Anatomy & Physiology
... Kidneys, ureters, bladder, & urethra. Functions in filtering nitrogenous waste from the blood (creates urea), maintains body’s water and salt balance, regulates body’s blood pressure, and acidbase balance. ...
... Kidneys, ureters, bladder, & urethra. Functions in filtering nitrogenous waste from the blood (creates urea), maintains body’s water and salt balance, regulates body’s blood pressure, and acidbase balance. ...
Human Body Poster Project
... Nose, trachea, lungs, alveoli (detail showing gas exchange), and diaphragm Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, and the liver Brain (with its lobes labeled and defined), spinal cord (only needs to go through the neck), sensory and motor neuron (to some part of the body), detail the ...
... Nose, trachea, lungs, alveoli (detail showing gas exchange), and diaphragm Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, and the liver Brain (with its lobes labeled and defined), spinal cord (only needs to go through the neck), sensory and motor neuron (to some part of the body), detail the ...
2014 Human Body Systems Project
... Nose, trachea, lungs, alveoli (detail showing gas exchange), and diaphragm Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, and the liver Brain (with its lobes labeled and defined), spinal cord (only needs to go through the neck), sensory and motor neuron (to some part of the body), detail the ...
... Nose, trachea, lungs, alveoli (detail showing gas exchange), and diaphragm Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, and the liver Brain (with its lobes labeled and defined), spinal cord (only needs to go through the neck), sensory and motor neuron (to some part of the body), detail the ...
Ch. 21 The Shoulder
... Shoulder Girdle Anatomy • Scapula • Flat bone on posterior/dorsal aspect of the body • Moves on the thoracic cage • “Socket” glenoid cavity • Acromion process • Upper/lateral aspect of scapula hard spot on top of shoulder ...
... Shoulder Girdle Anatomy • Scapula • Flat bone on posterior/dorsal aspect of the body • Moves on the thoracic cage • “Socket” glenoid cavity • Acromion process • Upper/lateral aspect of scapula hard spot on top of shoulder ...
Musculoskeletal System
... œefine key terms • U œnderstand the most common pathologies affecting these organs • U œnderstand orthopedic surgeries and how they relate to pathologies • R œecognize common eponyms and acronyms • Iœ dentify when other sections of CPT® or ICD-9-CM should be accessed • œ Know when HCPCS Level II cod ...
... œefine key terms • U œnderstand the most common pathologies affecting these organs • U œnderstand orthopedic surgeries and how they relate to pathologies • R œecognize common eponyms and acronyms • Iœ dentify when other sections of CPT® or ICD-9-CM should be accessed • œ Know when HCPCS Level II cod ...
Trigeminal (Gasserian) Ganglion Block
... • Anaesthesia of surgery of the face • Patients with severe underlying cardiopulmonary disease who require more than minor facial surgery • 1 to 3 mL of local anesthetic ...
... • Anaesthesia of surgery of the face • Patients with severe underlying cardiopulmonary disease who require more than minor facial surgery • 1 to 3 mL of local anesthetic ...
Simple Animals - Veritas Science
... elsewhere to grow 4)Gemmules resemble the polyp form of a Cnidarian 5) All sponges are male and female ...
... elsewhere to grow 4)Gemmules resemble the polyp form of a Cnidarian 5) All sponges are male and female ...
Chapter 32
... • There are about 11,000 species living today. • The cnidarian body plan combines a low metabolic rate with the ability to capture large prey, allowing cnidarians to survive in environments where prey is ...
... • There are about 11,000 species living today. • The cnidarian body plan combines a low metabolic rate with the ability to capture large prey, allowing cnidarians to survive in environments where prey is ...
BIO 110 Test 3 Review (All starred (*) questions are related to
... 10. What is Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)? 11. How do these three mechanisms help to maintain a stable GFR: a. Renal autoregulation b. Sympathetic nervous system stimulation c. Renin-angiotensin mechanism 12. What events happen in the proximal convoluted tubule? 13. What events happen in the nep ...
... 10. What is Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)? 11. How do these three mechanisms help to maintain a stable GFR: a. Renal autoregulation b. Sympathetic nervous system stimulation c. Renin-angiotensin mechanism 12. What events happen in the proximal convoluted tubule? 13. What events happen in the nep ...
Appendicular Skeleton
... The evolutionary history of the pelvic girdle is far simpler (fortunately!) than that of the pectoral girdle. Remember the pelvic girdle to attached to the vertebral column by the sacral ribs. This connection is considered an adaptation for transmitting the forces generated by the muscles of the hin ...
... The evolutionary history of the pelvic girdle is far simpler (fortunately!) than that of the pectoral girdle. Remember the pelvic girdle to attached to the vertebral column by the sacral ribs. This connection is considered an adaptation for transmitting the forces generated by the muscles of the hin ...
Animals with Bilateral Symmetry
... Most are microscopic Elongate body is protected by a cuticle that must be molted periodically (kinda like arthropod exoskeleton…) ...
... Most are microscopic Elongate body is protected by a cuticle that must be molted periodically (kinda like arthropod exoskeleton…) ...
Biology Chapter 38 notes Section 38
... Scorpions have large, pincerlike pedipalps, which they hold in a forward position. They also have a large stinger on the last segment of the abdomen, which is curled over the body. Only a few species of scorpions have venom that can be fatal to humans. Mites and Ticks Unlike spiders and scorpions, m ...
... Scorpions have large, pincerlike pedipalps, which they hold in a forward position. They also have a large stinger on the last segment of the abdomen, which is curled over the body. Only a few species of scorpions have venom that can be fatal to humans. Mites and Ticks Unlike spiders and scorpions, m ...
tissues - Perkins Science
... • Functions of Connective Tissue • Establishing the structural framework of the body • Transporting fluid and dissolved materials ...
... • Functions of Connective Tissue • Establishing the structural framework of the body • Transporting fluid and dissolved materials ...
46 Skeletal Muscular System
... 2) These cells, called neurons, are specialized to send and receive messages from muscles, glands, and other neurons throughout the body 3) Nervous tissue makes up your brain, spinal cord, and nerves 4) Nervous tissue provides sensation of the internal and external environment, and it integrates sen ...
... 2) These cells, called neurons, are specialized to send and receive messages from muscles, glands, and other neurons throughout the body 3) Nervous tissue makes up your brain, spinal cord, and nerves 4) Nervous tissue provides sensation of the internal and external environment, and it integrates sen ...
Human Development
... Mesoderm will form skeletal, muscular, urinary, reproductive, circulatory systems, as well as muscle and connective tissue layers of digestive and respiratory systems . Ectoderm will form skin and nervous system ...
... Mesoderm will form skeletal, muscular, urinary, reproductive, circulatory systems, as well as muscle and connective tissue layers of digestive and respiratory systems . Ectoderm will form skin and nervous system ...
Article in PDF
... contour was presenting feature noted in affected persons. Rotation and retraction of the scapula were limited, but they could carry out normal activities. Short costocoracoid ligament can be sometimes ossified so surgical treatment consists of excision of the ligament. The abnormality results in a p ...
... contour was presenting feature noted in affected persons. Rotation and retraction of the scapula were limited, but they could carry out normal activities. Short costocoracoid ligament can be sometimes ossified so surgical treatment consists of excision of the ligament. The abnormality results in a p ...
CH 16 YOUR BODY SYSTEMS
... The skeletal system provides a ___________, stable __________ capable of __________. The skeletal system __________ and __________ delicate internal ______________. Bones store important ____________ such as ___________ and ________________. Bones _____________ the body’s _________ __________. Red b ...
... The skeletal system provides a ___________, stable __________ capable of __________. The skeletal system __________ and __________ delicate internal ______________. Bones store important ____________ such as ___________ and ________________. Bones _____________ the body’s _________ __________. Red b ...
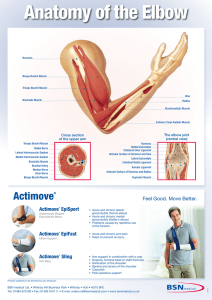
Actimove® - BSN medical India
... Brachialis Muscle Brachial Artery Median Nerve Ulnar Nerve Biceps Brachii Muscle ...
... Brachialis Muscle Brachial Artery Median Nerve Ulnar Nerve Biceps Brachii Muscle ...
Phylum Mollusca
... Mantle cavity contains many gills on both side of the animal Ctenidia = gills which are found in most Mollusca, consisting of a series of flat thin walled leaflets. Cilia on gills creates current for water to flow Nervous system Is a simple ladder system, which lacks ganglia, statocysts, tentacles, ...
... Mantle cavity contains many gills on both side of the animal Ctenidia = gills which are found in most Mollusca, consisting of a series of flat thin walled leaflets. Cilia on gills creates current for water to flow Nervous system Is a simple ladder system, which lacks ganglia, statocysts, tentacles, ...
Porifera
... • Cartilaginous fishes; well developed jaws and paired fins; continual water flow over gills (gas exchange); lateral line system (water pressure changes) • Closed circulatory system, gills • Life cycles: • Oviparous- eggs hatch outside mother’s body, frogs, fishes • Ovoviviparous- retain fertilized ...
... • Cartilaginous fishes; well developed jaws and paired fins; continual water flow over gills (gas exchange); lateral line system (water pressure changes) • Closed circulatory system, gills • Life cycles: • Oviparous- eggs hatch outside mother’s body, frogs, fishes • Ovoviviparous- retain fertilized ...
Section 25.1 Summary – pages 673
... compared to a sack within a sack. • These sacks are cell layers organized into tissues with distinct functions. ...
... compared to a sack within a sack. • These sacks are cell layers organized into tissues with distinct functions. ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.