How systems work together
... • Think about how bacteria and viruses enter the body. • They enter via the respiratory and digestive systems. • How do these system help out the immune system? • Sneezing, runny nose, and stomach acid help get rid of bacteria and viruses. ...
... • Think about how bacteria and viruses enter the body. • They enter via the respiratory and digestive systems. • How do these system help out the immune system? • Sneezing, runny nose, and stomach acid help get rid of bacteria and viruses. ...
3. Evolution of a body cavity
... • Coelomates are animals with a true coelom, a fluid filled body cavity completely lined by tissues derived from mesoderm. • The inner and outer layers of tissue that surround the cavity connect dorsally and ventrally to form mesenteries that ...
... • Coelomates are animals with a true coelom, a fluid filled body cavity completely lined by tissues derived from mesoderm. • The inner and outer layers of tissue that surround the cavity connect dorsally and ventrally to form mesenteries that ...
multicellular organisms
... These are some of the terms from this section which you should know. Write the meaning of each term in the space provided. ...
... These are some of the terms from this section which you should know. Write the meaning of each term in the space provided. ...
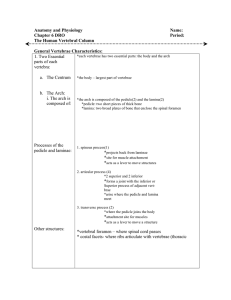
Anatomy and Physiology Name: Chapter 6 DRO Period: The Human
... *has a very large body, to support most of the weight of the upper body *least mobile- limited mobility *subjected to pressure and stress- easily herniated *has lateral processes which are rudimentary ribs- called costal processes *massive spinous process for attachment of large back muscles *cauda ...
... *has a very large body, to support most of the weight of the upper body *least mobile- limited mobility *subjected to pressure and stress- easily herniated *has lateral processes which are rudimentary ribs- called costal processes *massive spinous process for attachment of large back muscles *cauda ...
Chapter 36: Comparing Vertebrates
... Vertebrates perform the essential functions of life with a variety of body structures Evolutionary processes have modified certain basic structures over time As you move through the vertebrate classes from fishes to mammals, organ systems tend to become increasingly complex ...
... Vertebrates perform the essential functions of life with a variety of body structures Evolutionary processes have modified certain basic structures over time As you move through the vertebrate classes from fishes to mammals, organ systems tend to become increasingly complex ...
Animal groups and their coverings
... produced by mammary glands and are warm-blooded. Mammals are the only animals that have hair. It grows from the outer layer of the skin. A dense covering of hair is often called fur or wool and insulates. Glands in the skin release oils which help to keep the fur waterproof and protects against rain ...
... produced by mammary glands and are warm-blooded. Mammals are the only animals that have hair. It grows from the outer layer of the skin. A dense covering of hair is often called fur or wool and insulates. Glands in the skin release oils which help to keep the fur waterproof and protects against rain ...
Review Sheet – Human Body Systems
... The function of the digestive system is to break down food into small nutrient molecules. The nutrient molecules are absorbed into the blood and carried to the cells of your body. You eat a slice of pizza for lunch. Your pizza consists of bread, tomato sauce, and cheese. The pizza will travel throug ...
... The function of the digestive system is to break down food into small nutrient molecules. The nutrient molecules are absorbed into the blood and carried to the cells of your body. You eat a slice of pizza for lunch. Your pizza consists of bread, tomato sauce, and cheese. The pizza will travel throug ...
Animal Kingdom: Comparative Anatomy
... Carnivores, such as sharks have short digestive tracts that produce fastacting digestive enzymes. Herbivores have long intestines that have large colonies of bacteria that help in digesting the cellulose fibers in plant tissues. ...
... Carnivores, such as sharks have short digestive tracts that produce fastacting digestive enzymes. Herbivores have long intestines that have large colonies of bacteria that help in digesting the cellulose fibers in plant tissues. ...
3.1: The Hierarchy of Structure in Animals pg. 73 Hierarchy – an
... together to support the organism. Single celled organisms, bacteria and blue-green algae, must function on their own, with the cellular organelles maintaining cellular homeostasis. The cells that are apart of the a multicellular organism can not live on their own. Levels of Organization There are 7 ...
... together to support the organism. Single celled organisms, bacteria and blue-green algae, must function on their own, with the cellular organelles maintaining cellular homeostasis. The cells that are apart of the a multicellular organism can not live on their own. Levels of Organization There are 7 ...
III.4. Animals-I
... The cuticle is secreted (D) by a single layer of cells called the hypodermis that consists of two layers, a thin outer epicuticle and the much thicker procuticle beneath it. The procuticle contains chitin, which in some cases is strengthened by impregnation with calcium salts. Like vertebrate epithe ...
... The cuticle is secreted (D) by a single layer of cells called the hypodermis that consists of two layers, a thin outer epicuticle and the much thicker procuticle beneath it. The procuticle contains chitin, which in some cases is strengthened by impregnation with calcium salts. Like vertebrate epithe ...
Kingdom Animalia
... – Urochordates – only the larvae has a notochord and nerve cord, adults usually lose tail; includes Tunicates and Salps (marine) – Cephalochordates – notocord persists throughout animal’s life; includes Lancelots; the closest relatives to the Vertebrates ...
... – Urochordates – only the larvae has a notochord and nerve cord, adults usually lose tail; includes Tunicates and Salps (marine) – Cephalochordates – notocord persists throughout animal’s life; includes Lancelots; the closest relatives to the Vertebrates ...
Human Body Systems Cards
... Three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac Smooth: involuntary; lines organs; and most often squeezes to exert pressure on the space inside the tube or organ it surrounds in order to move material through it Cardiac: involuntary; interconnected network that helps heart contract efficiently Skeletal: ...
... Three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac Smooth: involuntary; lines organs; and most often squeezes to exert pressure on the space inside the tube or organ it surrounds in order to move material through it Cardiac: involuntary; interconnected network that helps heart contract efficiently Skeletal: ...
The Human Body
... 5. How many finger widths up from the notch will help you locate the inferior border of the heart? p. 68 A.) Four B.) One C.) Three *D.) Two 6. What is the main point of reference when describing the abdomen? p. 65 A.) Breastbone B.) Pelvis *C.) Naval D.) Stomach ...
... 5. How many finger widths up from the notch will help you locate the inferior border of the heart? p. 68 A.) Four B.) One C.) Three *D.) Two 6. What is the main point of reference when describing the abdomen? p. 65 A.) Breastbone B.) Pelvis *C.) Naval D.) Stomach ...
Introduction to Animals - Kent City School District
... gills for oxygen exchange, or for filter feeding, while in others, the slits ...
... gills for oxygen exchange, or for filter feeding, while in others, the slits ...
PDF version
... size. The coelom as a major support system. Annelida and other worms. Segmentation. 9) Mollusca. Larvae vs. direct development. Life history. Internal and external skeletons. Muscles and movement. 10) Ecdysozoa. Arthropoda. The diversity of arthropods. The evolution of segmentation. 11) The move to ...
... size. The coelom as a major support system. Annelida and other worms. Segmentation. 9) Mollusca. Larvae vs. direct development. Life history. Internal and external skeletons. Muscles and movement. 10) Ecdysozoa. Arthropoda. The diversity of arthropods. The evolution of segmentation. 11) The move to ...
Tissues
... • Tissues: a group of cells with similar structure and function • Histology: the study of tissues • There are 4 primary types of tissues: ...
... • Tissues: a group of cells with similar structure and function • Histology: the study of tissues • There are 4 primary types of tissues: ...
Cytoplasm The gel-like substance that surrounds the nucleus of a
... symptoms, history, laboratory, and clinical test results, and radiographic procedures Endoscope The instrument consisting of a rigid or flexible fiberoptic tube and optical system for observing the inside of a hollow organ or cavity Etiology The study of the cause of disease Fluoroscope The in ...
... symptoms, history, laboratory, and clinical test results, and radiographic procedures Endoscope The instrument consisting of a rigid or flexible fiberoptic tube and optical system for observing the inside of a hollow organ or cavity Etiology The study of the cause of disease Fluoroscope The in ...
Micro Lab Unit 1 Flashcards
... 60) What is the peripheral nervous system composed of? 61) The peripheral nerves send information to what other part of the nervous system? 62) What are the two parts of the central nervous system? 63) What are specialized nerve cells that detect specific stimuli such as light, touch or chemicals? 6 ...
... 60) What is the peripheral nervous system composed of? 61) The peripheral nerves send information to what other part of the nervous system? 62) What are the two parts of the central nervous system? 63) What are specialized nerve cells that detect specific stimuli such as light, touch or chemicals? 6 ...
Critical Thinking Questions
... The skeletal system releases additional calcium, and the circulatory system retains more sodium in the blood to provide muscles with ions for contraction. The digestive system increases the rate of digestion, and the excretory system ceases to provide tissues with more nutrients. The respiratory sys ...
... The skeletal system releases additional calcium, and the circulatory system retains more sodium in the blood to provide muscles with ions for contraction. The digestive system increases the rate of digestion, and the excretory system ceases to provide tissues with more nutrients. The respiratory sys ...
Lab 6
... Muscle tissue is composed of long, excitable cells that are capable of contraction. Inside each cell, there are many microfilaments arranged in parallel. These microfilaments are of two types: actin and myosin. When a muscle cell contracts, these microfilaments slide past each other, and the muscle ...
... Muscle tissue is composed of long, excitable cells that are capable of contraction. Inside each cell, there are many microfilaments arranged in parallel. These microfilaments are of two types: actin and myosin. When a muscle cell contracts, these microfilaments slide past each other, and the muscle ...
Chapter 24 Support and Movement of the Body
... • Two main types of tissue make up the skeleton= bone and cartilage. • Bone= tissue consisting of living bone cells and non living material they secrete. This nonliving substance made up of calcium, phosphorus, and microscopic fibers forms circular layers around the tiny blood vessels in bones. Each ...
... • Two main types of tissue make up the skeleton= bone and cartilage. • Bone= tissue consisting of living bone cells and non living material they secrete. This nonliving substance made up of calcium, phosphorus, and microscopic fibers forms circular layers around the tiny blood vessels in bones. Each ...
Phylum Echinodermata
... (usually along ambulacral grooves), tube feet -pedicellariae -dermal gills (=papulae) Body Organization -adult radially symmetrical, usually with five part (pentamerous) symmetry, or multiples of 5's -no distinct head or brain (no cephalization) -circulatory system greatly reduced and replaced, in f ...
... (usually along ambulacral grooves), tube feet -pedicellariae -dermal gills (=papulae) Body Organization -adult radially symmetrical, usually with five part (pentamerous) symmetry, or multiples of 5's -no distinct head or brain (no cephalization) -circulatory system greatly reduced and replaced, in f ...
Chapter 22
... VERTEBRATE BODY • All vertebrates have the same general architecture: a long internal tube that extends from mouth to anus, which is suspended within an internal body cavity called the coelom. • The coelom of many terrestrial vertebrates is divided into two parts. • Thoracic cavity contains the hear ...
... VERTEBRATE BODY • All vertebrates have the same general architecture: a long internal tube that extends from mouth to anus, which is suspended within an internal body cavity called the coelom. • The coelom of many terrestrial vertebrates is divided into two parts. • Thoracic cavity contains the hear ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.