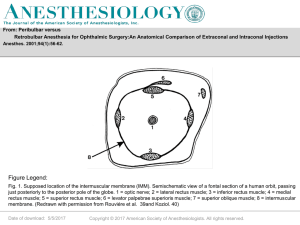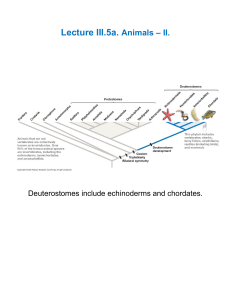
Lecture III.5a. Animals II.
... the mouth and exiting through gill slits in the pharyngeal wall. Locomotion is via contraction of dorsal and ventral (epaxial and hypaxial) trunk muscles that run segmentally the length of the animal. The muscles are supported by ribs (dorsal and ventral) that attach to the vertebral centra, which s ...
... the mouth and exiting through gill slits in the pharyngeal wall. Locomotion is via contraction of dorsal and ventral (epaxial and hypaxial) trunk muscles that run segmentally the length of the animal. The muscles are supported by ribs (dorsal and ventral) that attach to the vertebral centra, which s ...
Chapter 14 Part 1
... Hard blow to the back of the head may be fatal Cranial nerve malfunctions on same side as injury; ...
... Hard blow to the back of the head may be fatal Cranial nerve malfunctions on same side as injury; ...
Human Body Systems and Disease 7
... Though all cells perform the processes that keep humans alive, they also have specialized functions as well. Examples may be nerve cells (neurons), blood cells, and bone cells. Tissues A group of specialized cells that work together to perform the same function. There are four basic types of t ...
... Though all cells perform the processes that keep humans alive, they also have specialized functions as well. Examples may be nerve cells (neurons), blood cells, and bone cells. Tissues A group of specialized cells that work together to perform the same function. There are four basic types of t ...
System+Coloring+Book
... esophagus - the long tube between the mouth and the stomach. It uses rhythmic muscle movements (called peristalsis) to force food from the throat into the stomach. gall bladder - a small, sac-like organ located by the duodenum. It stores and releases bile (a digestive chemical which is produced in t ...
... esophagus - the long tube between the mouth and the stomach. It uses rhythmic muscle movements (called peristalsis) to force food from the throat into the stomach. gall bladder - a small, sac-like organ located by the duodenum. It stores and releases bile (a digestive chemical which is produced in t ...
Human Body Systems Project
... o Diagram that includes the major parts - mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas, and large intestine - and list the function(s) of each. o Describe the path food travels throughout the digestive system. o Describe physical and chemical digestion (digestive enzymes). o Describe ...
... o Diagram that includes the major parts - mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas, and large intestine - and list the function(s) of each. o Describe the path food travels throughout the digestive system. o Describe physical and chemical digestion (digestive enzymes). o Describe ...
Grasshopper Dissection Neil 2012
... 3. Beginning at the tip of the abdomen, make an incision (lengthwise) with scissors in the body covering slightly to the left of the middorsal line and along the entire length of the grasshopper. Make a similar cut on the ventral side, as well as up the front of the head. Keep the inner scissors poi ...
... 3. Beginning at the tip of the abdomen, make an incision (lengthwise) with scissors in the body covering slightly to the left of the middorsal line and along the entire length of the grasshopper. Make a similar cut on the ventral side, as well as up the front of the head. Keep the inner scissors poi ...
Body System Interactions
... A. digestive and endocrine B. reproductive and nervous C. muscular and skeletal D. excretoryand respiratory 14.) When a person breathes, the lungs absdrb oxygen, which is used by cells to carry out the process of A. respiration ...
... A. digestive and endocrine B. reproductive and nervous C. muscular and skeletal D. excretoryand respiratory 14.) When a person breathes, the lungs absdrb oxygen, which is used by cells to carry out the process of A. respiration ...
Week 1: Anatomical Terminology and Bones
... Many terms provide information about a structure’s shape, size, location or function or about the resemblance of one structure to another (e.g. deltoid muscle covering the shoulders is triangular like the symbol ‘delta’ and suffix ‘oid’ means ‘like’) Anatomical Position o The anatomical position ref ...
... Many terms provide information about a structure’s shape, size, location or function or about the resemblance of one structure to another (e.g. deltoid muscle covering the shoulders is triangular like the symbol ‘delta’ and suffix ‘oid’ means ‘like’) Anatomical Position o The anatomical position ref ...
BIOL 2401 Unit and Final Exam Study Guides
... 23. Compare somatic cell division and meiosis. 24. Do different types of stratified epithelium have blood vessels? How do they receive their nutrients? 25. What type of tissue displays a basemen membrane? 26. When an epithelium has a single layer of flat cells it will be classified as… 27. If a ...
... 23. Compare somatic cell division and meiosis. 24. Do different types of stratified epithelium have blood vessels? How do they receive their nutrients? 25. What type of tissue displays a basemen membrane? 26. When an epithelium has a single layer of flat cells it will be classified as… 27. If a ...
Reading Guide Pages 100-104 Reptiles
... How many loops do most reptiles have in their circulatory system? Two loops ...
... How many loops do most reptiles have in their circulatory system? Two loops ...
ERP 10 - Haiku Learning
... (9) The lactic acid system Type of reaction — anaerobic coupled Fuel used — glycogen The reaction occurs — in the sarcoplasm Energy yield — 2 ATP • Specific stages in the system — glycogen is broken down into glucose and in the absence of oxygen forms pyruvic acid • By-product — lactic acid • The sy ...
... (9) The lactic acid system Type of reaction — anaerobic coupled Fuel used — glycogen The reaction occurs — in the sarcoplasm Energy yield — 2 ATP • Specific stages in the system — glycogen is broken down into glucose and in the absence of oxygen forms pyruvic acid • By-product — lactic acid • The sy ...
Weekly Schedule of Blood, Inflammation and Immunity
... Identify the importance of mesoderm in embryological basis of the diseases. Recognize the various components & types of Connective Tissue. Identify the congenital anomalies of cartilages. Correlate the types, structure and function of bones and the mechanism of bone modeling and remodeling with back ...
... Identify the importance of mesoderm in embryological basis of the diseases. Recognize the various components & types of Connective Tissue. Identify the congenital anomalies of cartilages. Correlate the types, structure and function of bones and the mechanism of bone modeling and remodeling with back ...
The Deuterostomes
... • Closed circulatory system, may maintain internal body temperature (endotherm) or depend on the environment ...
... • Closed circulatory system, may maintain internal body temperature (endotherm) or depend on the environment ...
I -i j::
... Maintaining a constant body temperature, no matter what the temperature of its surroundings, is a condition that needs to be balanced in many organisms. This ability is important to the organism's survival. These organisms have many different body structures and behaviors that help maintain a consta ...
... Maintaining a constant body temperature, no matter what the temperature of its surroundings, is a condition that needs to be balanced in many organisms. This ability is important to the organism's survival. These organisms have many different body structures and behaviors that help maintain a consta ...
biology - HCC Learning Web
... Coelomates with three main body parts (muscular foot, visceral mass, mantle); coelom reduced; most have hard shell made of calcium carbonate Coelomates with segmented body wall and internal organs (except digestive tract, which is unsegmented) ...
... Coelomates with three main body parts (muscular foot, visceral mass, mantle); coelom reduced; most have hard shell made of calcium carbonate Coelomates with segmented body wall and internal organs (except digestive tract, which is unsegmented) ...
Photosynthesis
... Classified according to type of collagen and elastic fibers found in the matrix Cartilage cells (chondrocytes), lie in small chambers (lacunae) in the matrix ...
... Classified according to type of collagen and elastic fibers found in the matrix Cartilage cells (chondrocytes), lie in small chambers (lacunae) in the matrix ...
Sensory Cranial Nerves
... The eyeball focuses light which stimulates the retina. These signals are transmitted via the optic nerve, chiasm and tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus. Nervous impulses then travel via the optic radiations to terminate in the primary visual (calcarine) cortex. ...
... The eyeball focuses light which stimulates the retina. These signals are transmitted via the optic nerve, chiasm and tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus. Nervous impulses then travel via the optic radiations to terminate in the primary visual (calcarine) cortex. ...
Document
... cylindrical in shape and tapered at both ends. Along the sides there are small bristle like structures called setae to help with forward movement through the soil. Its body is divided into many sections which enables each body segment to perform separate, specialized functions. For example, the area ...
... cylindrical in shape and tapered at both ends. Along the sides there are small bristle like structures called setae to help with forward movement through the soil. Its body is divided into many sections which enables each body segment to perform separate, specialized functions. For example, the area ...
HISTOLOGY
... line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. They perform a variety of functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, and diffusion. The cells in epithelial tissue are tightly packed together with very little intercellular matrix. Becaus ...
... line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. They perform a variety of functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, and diffusion. The cells in epithelial tissue are tightly packed together with very little intercellular matrix. Becaus ...
The Thoracic Cage
... Also known as the spinal column It consists of 26 bones It is strong, flexible series of bones that bends in the anterior, posterior, and lateral aspects it encloses and protects the spinal cord Supports the head and it is an attachment point for the ribs and muscles of the back Openings between the ...
... Also known as the spinal column It consists of 26 bones It is strong, flexible series of bones that bends in the anterior, posterior, and lateral aspects it encloses and protects the spinal cord Supports the head and it is an attachment point for the ribs and muscles of the back Openings between the ...
introduction to animal evolution outline objectives
... Highly differentiated body cells which are organized into tissues, organs and organ systems for such specialized functions as digestion, internal transport, gas exchange, movement, coordination, excretion, and reproduction. Nervous tissue (impulse conduction) and muscle tissue (movement) are unique ...
... Highly differentiated body cells which are organized into tissues, organs and organ systems for such specialized functions as digestion, internal transport, gas exchange, movement, coordination, excretion, and reproduction. Nervous tissue (impulse conduction) and muscle tissue (movement) are unique ...
Biol 2402 - Northeast Texas Community College
... - arteries transport blood away from the heart; veins return blood to the heart; capillaries allow exchange between blood and tissue cells - the hepatic portal system function to filter all of the blood from digestive organs through the liver - the circulatory system of the fetus has specialized str ...
... - arteries transport blood away from the heart; veins return blood to the heart; capillaries allow exchange between blood and tissue cells - the hepatic portal system function to filter all of the blood from digestive organs through the liver - the circulatory system of the fetus has specialized str ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.