Target 1: Animal Body Plans and Phylogeny - APBio10-11
... internally fertilized, amniotic egg. This amniotic egg, first seen in reptiles as amphibians’ eggs are still externally developed, helps increase the chance that there is healthy off-spring. Also, the leathery egg and protects the reptile baby, the brittle egg that protects the bird baby and the pla ...
... internally fertilized, amniotic egg. This amniotic egg, first seen in reptiles as amphibians’ eggs are still externally developed, helps increase the chance that there is healthy off-spring. Also, the leathery egg and protects the reptile baby, the brittle egg that protects the bird baby and the pla ...
Anatomy Six Anterior Hip
... • The ACL attaches from the anterior tibia to the posterior femur – Limits anterior translation of tibia when the femur is fixed and posterior translation of femur when the tibia is fixed – Limits hyperextension of the knee (becomes taut) – Limits medial rotation of tibia and lateral rotation of fem ...
... • The ACL attaches from the anterior tibia to the posterior femur – Limits anterior translation of tibia when the femur is fixed and posterior translation of femur when the tibia is fixed – Limits hyperextension of the knee (becomes taut) – Limits medial rotation of tibia and lateral rotation of fem ...
university of bari medical school bari english medical
... 37. Reil’ bundle (medial lemniscus): origin, course, end, content, function, drawing required 38. Acoustic fascicle (lateral lemniscus): origin, course, end, function, drawing required 39. Taste path, drawing required 40. Midsagittal section through the eyeball, drawing required 41. The extrinsic mu ...
... 37. Reil’ bundle (medial lemniscus): origin, course, end, content, function, drawing required 38. Acoustic fascicle (lateral lemniscus): origin, course, end, function, drawing required 39. Taste path, drawing required 40. Midsagittal section through the eyeball, drawing required 41. The extrinsic mu ...
Chapter-23
... • Multicelled heterotrophs (ingest other organisms) • Grow and develop through a series of stages • Actively move about during all or part of life cycle ...
... • Multicelled heterotrophs (ingest other organisms) • Grow and develop through a series of stages • Actively move about during all or part of life cycle ...
WILDERNESS AND MOUNTAIN MEDICINE
... • Branches from the posterior division include: • 1) Auriculotemporal nerve which ascends behind the temperomandibular joint medial to the parotid gland. It supplies the skin of the auricle, the external auditory meatus, the temperomandibular joint and the scalp. • 2)Lingual nerve which enters the m ...
... • Branches from the posterior division include: • 1) Auriculotemporal nerve which ascends behind the temperomandibular joint medial to the parotid gland. It supplies the skin of the auricle, the external auditory meatus, the temperomandibular joint and the scalp. • 2)Lingual nerve which enters the m ...
Arthropods (Notebook Copy)
... Chitinous teeth in stomach grind food Wastes leave through anus Green glands filter wastes from blood & help with salt balance Open circulatory system with heart to pump blood to gills & body cells Ostia - one way valves allowing blood from dorsal sinus to reenter heart Gills attached to walking leg ...
... Chitinous teeth in stomach grind food Wastes leave through anus Green glands filter wastes from blood & help with salt balance Open circulatory system with heart to pump blood to gills & body cells Ostia - one way valves allowing blood from dorsal sinus to reenter heart Gills attached to walking leg ...
Chordates
... • Have a notochord at some stage in life. • Have a dorsal tubular nerve cord ( spinal cord) • Have pharyngeal gill slits at some stage in life • Ventral Heart & closed circulatory systems ...
... • Have a notochord at some stage in life. • Have a dorsal tubular nerve cord ( spinal cord) • Have pharyngeal gill slits at some stage in life • Ventral Heart & closed circulatory systems ...
Eye Anatomy - Cloudfront.net
... Clear, flexible structure Behind the iris & pupil The lens & ciliary body help control fine focusing of light as it passes through the eye http://www.smartplanet.com/business/blog/smart-takes/artificial-lens-implant-to-givepatients-high-definition-vision-better-than-2020/2558/ ...
... Clear, flexible structure Behind the iris & pupil The lens & ciliary body help control fine focusing of light as it passes through the eye http://www.smartplanet.com/business/blog/smart-takes/artificial-lens-implant-to-givepatients-high-definition-vision-better-than-2020/2558/ ...
Evolution of the Animal Body Plan
... Osteichthyes both evolved. At the end of the Devonian, the first amphibians also appeared. • Sharks, skates, and rays make up Class Chondrichthyes. • They are called cartilaginous fish because their skeletons are made of cartilage, rather than bone. They have tooth-like scales embedded in their skin ...
... Osteichthyes both evolved. At the end of the Devonian, the first amphibians also appeared. • Sharks, skates, and rays make up Class Chondrichthyes. • They are called cartilaginous fish because their skeletons are made of cartilage, rather than bone. They have tooth-like scales embedded in their skin ...
32animalevolution
... evolutionary trend toward the concentration of sensory equipment on the anterior end. – Cephalization also includes the development of a central nervous system concentrated in the head and extending toward the tail as a longitudinal nerve cord. • The symmetry of an animal generally fits its lifestyl ...
... evolutionary trend toward the concentration of sensory equipment on the anterior end. – Cephalization also includes the development of a central nervous system concentrated in the head and extending toward the tail as a longitudinal nerve cord. • The symmetry of an animal generally fits its lifestyl ...
Introduction
... soft, worm-like animals with flattened, elongated bodies. They exhibit several important structural advances over the cnidarians, including three distinct tissue layers (triploblastic construction), bilateral symmetry, and several welldeveloped organ systems. Approximately 13,000 species of flatworm ...
... soft, worm-like animals with flattened, elongated bodies. They exhibit several important structural advances over the cnidarians, including three distinct tissue layers (triploblastic construction), bilateral symmetry, and several welldeveloped organ systems. Approximately 13,000 species of flatworm ...
Diversity of Animals
... All animals need oxygen to survive. There are a few methods animals can use to obtain oxygen. The main methods of gaining oxygen are as follows: 1. Integumentary exchange - gases diffuse across the skin or body covering. This is used by flatworms, earthworms, and amphibians. 2. Tracheal respiration ...
... All animals need oxygen to survive. There are a few methods animals can use to obtain oxygen. The main methods of gaining oxygen are as follows: 1. Integumentary exchange - gases diffuse across the skin or body covering. This is used by flatworms, earthworms, and amphibians. 2. Tracheal respiration ...
Unit XIV: Excretion
... A build up wastes would become ________ to the organism Those wastes maybe be _____________________________ ___________________________________________ ...
... A build up wastes would become ________ to the organism Those wastes maybe be _____________________________ ___________________________________________ ...
Worms and Mollusks
... • Digestive waste passes out through the anus at the end of the digestive tract • Nephridia: excretory organs that filter fluid in the coelom ...
... • Digestive waste passes out through the anus at the end of the digestive tract • Nephridia: excretory organs that filter fluid in the coelom ...
The Eye
... of the nervous system, responsible for sight. Contained within the orbits of the skull, the eyes are protected from injury by pads of fat. Factoid: The word “eye” has a long history, including Old English “ege” and Proto-Germanic “*augon.” Some cognates are Greek “okkos” and Latin “oculus,” both mea ...
... of the nervous system, responsible for sight. Contained within the orbits of the skull, the eyes are protected from injury by pads of fat. Factoid: The word “eye” has a long history, including Old English “ege” and Proto-Germanic “*augon.” Some cognates are Greek “okkos” and Latin “oculus,” both mea ...
Bird Dissection
... tube is the first part of the digestive system that is visible to you. 25. The lower part of the esophagus widens into a large, hard object called the crop. 26. Below the crop is the true stomach, which has two parts. The upper part is called the proventriculus. In this part of the stomach, digestiv ...
... tube is the first part of the digestive system that is visible to you. 25. The lower part of the esophagus widens into a large, hard object called the crop. 26. Below the crop is the true stomach, which has two parts. The upper part is called the proventriculus. In this part of the stomach, digestiv ...
Sponge_and_Cnidarians
... • Sexually: When both sexes release gametes during the spawning season. ...
... • Sexually: When both sexes release gametes during the spawning season. ...
Body Orientation Test-Chp. 1 Name Matching: Match the letter(s) to
... 29. The study of how the body and its parts work or function is A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Biology D. Analogy 30. The study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts. A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Biology D. Analogy Short Answer: Using complete sentences answer the following. 31. Describe ...
... 29. The study of how the body and its parts work or function is A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Biology D. Analogy 30. The study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts. A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Biology D. Analogy Short Answer: Using complete sentences answer the following. 31. Describe ...
NAME____________________________________ MUSCULAR
... 11. Is this disease contagious? How do you get it? ___________________________________________________________________________________ 12. Which version of MD affects both boys and girls equally? ___________________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is a muscle ...
... 11. Is this disease contagious? How do you get it? ___________________________________________________________________________________ 12. Which version of MD affects both boys and girls equally? ___________________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is a muscle ...
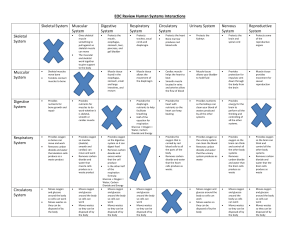
EOC Review Human Systems Interactions Skeletal System Muscular
... and glucose around the body so cells can work Moves wastes so they can be disposed of by the body ...
... and glucose around the body so cells can work Moves wastes so they can be disposed of by the body ...
5. Name 2 ways forelimbs are different than hind limbs.
... particularly fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Usually they are located just on the inside of the abdominal wall. Peritoneum A spider web like membrane that covers many of the organs, you may have to carefully pick it off to get a clear view. Liver--The l ...
... particularly fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Usually they are located just on the inside of the abdominal wall. Peritoneum A spider web like membrane that covers many of the organs, you may have to carefully pick it off to get a clear view. Liver--The l ...
Basic Terminology
... Medial – toward midline of the body Lateral – away from midline of the body Proximal – toward point of attachment Distal – away from point of attachment Superior – toward the top of the head Inferior – toward the bottom of the feet ...
... Medial – toward midline of the body Lateral – away from midline of the body Proximal – toward point of attachment Distal – away from point of attachment Superior – toward the top of the head Inferior – toward the bottom of the feet ...
Interaction of Systems - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... The circulatory system interacts with all organ systems in the body delivering oxygen and nutrients and removing carbon dioxide and wastes. One system can supply the necessary materials to all other systems, without these materials the other organ systems could not function— i.e. this interaction is ...
... The circulatory system interacts with all organ systems in the body delivering oxygen and nutrients and removing carbon dioxide and wastes. One system can supply the necessary materials to all other systems, without these materials the other organ systems could not function— i.e. this interaction is ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.