* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Body Systems Cards
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
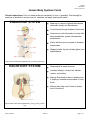
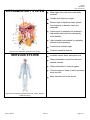
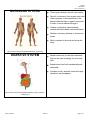
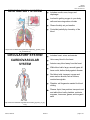
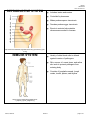
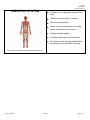
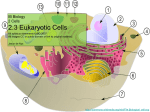
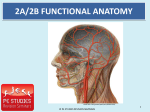
Biology HS/Science Unit: 13 Lesson: 01 Human Body Systems Cards Teacher Instructions: Print out these cards onto cardstock (in color, if possible). Print enough for each pair of students to receive one set. Laminate, cut apart, and bag the cards. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Made up of a series of glands that release chemicals directly into bloodstream Controls body through release of hormones Hormones provide information to body cells about metabolism, growth, development, and behavior. Works with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis Organs include: thyroid, pituitary gland, and hypothalamus http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Illu_endocrine_system.png EXCRETORY SYSTEM Responsible for waste removal Includes: kidneys, urinary tract, bladder, ureters, and urethra Kidneys filter blood to remove wastes from it, helping to maintain homeostasis of body fluids. Kidneys also help control level of sodium level in the blood. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Illu_urinary_system_neutral. png ©2012, TESCCC 01/22/13 page 1 of 6 Biology HS/Science Unit: 13 Lesson: 01 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Main organ is the skin and covers body surfaces Flexible and responsive organ Exterior layer of epidermis helps protect from exposure to bacteria, heat, and chemicals Interior layer of epidermis has melanin to help protect body cells from damage by solar radiation Helps maintain homeostasis by regulating internal body temperature Functions as a sense organ Produces essential vitamins http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Haut_w2.png NERVOUS SYSTEM Includes: nerves, brain, and spinal cord Relays information to and from skin and skeletal muscles Relays information to internal organs Controls organs in times of stress and when body is at rest Basic structure unit is the neuron http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nervous_system_diagram_ %28dumb%29.png ©2012, TESCCC 01/22/13 page 2 of 6 Biology HS/Science Unit: 13 Lesson: 01 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac Smooth: involuntary; lines organs; and most often squeezes to exert pressure on the space inside the tube or organ it surrounds in order to move material through it Cardiac: involuntary; interconnected network that helps heart contract efficiently Skeletal: voluntary; attaches to and moves bones Able to contract to do work and move the body http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Muscular_System.jpg DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Breaks down food you eat into molecules that can be used as energy for your body cells Breaks down food both mechanically and chemically Includes: mouth, stomach, small and large intestines, and esophagus http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Digestive_system_diagram_ numbered.svg ©2012, TESCCC 01/22/13 page 3 of 6 Biology HS/Science Unit: 13 Lesson: 01 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Includes: mouth, nose, lungs, and diaphragm Involved in getting oxygen to your body cells and removing carbon dioxide Cleans the dirty air you breathe Controlled partially by chemistry of the blood http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Respiratory_system_compl ete_numbered.svg CIRCULATORY SYSTEM/ Includes: heart, veins, and arteries CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Veins carry blood to the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. White blood cells: large; several types; all have nuclei; defend body against disease Red blood cells: transport oxygen and some carbon dioxide; lack a nucleus; contain hemoglobin Platelets: cell fragments needed for blood clotting Plasma: liquid; has proteins; transports red and white blood cells, platelets, nutrients, enzymes, hormones, gases, and inorganic salts http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Circulatory_System_no_tag s.svg ©2012, TESCCC 01/22/13 page 4 of 6 Biology HS/Science Unit: 13 Lesson: 01 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Includes: testes and ovaries Controlled by hormones Males produce sperm via meiosis. Females produce eggs via meiosis. Events in meiosis help maintain chromosome number in humans. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Female_reproductive_syste m.svg IMMUNE SYSTEM Variety of white blood cells to defend against invasion of pathogens Skin, mucus, oil, sweat, tears, and saliva also work to prevent pathogens from entering body Consists of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, and thymus http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:TELymphatic_system_diagram.svg ©2012, TESCCC 01/22/13 page 5 of 6 Biology HS/Science Unit: 13 Lesson: 01 SKELETAL SYSTEM Includes: bones, ligaments, tendons, and joints Produces red blood cells in marrow Stores minerals and fat Allows for body movement by providing points of attachment for muscles Protects internal organs Provides a framework for body tissues Two types of bone tissue (compact bone and spongy bone) that differ in density http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Skeletal_System.png ©2012, TESCCC 01/22/13 page 6 of 6