Chapter 19-Aquatic Mandibulates
... Tagmata are usually head, thorax, and abdomen—not homologous across all taxa. Caridoid facies arrangement of tagmata is the ancestral plan. Dorsal covering is the carapace; May cover most of body or just the cephalothorax. ...
... Tagmata are usually head, thorax, and abdomen—not homologous across all taxa. Caridoid facies arrangement of tagmata is the ancestral plan. Dorsal covering is the carapace; May cover most of body or just the cephalothorax. ...
Chapter 19
... maxillae on the head. The body may be divided into a head and trunk, or into a head, thorax, and abdomen. In most crustaceans, one or more thoracic segments are fused with the cephalothorax. Uniramians are nearly all terrestrial; Crustacea are mostly marine with a few freshwater. ...
... maxillae on the head. The body may be divided into a head and trunk, or into a head, thorax, and abdomen. In most crustaceans, one or more thoracic segments are fused with the cephalothorax. Uniramians are nearly all terrestrial; Crustacea are mostly marine with a few freshwater. ...
Anatomical Terms Worksheet
... Fill in the missing words to make the passage correct using words from the word bank. reference, side, stand, body, arms, hands, anatomical, forward All anatomical terms have a ________________ point which is called the _______________ position. This is a ________________ position where you ________ ...
... Fill in the missing words to make the passage correct using words from the word bank. reference, side, stand, body, arms, hands, anatomical, forward All anatomical terms have a ________________ point which is called the _______________ position. This is a ________________ position where you ________ ...
Ch. 10 Neurology
... -A reflex is a rapid, involuntary muscle reaction that is controlled by the spinal cord. -The spinal cord reacts immediately to certain types of sensory information, such as sudden pain. ...
... -A reflex is a rapid, involuntary muscle reaction that is controlled by the spinal cord. -The spinal cord reacts immediately to certain types of sensory information, such as sudden pain. ...
BY 124 Mock Exam 2
... 52) Which of the following could be considered the most recent common ancestor of living tetrapods? A) an armored, jawed placoderm with two pairs of appendages B) a salamander that had legs supported by a bony skeleton but moved with the side-to-side bending typical of fishes C) an early ray-finned ...
... 52) Which of the following could be considered the most recent common ancestor of living tetrapods? A) an armored, jawed placoderm with two pairs of appendages B) a salamander that had legs supported by a bony skeleton but moved with the side-to-side bending typical of fishes C) an early ray-finned ...
Body Systems Quiz 2: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
... those nutrients to the cells of the body. C. The respiratory system sends signals to parts of your body and the circulatory system carries those ...
... those nutrients to the cells of the body. C. The respiratory system sends signals to parts of your body and the circulatory system carries those ...
anatomy - Crossword Labs
... 5. There are a lot of these in the human body. 8. The scientific name for calf muscle. 9. The bone in your knee. 10. The muscle behind your knee. 11. These are the bones in your fingers. 13. The muscle posterior to the humerus. 14. What is the biggest bone in your body. 15. The muscles in your thigh ...
... 5. There are a lot of these in the human body. 8. The scientific name for calf muscle. 9. The bone in your knee. 10. The muscle behind your knee. 11. These are the bones in your fingers. 13. The muscle posterior to the humerus. 14. What is the biggest bone in your body. 15. The muscles in your thigh ...
Multiple Choice Questions – Answers
... D Deoxygenated blood [True] The correct answer is D. All veins carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart with the exception of the pulmonary vein which carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. 5. The heart is made up of which type of muscle: A Skeletal muscle B Smooth muscle C ...
... D Deoxygenated blood [True] The correct answer is D. All veins carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart with the exception of the pulmonary vein which carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. 5. The heart is made up of which type of muscle: A Skeletal muscle B Smooth muscle C ...
apLP 8-12 Sept - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... 1. TSW will recite the words associated with exterior areas of the body.. 2. TSW will be able to describe the areas of the body in both anatomical and ...
... 1. TSW will recite the words associated with exterior areas of the body.. 2. TSW will be able to describe the areas of the body in both anatomical and ...
Anatomy of the Female Genital Tract & Pelvic Floor
... – Wall of uterus consists of 3 layers: • Perimetrium/serosa - outer serous coat, peritoneum supported by thin layer of connective tissue • myometrium - 12-15 mm smooth muscle, main branches of blood vessels and nerves of uterus are in this layer • endometrium - inner mucous coat ...
... – Wall of uterus consists of 3 layers: • Perimetrium/serosa - outer serous coat, peritoneum supported by thin layer of connective tissue • myometrium - 12-15 mm smooth muscle, main branches of blood vessels and nerves of uterus are in this layer • endometrium - inner mucous coat ...
K CHAPTER 2: BODY TISSUES AND MEMBRANES At the end of
... which protect the underlying structures from abrasion) 2. Acting as barriers( the skin acts as a barrier to water and reduce water loss from the body; barrier to many toxic molecules and microorganisms) 3. Permitting the passage of substances (Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the air ...
... which protect the underlying structures from abrasion) 2. Acting as barriers( the skin acts as a barrier to water and reduce water loss from the body; barrier to many toxic molecules and microorganisms) 3. Permitting the passage of substances (Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the air ...
Human Body Organization
... Connective tissues are dispersed cells in an extracellular matrix that they secrete. The matrix contains protein fibers: • collagen - strong and resistant to stretch, supports skin and connections between muscles and bones; • elastin - can be stretched and then recoils; found in tissues that stretch ...
... Connective tissues are dispersed cells in an extracellular matrix that they secrete. The matrix contains protein fibers: • collagen - strong and resistant to stretch, supports skin and connections between muscles and bones; • elastin - can be stretched and then recoils; found in tissues that stretch ...
Study Questions 1
... How is it possible to have a low flow rate over capillary beds, given that each capillary is much narrower than the arteries and arterioles that feed them? ...
... How is it possible to have a low flow rate over capillary beds, given that each capillary is much narrower than the arteries and arterioles that feed them? ...
File
... Like flatworms annelids have a mesoderm with muscle, a CNS, and an Excretory system. More advanced Complete digestive system has: 1. mouth at one end, 2. a long tube with specialized parts in the ...
... Like flatworms annelids have a mesoderm with muscle, a CNS, and an Excretory system. More advanced Complete digestive system has: 1. mouth at one end, 2. a long tube with specialized parts in the ...
Characteristics of Kingdom Animalia
... Tube within a tube Cephalization (with few exceptions) 4-part body plan 1. Notochord – support and attachment (runs through trunk). It is a flexible rod-shaped body found in embryos of all chordates. It is composed of cells derived from the mesoderm and defines the primitive axis of the embryo. In s ...
... Tube within a tube Cephalization (with few exceptions) 4-part body plan 1. Notochord – support and attachment (runs through trunk). It is a flexible rod-shaped body found in embryos of all chordates. It is composed of cells derived from the mesoderm and defines the primitive axis of the embryo. In s ...
Chapter 5 Review File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 1. Use of the _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ ensures that health-care providers will use the same starting point when describing the body and will understand one another’s references. 2. A(n) _________________________ is the kind of flat surface that wo ...
... 1. Use of the _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ ensures that health-care providers will use the same starting point when describing the body and will understand one another’s references. 2. A(n) _________________________ is the kind of flat surface that wo ...
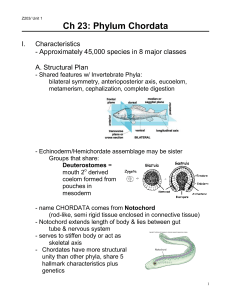
Ch 23: Phylum Chordata
... coelom formed from pouches in mesoderm name CHORDATA comes from Notochord (rodlike, semi rigid tissue enclosed in connective tissue) Notochord extends length of body & lies between gut tube & nervous system serves to stiffen body or act as skeletal axis Chordates have more structu ...
... coelom formed from pouches in mesoderm name CHORDATA comes from Notochord (rodlike, semi rigid tissue enclosed in connective tissue) Notochord extends length of body & lies between gut tube & nervous system serves to stiffen body or act as skeletal axis Chordates have more structu ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Social Circle City Schools
... - phylum Cnidaria and Ctenophora - has a top and a bottom - adapted for sessile (not motile) lifestyle - develop two tissue layers: ectoderm (outer covering) and endoderm (digestive tube lining) ...
... - phylum Cnidaria and Ctenophora - has a top and a bottom - adapted for sessile (not motile) lifestyle - develop two tissue layers: ectoderm (outer covering) and endoderm (digestive tube lining) ...
Nervous tissue
... Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form & Function 1. How has exchange with the environment evolved? 2. Reminder…what is the hierarchy of biological organization? 3. What is a tissue & what are the 4 types? 4. What is metabolism? 5. What is homeostasis & how is it achieved? 6. What are the 2 ty ...
... Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form & Function 1. How has exchange with the environment evolved? 2. Reminder…what is the hierarchy of biological organization? 3. What is a tissue & what are the 4 types? 4. What is metabolism? 5. What is homeostasis & how is it achieved? 6. What are the 2 ty ...
chordates - papbiobellaire
... Endoskeleton for support, protection, muscle attachment Bone or cartilage replaces notochord Enlarged brain case (cranium) with spinal cord that is surrounded by bones (vertebrae) Definite body form- head, neck, trunk, tail Body covering- (skin, scales, feathers, hair) may be replaced by shedding or ...
... Endoskeleton for support, protection, muscle attachment Bone or cartilage replaces notochord Enlarged brain case (cranium) with spinal cord that is surrounded by bones (vertebrae) Definite body form- head, neck, trunk, tail Body covering- (skin, scales, feathers, hair) may be replaced by shedding or ...
Arthropoda
... In the exoskeleton of arthropods, there is a layer of waterproof wax. This feature was fundamental in allowing primitive arthropods from the sea to survive on dry land without losing excessive water to the environment. ...
... In the exoskeleton of arthropods, there is a layer of waterproof wax. This feature was fundamental in allowing primitive arthropods from the sea to survive on dry land without losing excessive water to the environment. ...
Name: Date: Period:____ Final Review: Study Guide # 3 TOPICS
... Cartilaginous – Sharks & Rays Bony – 95% of fish such as salmon, goldfish, trout, bass, tuna, etc. Frogs Toads Salamanders ...
... Cartilaginous – Sharks & Rays Bony – 95% of fish such as salmon, goldfish, trout, bass, tuna, etc. Frogs Toads Salamanders ...
Bi 212, Lab 1
... epidermis derived from ectoderm b. circular muscles derived from mesoderm c. longitudinal muscles derived from mesoderm d. coelom (a type of body cavity) e. muscle layer on intestine side of coelom (probably both circular and longitudinal, but difficult to tell in the cross sections) derived from me ...
... epidermis derived from ectoderm b. circular muscles derived from mesoderm c. longitudinal muscles derived from mesoderm d. coelom (a type of body cavity) e. muscle layer on intestine side of coelom (probably both circular and longitudinal, but difficult to tell in the cross sections) derived from me ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.