Fishes, Amphibians, Birds, Reptiles, Mammals
... Respiratory: Gills, Skin, Lungs Circulatory: 3 chambered heart Reproduction: External Fertilization and development • Examples: Frogs, Salamanders ...
... Respiratory: Gills, Skin, Lungs Circulatory: 3 chambered heart Reproduction: External Fertilization and development • Examples: Frogs, Salamanders ...
It`s Time For Earth Science Chapter 1
... anterior surface of the humerus; movements include bending and extending arms. ...
... anterior surface of the humerus; movements include bending and extending arms. ...
What is the Role that Your System Plays In the Body?
... power and strength. In most cases, a skeletal muscle is attached to one end of a bone. It stretches all the way across a joint and then attaches again to another bone. ...
... power and strength. In most cases, a skeletal muscle is attached to one end of a bone. It stretches all the way across a joint and then attaches again to another bone. ...
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic
... Spinal cord made up of spinal nerves nerve impulses & spinal reflexes Encased in vertebra ...
... Spinal cord made up of spinal nerves nerve impulses & spinal reflexes Encased in vertebra ...
Document
... – Protection. Forms boundary of individual, barrier to external dangers and valuable internal materials – Sensing. Can gather information about environment: temperature, pressure, light, damage to integument – Communication. Since visible to others, can send signals with skin color or structures (ha ...
... – Protection. Forms boundary of individual, barrier to external dangers and valuable internal materials – Sensing. Can gather information about environment: temperature, pressure, light, damage to integument – Communication. Since visible to others, can send signals with skin color or structures (ha ...
Musculoskeletal System - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... childhood. Children’s bones are softer than the bones of adults. The number of bones found in a human body is ~ 206, this is because what one source describes as a single bone formed from several parts may be described by another source as several different bones working together. The bones support ...
... childhood. Children’s bones are softer than the bones of adults. The number of bones found in a human body is ~ 206, this is because what one source describes as a single bone formed from several parts may be described by another source as several different bones working together. The bones support ...
The Skeletal System Two Parts: - axial skeleton 3 Parts – skull
... Two Parts: - axial skeleton 3 Parts – skull, thorax, (pelvis), & vertebral column - appendicular skeleton 4 Parts–left and right, upper and lower extremities Classification of Bones Wolff’s Law: ...
... Two Parts: - axial skeleton 3 Parts – skull, thorax, (pelvis), & vertebral column - appendicular skeleton 4 Parts–left and right, upper and lower extremities Classification of Bones Wolff’s Law: ...
Wrist and hand
... – The congruency of the IP joint surfaces contributes greatly to finger joint stability The proximal IP joint is a hinged joint capable of flexion and extension The distal IP joint has similar structures but less stability and allows some hyperextension. ...
... – The congruency of the IP joint surfaces contributes greatly to finger joint stability The proximal IP joint is a hinged joint capable of flexion and extension The distal IP joint has similar structures but less stability and allows some hyperextension. ...
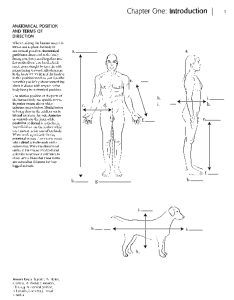
Chapter One: Introduction
... Cells consist of an enclosing plasma membrane, an inner cytoplasm with numerous organelles, and other cellular structures. The fluid portion of the cell is called the cytosol. Color the cytosol in last after you color the rest of the cellular structures. One of the major structures in the cell is th ...
... Cells consist of an enclosing plasma membrane, an inner cytoplasm with numerous organelles, and other cellular structures. The fluid portion of the cell is called the cytosol. Color the cytosol in last after you color the rest of the cellular structures. One of the major structures in the cell is th ...
Clues
... 1. The normal type of ___ is negative. 7. The ___ portion of the body consists of the limbs and shoulder and hip girdles. 9. Directional term that means the back of the body. 10. A plane that divides the body vertically into anterior and posterior portions, also known as coronal. 11. Double serous m ...
... 1. The normal type of ___ is negative. 7. The ___ portion of the body consists of the limbs and shoulder and hip girdles. 9. Directional term that means the back of the body. 10. A plane that divides the body vertically into anterior and posterior portions, also known as coronal. 11. Double serous m ...
Lung and Airway Anatomy - The Anatomy of Sea
... by complete cartilaginous rings that are usually white, except in decomposing animals or some ...
... by complete cartilaginous rings that are usually white, except in decomposing animals or some ...
Lab Objectives for Quiz 5
... malleus incus stapes – in oval window auditory tube inner ear vestibule - round window cochlea - organ of Corti semicircular canals vestibular branch and cochlear branch of vestibulocochlear nerve ...
... malleus incus stapes – in oval window auditory tube inner ear vestibule - round window cochlea - organ of Corti semicircular canals vestibular branch and cochlear branch of vestibulocochlear nerve ...
The Thoracic Cavity
... • Lining the Walls of Alveoli – Respiratory Membrane • Type I cells = simple squamous epithelial cells • Basal lamina and fine areolar CT • Covered with capillaries and elastic fibers ...
... • Lining the Walls of Alveoli – Respiratory Membrane • Type I cells = simple squamous epithelial cells • Basal lamina and fine areolar CT • Covered with capillaries and elastic fibers ...
Lesson 3: How do organs work together?
... The muscle and skeletal systems work together to move your body. Muscles work in pairs to move bones. Try this. Hold your arm out straight in front of you. Bend your elbow. The muscle on the bottom of your arm relaxes. The muscle on top of your upper arm tightens. This pulls on the bone of your uppe ...
... The muscle and skeletal systems work together to move your body. Muscles work in pairs to move bones. Try this. Hold your arm out straight in front of you. Bend your elbow. The muscle on the bottom of your arm relaxes. The muscle on top of your upper arm tightens. This pulls on the bone of your uppe ...
introduction to - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... pancreas and liver, the major glands of the digestive tract. The large intestine consists of the cecum (which receives the terminal part of the ileum), appendix, colon (ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid), rectum, and anal canal. Most reabsorption of water occurs in the ascending colon. ...
... pancreas and liver, the major glands of the digestive tract. The large intestine consists of the cecum (which receives the terminal part of the ileum), appendix, colon (ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid), rectum, and anal canal. Most reabsorption of water occurs in the ascending colon. ...
Digestive and Excretory Systems
... Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular organism include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. ▶ A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Specialized cells are uniquely suited to perform particular functions. ▶ Groups of similar cells t ...
... Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular organism include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. ▶ A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Specialized cells are uniquely suited to perform particular functions. ▶ Groups of similar cells t ...
INVERTEBRATES
... (a mouth but no anus). -No skeletal, ciculatory or respiratory systems. -The nervous system is a pair of anterior ganglia connected to longitudinal nerve chords. -Hermaphrodites. The y can fertilise themselves. -Parasites. ...
... (a mouth but no anus). -No skeletal, ciculatory or respiratory systems. -The nervous system is a pair of anterior ganglia connected to longitudinal nerve chords. -Hermaphrodites. The y can fertilise themselves. -Parasites. ...
Circulatory system
... compound eyes, several pairs of appendages modified for piercing and sucking • Thorax has three pairs of walking legs • Abdomen usually the largest of the three sections on the body ...
... compound eyes, several pairs of appendages modified for piercing and sucking • Thorax has three pairs of walking legs • Abdomen usually the largest of the three sections on the body ...
Animals may be characterized by the presence of a coelom
... Diploblasts contain two germ layers (inner endoderm and outer ectoderm), while triploblasts contain three germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm). The endoderm becomes the digestive and respiratory tracts; the ectoderm becomes the outer epithelial covering of the body surface and the central ...
... Diploblasts contain two germ layers (inner endoderm and outer ectoderm), while triploblasts contain three germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm). The endoderm becomes the digestive and respiratory tracts; the ectoderm becomes the outer epithelial covering of the body surface and the central ...
Chapter 32 Notes
... higher, from 10 to 20 million to as many as 100 to 200 million. Concept 32.1 Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers There are exceptions to nearly every criterion for distinguishing an animal from other life forms. However, five criter ...
... higher, from 10 to 20 million to as many as 100 to 200 million. Concept 32.1 Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers There are exceptions to nearly every criterion for distinguishing an animal from other life forms. However, five criter ...
Anatomy of the shoulder and its arthroscopic considerations
... Soft spot bordered anteriorly by the posterior margin of the clavicle, lateral by the medial border of the acromion, posteriorly by the scapular spine Passage through the trapezius and the muscle belly of the ...
... Soft spot bordered anteriorly by the posterior margin of the clavicle, lateral by the medial border of the acromion, posteriorly by the scapular spine Passage through the trapezius and the muscle belly of the ...
Porifera
... • proteinaceous matrix that contains skeletal material and certain cell types • equivalent to the connective tissue in other organisms • made of collagen and spongin ...
... • proteinaceous matrix that contains skeletal material and certain cell types • equivalent to the connective tissue in other organisms • made of collagen and spongin ...
DISSECTION OF AN EARTHWORM
... prostronium. Use a hand lens to see the parts, then do a proper biological diagram of the anterior end of the worm. Does the mouth run vertically or horizontally?7 8. Examine the posterior end of the worm. Use a hand lens to see the parts, then do a proper biological diagram of the posterior end of ...
... prostronium. Use a hand lens to see the parts, then do a proper biological diagram of the anterior end of the worm. Does the mouth run vertically or horizontally?7 8. Examine the posterior end of the worm. Use a hand lens to see the parts, then do a proper biological diagram of the posterior end of ...
Kingdom Animalia – Cnidaria corals, sea anemones, jelly fish, box
... Have tissue level of organization, with three tissue layers (triploblastic – with endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm) Have bilateral symmetry Have only one opening to the body cavity / digestive cavity Have cephalization (and at least at some stage of their lives, so will all the animals that we’ll di ...
... Have tissue level of organization, with three tissue layers (triploblastic – with endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm) Have bilateral symmetry Have only one opening to the body cavity / digestive cavity Have cephalization (and at least at some stage of their lives, so will all the animals that we’ll di ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.