Lab 6 – Phylum Arthropoda
... 2) The name of the phylum reflects another diagnostic character: jointed feet (arthro, joint; poda, foot). The variety of functions performed by arthropod appendages is noteworthy, and includes walking, swimming, prey capture and handling, copulation, and sensory perception. No other invertebrate gr ...
... 2) The name of the phylum reflects another diagnostic character: jointed feet (arthro, joint; poda, foot). The variety of functions performed by arthropod appendages is noteworthy, and includes walking, swimming, prey capture and handling, copulation, and sensory perception. No other invertebrate gr ...
LABORATORY EXERCISE 6 PHYLUM ARTHROPODA
... arthropod originate? How does this compare with the mechanism in a mollusc? Enter your data on the master sheet which will be in lab. This sheet, or the information on this sheet, will be made available to the class. Before next week, use the Microsoft Excel (see separate instruction sheet on use of ...
... arthropod originate? How does this compare with the mechanism in a mollusc? Enter your data on the master sheet which will be in lab. This sheet, or the information on this sheet, will be made available to the class. Before next week, use the Microsoft Excel (see separate instruction sheet on use of ...
Chapter 18 - San Diego Mesa College
... the radiation of diversity in the kingdom Animalia proceeded based on the evolution of a number of distinct "hallmark" features or characteristics ...
... the radiation of diversity in the kingdom Animalia proceeded based on the evolution of a number of distinct "hallmark" features or characteristics ...
Overview
... tissue capsule. A simple squamous mesothelium rests on this capsule. 4. Pleural mesothelial cells have sparse apical microvilli, secrete watery lubricants into the pleural cavity, and rest on a thin basement membrane. 5. The mesothelium defines the two pleural cavity boundaries and allows the lungs ...
... tissue capsule. A simple squamous mesothelium rests on this capsule. 4. Pleural mesothelial cells have sparse apical microvilli, secrete watery lubricants into the pleural cavity, and rest on a thin basement membrane. 5. The mesothelium defines the two pleural cavity boundaries and allows the lungs ...
MBBS first Prof. Syllabus, uploaded on 2014-05-17
... Intercostal vessels and nerves, Cavity of thorax & inlet (upper opening), Lungs (External features), Trachea, bronchial tree and bronchopulmonary segments, Superior mediastinum, Pericardial sinuses, Surface features and surface Anatomy of Heart, Vessels of heart, Ventricular chambers, Posterior medi ...
... Intercostal vessels and nerves, Cavity of thorax & inlet (upper opening), Lungs (External features), Trachea, bronchial tree and bronchopulmonary segments, Superior mediastinum, Pericardial sinuses, Surface features and surface Anatomy of Heart, Vessels of heart, Ventricular chambers, Posterior medi ...
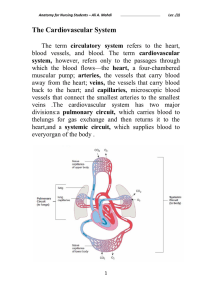
The Cardiovascular System
... constitutes most of the anterioraspect of the heart, while the left ventricle forms theapex and inferoposterior aspect. The atria (sing. Atrium) exhibit thin flaccid walls correspondingto their light workload—all they do is pump blood into theventricles immediately below. They are separated from eac ...
... constitutes most of the anterioraspect of the heart, while the left ventricle forms theapex and inferoposterior aspect. The atria (sing. Atrium) exhibit thin flaccid walls correspondingto their light workload—all they do is pump blood into theventricles immediately below. They are separated from eac ...
Lab #5: Animal Digestion
... As you may recall from our study of animal diversity, the evolution of digestive structures and systems played a big part in the changes we saw in various animal bodies. Briefly, we began our look at the animal kingdom by examining the animals with body cavities that took on numerous roles for the o ...
... As you may recall from our study of animal diversity, the evolution of digestive structures and systems played a big part in the changes we saw in various animal bodies. Briefly, we began our look at the animal kingdom by examining the animals with body cavities that took on numerous roles for the o ...
Diversity of Vertebrate Animals
... Some fish evolved adaptations minimally adequate for life on dry land while retaining a need to reproduce in water. These became amphibians: “Amphi” means “pertaining to opposite ends”, in this case water and land. Many amphibians reproduce in water, emerging from jelly-coated eggs as aquatic larvae ...
... Some fish evolved adaptations minimally adequate for life on dry land while retaining a need to reproduce in water. These became amphibians: “Amphi” means “pertaining to opposite ends”, in this case water and land. Many amphibians reproduce in water, emerging from jelly-coated eggs as aquatic larvae ...
The Animal Kingdom
... – Hydrostatic skeletons: water or another fluid provides pressure pushing out from the inside of the animal to provide support (like a water balloon) ...
... – Hydrostatic skeletons: water or another fluid provides pressure pushing out from the inside of the animal to provide support (like a water balloon) ...
The Triploblastic Aceolomate- Phylum Platyhelminthes Chapter 10
... • Dorsal= back side • Ventral= belly side ...
... • Dorsal= back side • Ventral= belly side ...
CH 27-1 FOLDABLE CONTENT FOR FOLDABLES
... about more rapidly than a radially symmetrical body. Worms can move forward in a single direction rather than remaining stationary or drifting in currents. ALSO, the mouth, sense organs & brain (if there is one!) are usually located at the anterior end, or head of the body. This allows the worm to l ...
... about more rapidly than a radially symmetrical body. Worms can move forward in a single direction rather than remaining stationary or drifting in currents. ALSO, the mouth, sense organs & brain (if there is one!) are usually located at the anterior end, or head of the body. This allows the worm to l ...
Nerve supply of the human vastus medialis muscle
... branch, supplies the upper lateral portion of the muscle. The other part, a medial branch, supplies the middle and lower portion of the muscle. There is a distalward increase in the numbers of nerve fibres supplying the muscle, with the lowermost muscle fibres receiving the richest nerve supply. The ...
... branch, supplies the upper lateral portion of the muscle. The other part, a medial branch, supplies the middle and lower portion of the muscle. There is a distalward increase in the numbers of nerve fibres supplying the muscle, with the lowermost muscle fibres receiving the richest nerve supply. The ...
Phylum Cnidaria
... 2. I can describe the life cycle of a cnidarian. 3. I can differentiate between the different classes of ...
... 2. I can describe the life cycle of a cnidarian. 3. I can differentiate between the different classes of ...
Tissues
... • Groups of cells with a common function • Four primary tissues • Epithelia • Connective tissues ...
... • Groups of cells with a common function • Four primary tissues • Epithelia • Connective tissues ...
Emergence of Arthropods
... • Sacculus - Actively remove and secrete material from blood into excretory lumen • metabolic waste removal and water and ion balance • Thin areas of cuticle – Gill surfaces ...
... • Sacculus - Actively remove and secrete material from blood into excretory lumen • metabolic waste removal and water and ion balance • Thin areas of cuticle – Gill surfaces ...
Directional Terms cont
... farther from the trunk or farther from another specified point of reference than another part (fingers are distal to the wrist). • Superficial: means situated near the surface. Peripheral also means outward or near the surface. • Deep: is used to describe parts that are more internal. ...
... farther from the trunk or farther from another specified point of reference than another part (fingers are distal to the wrist). • Superficial: means situated near the surface. Peripheral also means outward or near the surface. • Deep: is used to describe parts that are more internal. ...
Unit 2 respiratory system 3.58MB 2017-03-29 17
... 6. What is the role of chemoreceptors during exercise? 7. What are the Aortic Arch and Carotid Arteries and what is their role when controlling breathing? ...
... 6. What is the role of chemoreceptors during exercise? 7. What are the Aortic Arch and Carotid Arteries and what is their role when controlling breathing? ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... C. The growth of toe knuckle hair D. The combining of simple sugars to form a disaccharide or starch. 22. These molecules promote chemical reactions within cells. They do this by lowering the amount of activation energy required for the reaction to occur. A. Enzyme B. Protein synthesis molecules C. ...
... C. The growth of toe knuckle hair D. The combining of simple sugars to form a disaccharide or starch. 22. These molecules promote chemical reactions within cells. They do this by lowering the amount of activation energy required for the reaction to occur. A. Enzyme B. Protein synthesis molecules C. ...
Major Divisions of Life
... such as lakes, ponds, and meadows, while others can be found in stone walls and roofs. ...
... such as lakes, ponds, and meadows, while others can be found in stone walls and roofs. ...
Slide 1 - OCCC.edu
... Connective tissues function to “connect” tissues to other tissues or one structure to another ...
... Connective tissues function to “connect” tissues to other tissues or one structure to another ...
LAB ONE: DIFFUSION AND OSSMOSIS
... The avian skeleton has become dramatically modified to facilitate flight. In most bird species, bones have become pneumatic, that is, they have cavities filled with air. Bones of the limbs have become elongate, and those of the tail shortened. Pelvic bones, as well as finger bones, are fused to prov ...
... The avian skeleton has become dramatically modified to facilitate flight. In most bird species, bones have become pneumatic, that is, they have cavities filled with air. Bones of the limbs have become elongate, and those of the tail shortened. Pelvic bones, as well as finger bones, are fused to prov ...
supporting connective tissue
... SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE - found in the walls of blood vessels, around hollow organs (urinary bladder), in layers around respiratory, circulatory, digestive, and reproductive tracts - cells are small and slender, tapering to a point at each end; each has one nucleus - actin and myosin filaments are scat ...
... SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE - found in the walls of blood vessels, around hollow organs (urinary bladder), in layers around respiratory, circulatory, digestive, and reproductive tracts - cells are small and slender, tapering to a point at each end; each has one nucleus - actin and myosin filaments are scat ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.