell activity. It takes about 3-4 weeks for this process to occur. You have the immediate improvement in appearance from the dermal fillers coupled with a more lasting effect from the regenerative approach using prp. Obviously, the combined procedures is more cost ...
Body Planes, Directions, & Cavities
... Thoracic cavity: contains esophagus, trachea, bronchi, lungs, & heart, lg. blood vessels Abdomino-pelvic cavity Upper Abdominal cavity: stomach, large intestine (colon), small intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen Lower abdominal-pelvic cavity: urinary bladder, reproductive organs, las ...
... Thoracic cavity: contains esophagus, trachea, bronchi, lungs, & heart, lg. blood vessels Abdomino-pelvic cavity Upper Abdominal cavity: stomach, large intestine (colon), small intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen Lower abdominal-pelvic cavity: urinary bladder, reproductive organs, las ...
Chapter 29 Foldable Work Comparing Invertebrates
... OUTSIDE: Circulation; INSIDE: (Key Concept page 754) OUTSIDE: Open Circulatory System INSIDE: (Define according to glossary) OUTSIDE: Closed Circulatory System INSIDE: (Define according to glossary) ...
... OUTSIDE: Circulation; INSIDE: (Key Concept page 754) OUTSIDE: Open Circulatory System INSIDE: (Define according to glossary) OUTSIDE: Closed Circulatory System INSIDE: (Define according to glossary) ...
Ear Anatomy Auricle Anatomy: – Elastic cartilage that is covered with
... External Acoustic Meatus: § Anatomy: – Approximately 2-3 cm in an adult – The medial 2/3 of the canal is bony and lined with thin skin – The lateral 1/3 has some ceruminous and sebaceous glands in the subcutaneous tissue that produces cerumen (earwax). § Function: – Transmits collected sounds from ...
... External Acoustic Meatus: § Anatomy: – Approximately 2-3 cm in an adult – The medial 2/3 of the canal is bony and lined with thin skin – The lateral 1/3 has some ceruminous and sebaceous glands in the subcutaneous tissue that produces cerumen (earwax). § Function: – Transmits collected sounds from ...
Grade Five Big Idea 14 Human Body 2014 T. Guide.tx
... Ask: What do know about the organs in the human body and their functions? Click on the hyperlink Body a Building and explore organs in the body systems. Ask how do think organs in the body form? ...
... Ask: What do know about the organs in the human body and their functions? Click on the hyperlink Body a Building and explore organs in the body systems. Ask how do think organs in the body form? ...
The Lobster Conservancy
... A glimpse at lobsters By Kevin Kim This poster will walk through the physiological structures and function of lobsters. It will start off with its general body plan and move on to physiological systems including circulatory, respiratory, digestive, nervous and reproductive systems. Body plan Lobster ...
... A glimpse at lobsters By Kevin Kim This poster will walk through the physiological structures and function of lobsters. It will start off with its general body plan and move on to physiological systems including circulatory, respiratory, digestive, nervous and reproductive systems. Body plan Lobster ...
Axilla - eCurriculum
... you know this before we get into the upper extremity (lots more blood vessels to learn there). LEARN Grants Atlas 12 th ed Table 6.3 and Fig 6.22, 6.7 (carry it around all day if you have too, but learn it). Be able to map out the arterial tree by memory, if you can’t do this you will be in trou ...
... you know this before we get into the upper extremity (lots more blood vessels to learn there). LEARN Grants Atlas 12 th ed Table 6.3 and Fig 6.22, 6.7 (carry it around all day if you have too, but learn it). Be able to map out the arterial tree by memory, if you can’t do this you will be in trou ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.