Types of Tissues A tissue is composed of similarly specialized cells
... entire body surface and most of the body’s inner cavities. On the external surface, it protects the body from injury, drying out, and possible pathogen (virus and bacterium) invasion. On internal surfaces, epithelial tissue may be specialized for other functions in addition to protection. For exampl ...
... entire body surface and most of the body’s inner cavities. On the external surface, it protects the body from injury, drying out, and possible pathogen (virus and bacterium) invasion. On internal surfaces, epithelial tissue may be specialized for other functions in addition to protection. For exampl ...
Chapter 27: Evolution
... reproduce and require moist habitats. • Frog tadpoles metamorphose into terrestrial adults with lungs. ...
... reproduce and require moist habitats. • Frog tadpoles metamorphose into terrestrial adults with lungs. ...
An Overview of Body Systems
... (a) Flow between arteries and veins 2) The heart is a 4-chambered pump. 3) The left side of the heart pumps blood through the arteries to the capillaries. 4) At the capillaries, the blood releases nutrients, oxygen, and other necessary molecules into the body tissues. 5) Also at the capillaries, the ...
... (a) Flow between arteries and veins 2) The heart is a 4-chambered pump. 3) The left side of the heart pumps blood through the arteries to the capillaries. 4) At the capillaries, the blood releases nutrients, oxygen, and other necessary molecules into the body tissues. 5) Also at the capillaries, the ...
Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes
... cavity. *serous fluid – between serous layers. – allows organs to slide easily across cavity walls. c. Specific serous membranes 1. peritoneum – surrounds organs in abdominal cavity. 2. Pleura – around lungs 3. Pericardium – around heart ...
... cavity. *serous fluid – between serous layers. – allows organs to slide easily across cavity walls. c. Specific serous membranes 1. peritoneum – surrounds organs in abdominal cavity. 2. Pleura – around lungs 3. Pericardium – around heart ...
Blocks of the ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric
... They pass anterolateral to quadratus lumborum and pierce the Transversus Abdominis muscle close to the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS). ...
... They pass anterolateral to quadratus lumborum and pierce the Transversus Abdominis muscle close to the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS). ...
11. phylum annelida
... parasitic, most annelids are free-living on both land and in the aquatic realm. They are elongated worms, cylindrical in cross-section and possess muscular body walls. The feature setting annelids apart from other worm-like animals is segmentation (metamerism), a serial repetition of both external a ...
... parasitic, most annelids are free-living on both land and in the aquatic realm. They are elongated worms, cylindrical in cross-section and possess muscular body walls. The feature setting annelids apart from other worm-like animals is segmentation (metamerism), a serial repetition of both external a ...
INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL DIVERSITY
... of all appendages observed in animals Hypothesis is that all animal appendages have some degree of genetic homology that they are all derived from appendages that were present in a common ancestor. This hypothesis is controversial, however, and research continues ...
... of all appendages observed in animals Hypothesis is that all animal appendages have some degree of genetic homology that they are all derived from appendages that were present in a common ancestor. This hypothesis is controversial, however, and research continues ...
04 CRAYFISH 2009
... Base of 3rd walking legs Base of 5th walking legs Mature at 5 to 6 years Live for 15 to 20 years ...
... Base of 3rd walking legs Base of 5th walking legs Mature at 5 to 6 years Live for 15 to 20 years ...
Cells→ Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems
... the digestive system, constantly interacts with your endocrine system and spreads hormones throughout your body. Examples of Systems It's easy to point out a few in your body. The two you think of the most are probably your respiratory (getting oxygen into your body and carbon dioxide out) and diges ...
... the digestive system, constantly interacts with your endocrine system and spreads hormones throughout your body. Examples of Systems It's easy to point out a few in your body. The two you think of the most are probably your respiratory (getting oxygen into your body and carbon dioxide out) and diges ...
File - Biology with Ms. Murillo
... White Blood Cells and Platelets = The white blood cells are the mobile elements of the body's defense system. Platelets are small cell fragments which play an important part in blood clotting. These two components make up about 0.2% of blood volume. Red Blood Cells = Also called erythrocytes, red bl ...
... White Blood Cells and Platelets = The white blood cells are the mobile elements of the body's defense system. Platelets are small cell fragments which play an important part in blood clotting. These two components make up about 0.2% of blood volume. Red Blood Cells = Also called erythrocytes, red bl ...
Chapter 5 Tissue Notes File
... particular function -includes extracellular fluid and intercellular materials (products that exist between cells) -4 major types • epithelial • connective • muscle • nerve Epithelial Tissue (epithelium): consists of cells that are very closely packed together w/ little or no intercellular materials ...
... particular function -includes extracellular fluid and intercellular materials (products that exist between cells) -4 major types • epithelial • connective • muscle • nerve Epithelial Tissue (epithelium): consists of cells that are very closely packed together w/ little or no intercellular materials ...
ANIMAL SYSTEMS TEST (ch
... ____ 22. In insects, gas exchange takes place through a network of a. tracheal tubes. c. book lungs. b. mantle cavities. d. blood vessels. ____ 23. Most flatworms are small and very thin. Therefore, they can supply their cells with oxygen and remove metabolic wastes by means of a. simple diffusion ...
... ____ 22. In insects, gas exchange takes place through a network of a. tracheal tubes. c. book lungs. b. mantle cavities. d. blood vessels. ____ 23. Most flatworms are small and very thin. Therefore, they can supply their cells with oxygen and remove metabolic wastes by means of a. simple diffusion ...
Frog Virtual Lab
... ix. What occurs in the stomach for the first time and what two digestive organs does it connect? ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ x. What is the purpose of the gallbladder? ________________________________________________ ____________ ...
... ix. What occurs in the stomach for the first time and what two digestive organs does it connect? ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ x. What is the purpose of the gallbladder? ________________________________________________ ____________ ...
BODY SYSTEMS: FUNCTIONS AND INTERACTIONS
... 1. __C__ to carry nutrients, water, and oxygen to the body cells 2. __S__ to protect body organs 3. __R__ to pass oxygen from the air to the blood 4. _C, E_ to remove wastes from the body cells 5. __D__ to change food to a form that the body cells can use 6. __S__ to give the body its basic shape an ...
... 1. __C__ to carry nutrients, water, and oxygen to the body cells 2. __S__ to protect body organs 3. __R__ to pass oxygen from the air to the blood 4. _C, E_ to remove wastes from the body cells 5. __D__ to change food to a form that the body cells can use 6. __S__ to give the body its basic shape an ...
Section 26.1 Summary – pages 693-697
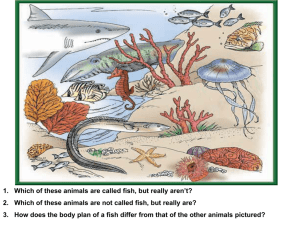
... 1. Which of these animals are called fish, but really aren’t? 2. Which of these animals are not called fish, but really are? 3. How does the body plan of a fish differ from that of the other animals pictured? ...
... 1. Which of these animals are called fish, but really aren’t? 2. Which of these animals are not called fish, but really are? 3. How does the body plan of a fish differ from that of the other animals pictured? ...
Document
... and left sides •Midsagittal = equal left and right sides. •Transverse or Horizontal: horizontal line that separates body into superior and inferior or top and bottom •Coronal or Frontal: Vertical line that separates body into ventral (anterior) and dorsal (posterior) or front and back portions ...
... and left sides •Midsagittal = equal left and right sides. •Transverse or Horizontal: horizontal line that separates body into superior and inferior or top and bottom •Coronal or Frontal: Vertical line that separates body into ventral (anterior) and dorsal (posterior) or front and back portions ...
CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS - All Saints Academy Dunstable
... 6]____ is sorting organisms into groups. 7]Living things are called ____ 8] A animal which can’t control its internal body temperature is ________ _________ • 9] ________ have body divided into five parts. • 10] The basic unit of classification is ______. ...
... 6]____ is sorting organisms into groups. 7]Living things are called ____ 8] A animal which can’t control its internal body temperature is ________ _________ • 9] ________ have body divided into five parts. • 10] The basic unit of classification is ______. ...
Invertebrates II
... it cannot be used for sensing and detecting stimuli; instead, antennae and sensory bristles are used. Arthropods are coelomates although the coelom is lost during development; the body cavity of the mature arthropod has a different origin, developing from the hemocoel. There are usually some signs o ...
... it cannot be used for sensing and detecting stimuli; instead, antennae and sensory bristles are used. Arthropods are coelomates although the coelom is lost during development; the body cavity of the mature arthropod has a different origin, developing from the hemocoel. There are usually some signs o ...
Invertebrates II
... it cannot be used for sensing and detecting stimuli; instead, antennae and sensory bristles are used. Arthropods are coelomates although the coelom is lost during development; the body cavity of the mature arthropod has a different origin, developing from the hemocoel. There are usually some signs o ...
... it cannot be used for sensing and detecting stimuli; instead, antennae and sensory bristles are used. Arthropods are coelomates although the coelom is lost during development; the body cavity of the mature arthropod has a different origin, developing from the hemocoel. There are usually some signs o ...
Chapter 1
... A. hierarchy of structural organization 1. chemical = atoms bonded together to make up molecules ...
... A. hierarchy of structural organization 1. chemical = atoms bonded together to make up molecules ...
1 anatomy terms and planes - PA
... Anatomical Position • This is a reference position that allows for the use of consistent directional terminology. • All descriptions of location are made from within anatomical position. Subject is facing forward with palms forward, thumbs facing to the sides. ...
... Anatomical Position • This is a reference position that allows for the use of consistent directional terminology. • All descriptions of location are made from within anatomical position. Subject is facing forward with palms forward, thumbs facing to the sides. ...
Major Characteristics
... feeders or herbivores; frogs are carnivores *have stomach, small intestines, large intestines, cloaca ...
... feeders or herbivores; frogs are carnivores *have stomach, small intestines, large intestines, cloaca ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.