Nervous MusclesSkeleton
... organs (eyes, ears, etc) to the spinal cord and brain • Motor: carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands • Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them ...
... organs (eyes, ears, etc) to the spinal cord and brain • Motor: carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands • Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them ...
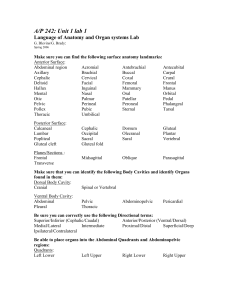
Language of Anatomy and Organ systems Lab
... Be able to place organs into the Abdominal Quadrants and Abdominopelvic regions: Quadrants: Left Lower Left Upper Right Lower Right Upper ...
... Be able to place organs into the Abdominal Quadrants and Abdominopelvic regions: Quadrants: Left Lower Left Upper Right Lower Right Upper ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology I
... • F = less than 180 points Attendance: 5 points will be deducted for every lab missed without documentation ...
... • F = less than 180 points Attendance: 5 points will be deducted for every lab missed without documentation ...
Cells and tissues
... the body • blood functions are, transportation, regulation and defence • blood vessels are arteries, veins and ...
... the body • blood functions are, transportation, regulation and defence • blood vessels are arteries, veins and ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 4: “Cells, Tissues, Organs & Organ Systems”
... •Smoking •Drugs and alcohol •Lack of exercise ...
... •Smoking •Drugs and alcohol •Lack of exercise ...
Human Anatomy - Perry Local Schools
... Identify the planes of reference used to locate structures within the body. Describe the anatomical position. Define and be able to properly use the descriptive and directional terms that refer to the body. List the regions of the body and the principal areas that make up each region. Explain why it ...
... Identify the planes of reference used to locate structures within the body. Describe the anatomical position. Define and be able to properly use the descriptive and directional terms that refer to the body. List the regions of the body and the principal areas that make up each region. Explain why it ...
Phylum Chordata - Cloudfront.net
... camouflaging, shedding their tail & regrowing it • Snakes are lizards with no limbs, ears, and eyelids . • Snakes move by wriggling its long, thin, muscular body. • Have cool, dry, and smooth scaly skin • Snakes eat small animals by either injecting poison through fangs or strangling their prey thro ...
... camouflaging, shedding their tail & regrowing it • Snakes are lizards with no limbs, ears, and eyelids . • Snakes move by wriggling its long, thin, muscular body. • Have cool, dry, and smooth scaly skin • Snakes eat small animals by either injecting poison through fangs or strangling their prey thro ...
Organ Systems - Montville.net
... Name an organ system and list as many organs as you can think of that are within that system. ...
... Name an organ system and list as many organs as you can think of that are within that system. ...
5th grade animal systems study guide
... stores and filters blood, and takes part in many metabolic functions such as the conversion of sugars into glycogen b. kidney – waste-removing vertebrate organ; either of a pair of organs in the abdomen of vertebrates that filter waste liquid c. bladder – bodily sac for liquid or gas d. skin – natur ...
... stores and filters blood, and takes part in many metabolic functions such as the conversion of sugars into glycogen b. kidney – waste-removing vertebrate organ; either of a pair of organs in the abdomen of vertebrates that filter waste liquid c. bladder – bodily sac for liquid or gas d. skin – natur ...
Chapter 1 - Choteau Schools
... – Includes, bones, ligaments, and cartilage – Provides a framework – Protects softer tissues – Serves as a place of attachment for muscles – Produces blood cells and stores inorganic salts in tissues within bones ...
... – Includes, bones, ligaments, and cartilage – Provides a framework – Protects softer tissues – Serves as a place of attachment for muscles – Produces blood cells and stores inorganic salts in tissues within bones ...
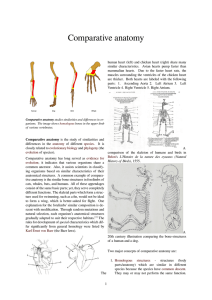
Comparative anatomy
... Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the A evolution of species). comparison of the skeleton of humans and birds in Comparative anatomy has long served as evidence for Belon's ...
... Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the A evolution of species). comparison of the skeleton of humans and birds in Comparative anatomy has long served as evidence for Belon's ...
Compendium 1-3
... - Tissue level- Tissue made of similar cells and the materials surrounding them. Tissues are 4 different types, epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous - Organ level- An organ is made up of 2 or more tissue types, performing a common function - Organ System level- A group of organs that together ...
... - Tissue level- Tissue made of similar cells and the materials surrounding them. Tissues are 4 different types, epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous - Organ level- An organ is made up of 2 or more tissue types, performing a common function - Organ System level- A group of organs that together ...
Chapter 10 Pt 1 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Diploblastic Organization Derived from 2 embryological layers: ...
... Diploblastic Organization Derived from 2 embryological layers: ...
Evolution and Classification of Fishes
... inside out – enters through gills, skin, or anus. - No vertebrae, but do have a cranium and an endoskeleton ...
... inside out – enters through gills, skin, or anus. - No vertebrae, but do have a cranium and an endoskeleton ...
Fish Notes
... inside out – enters through gills, skin, or anus. - No vertebrae, but do have a cranium and an endoskeleton ...
... inside out – enters through gills, skin, or anus. - No vertebrae, but do have a cranium and an endoskeleton ...
Animals with a body cavity lying between the digestive tract and
... • A coelom (lined with peritoneum) is a space between the gut and body wall that allows internal organs to expand and operate freely. A peritoneum is a smooth transparent membrane that lines the abdomen and doubles back over the surfaces of the internal organs to form a continuous sac. • Some animal ...
... • A coelom (lined with peritoneum) is a space between the gut and body wall that allows internal organs to expand and operate freely. A peritoneum is a smooth transparent membrane that lines the abdomen and doubles back over the surfaces of the internal organs to form a continuous sac. • Some animal ...
1 - Holy Family School
... parts of the body The tube of nerves that run through your spine, or backbone A group of neurons that carries signals from the brain to the body and from the body to the brain A body system made of the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine which changes food so it can be used as energy by th ...
... parts of the body The tube of nerves that run through your spine, or backbone A group of neurons that carries signals from the brain to the body and from the body to the brain A body system made of the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine which changes food so it can be used as energy by th ...
Body Systems in Vertebrate Animals
... sensory receptor and a sensory organ; differentiate between central and peripheral nervous systems, and between cranial and spinal nerves; list hormonecontrolled processes in animals; identify the structures of a vertebrate’s digestive system and describe their functions; explain the key role of the ...
... sensory receptor and a sensory organ; differentiate between central and peripheral nervous systems, and between cranial and spinal nerves; list hormonecontrolled processes in animals; identify the structures of a vertebrate’s digestive system and describe their functions; explain the key role of the ...
Vocabulary for Human Body Systems
... -ligaments: tissues that connect bones, hold organs in place -muscles: tissues that cause motion in the body when contracted -musculoskeletal: the muscular and skeletal systems -resistance: exercise that involves working your muscles against free weights or your body’s own weight (walking, running, ...
... -ligaments: tissues that connect bones, hold organs in place -muscles: tissues that cause motion in the body when contracted -musculoskeletal: the muscular and skeletal systems -resistance: exercise that involves working your muscles against free weights or your body’s own weight (walking, running, ...
Review PowerPoint
... cardiac muscle • Moves blood through the body • Found only in the heart • Involuntary muscle ...
... cardiac muscle • Moves blood through the body • Found only in the heart • Involuntary muscle ...
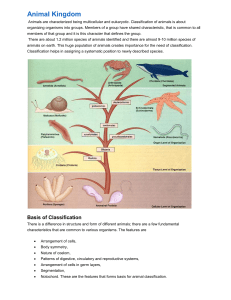
Animal Kingdom
... Organ system Level of Organization - In animals where organs have associated to form functional systems where each system is concerned with a specific physiological function are said to exhibit organ system level of organization. Example: Annelids, Arthropods, Mollusks, Echinoderms and ...
... Organ system Level of Organization - In animals where organs have associated to form functional systems where each system is concerned with a specific physiological function are said to exhibit organ system level of organization. Example: Annelids, Arthropods, Mollusks, Echinoderms and ...
Systems Review
... arteries are the vessels that carry blood away from the heart capillaries connect arteries and veins and are the smallest vessels in the body; this is where substances enter and leave the blood stream veins are the vessels that carry blood back to the heart this system is a closed system, because bl ...
... arteries are the vessels that carry blood away from the heart capillaries connect arteries and veins and are the smallest vessels in the body; this is where substances enter and leave the blood stream veins are the vessels that carry blood back to the heart this system is a closed system, because bl ...
brain: control center of the body, which does everything from
... Blood provides important nourishment to all body organs and tissues. stomach: storage organ for large quantities of food. Protein in your food is digested here. liver: body’s largest organ. Its two main functions are to process nutrients from the intestine and to remove unwanted or harmful chemicals ...
... Blood provides important nourishment to all body organs and tissues. stomach: storage organ for large quantities of food. Protein in your food is digested here. liver: body’s largest organ. Its two main functions are to process nutrients from the intestine and to remove unwanted or harmful chemicals ...
Physiology (17%) Sample Test Prep Questions
... Answer: B Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms -------------------------------------------------------------Grade 7 (5c Physiology) Students know how bones and muscles work together to provide a structural framework for movement. Summary: The skeletal system in animals provides support a ...
... Answer: B Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms -------------------------------------------------------------Grade 7 (5c Physiology) Students know how bones and muscles work together to provide a structural framework for movement. Summary: The skeletal system in animals provides support a ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.