invertebrates_th_grade
... The cuticle protects the earthworm from harmful parasites and substances Cuticle must be thin and its epidermis kept moist for ...
... The cuticle protects the earthworm from harmful parasites and substances Cuticle must be thin and its epidermis kept moist for ...
Integumentary System: Cutting Dead Cells
... Page 8 of 10 As well as interacting with the body systems as explained above, the integumentary system also contributes to numerous physiological processes, especially those involved in the regulation of the body’s internal environment so as to maintain a stable condition. An example is provided by ...
... Page 8 of 10 As well as interacting with the body systems as explained above, the integumentary system also contributes to numerous physiological processes, especially those involved in the regulation of the body’s internal environment so as to maintain a stable condition. An example is provided by ...
Tissues - Dr. Wilson`s Site
... membranes is the basis for their excitation ◦ respond quickly to outside stimulus by means of changes in membrane potential ◦ nerves – changes result in rapid transmission of signals to other cells ◦ muscles – changes result in contraction, shortening of the cell ...
... membranes is the basis for their excitation ◦ respond quickly to outside stimulus by means of changes in membrane potential ◦ nerves – changes result in rapid transmission of signals to other cells ◦ muscles – changes result in contraction, shortening of the cell ...
Human Body Web Quest
... Include in your answer--Protection, storage, movement, and blood cell formation. 5a. How many bones are babies born with? 5b. How many bones do adults have? 5c. Why do babies have more bones than adults? ...
... Include in your answer--Protection, storage, movement, and blood cell formation. 5a. How many bones are babies born with? 5b. How many bones do adults have? 5c. Why do babies have more bones than adults? ...
File
... without assistance from other systems. For example, the circulatory system carries oxygen to the cells of the body and removes carbon dioxide. The respiratory system supplies oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the body. The respiratory system depends on the circulatory system to deliver oxygen t ...
... without assistance from other systems. For example, the circulatory system carries oxygen to the cells of the body and removes carbon dioxide. The respiratory system supplies oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the body. The respiratory system depends on the circulatory system to deliver oxygen t ...
worm vocab only - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... One of the external bristles on annelids ______________ Seta (Setae) A pair of nerve clusters that serve as a brain at the anterior end Cerebral ganglia of some invertebrates _________________ A thickened section around clitellum an earthworm’s body that ______________ produces mucous for reproduct ...
... One of the external bristles on annelids ______________ Seta (Setae) A pair of nerve clusters that serve as a brain at the anterior end Cerebral ganglia of some invertebrates _________________ A thickened section around clitellum an earthworm’s body that ______________ produces mucous for reproduct ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... chewing muscles] VII. Facial [sense of taste, facial expression] IX. Glossopharyngeal [sense of taste, swallowing] X. Vagus [sensory and motor to larynx, heart, lungs, digestive system] XI. Accessory [shoulder and head] XII. Hypoglossal [tongue] severe head injury often damages one or more cranial n ...
... chewing muscles] VII. Facial [sense of taste, facial expression] IX. Glossopharyngeal [sense of taste, swallowing] X. Vagus [sensory and motor to larynx, heart, lungs, digestive system] XI. Accessory [shoulder and head] XII. Hypoglossal [tongue] severe head injury often damages one or more cranial n ...
first 5 pages
... Insects and Their Relatives Insects and their relatives have been coexisting with man for thousands of years. Although many people may consider insects as undesirable pests, of the approximately 850,000 identified species (with an estimated one million different species in existence) it is generall ...
... Insects and Their Relatives Insects and their relatives have been coexisting with man for thousands of years. Although many people may consider insects as undesirable pests, of the approximately 850,000 identified species (with an estimated one million different species in existence) it is generall ...
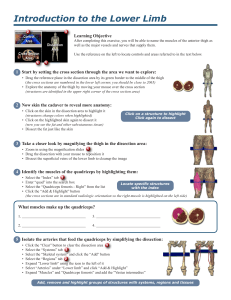
Introduction to the Lower Limb
... 6 Follow the lateral circumflex femoral artery to the muscles it supplies: • Locate the right “Lateral circumflex femoral artery” in the dissection (it is anterior to the superior portion of the vastus intermedius) • Right-click on the artery as it crosses in front of the vastus intermedius and ...
... 6 Follow the lateral circumflex femoral artery to the muscles it supplies: • Locate the right “Lateral circumflex femoral artery” in the dissection (it is anterior to the superior portion of the vastus intermedius) • Right-click on the artery as it crosses in front of the vastus intermedius and ...
VI. PHYLUM CHORDATA - Subphylum Vertebrata
... • Notochord secretes proteins that make up somites – differentiate into vertebrae, ribs, skeletal muscles of trunk • Pronounced cephalization • Closed circulatory system with chambered heart ...
... • Notochord secretes proteins that make up somites – differentiate into vertebrae, ribs, skeletal muscles of trunk • Pronounced cephalization • Closed circulatory system with chambered heart ...
The Body in the Old Testament
... a reference to 'the pouring out of the milky seminal fluid into the female organism.' ...
... a reference to 'the pouring out of the milky seminal fluid into the female organism.' ...
Invertebrate
... • The radiata are said to be diploblastic because they have two germ layers. – The ectoderm, covering the surface of the embryo, give rise to the outer covering and, in some phyla, the central nervous system. – The endoderm, the innermost layer, lines the developing digestive tube, or archenteron, a ...
... • The radiata are said to be diploblastic because they have two germ layers. – The ectoderm, covering the surface of the embryo, give rise to the outer covering and, in some phyla, the central nervous system. – The endoderm, the innermost layer, lines the developing digestive tube, or archenteron, a ...
9. phylum platyhelminthes
... suckers. Flukes are primarily endoparasitic with a few species ectoparasitic on the gills of fish. They lack cilia on their body covering (tegument). Trematodes have a fascinating and complex life cycle. Two or more hosts are involved. The final or primary host is a vertebrate and intermediate host ...
... suckers. Flukes are primarily endoparasitic with a few species ectoparasitic on the gills of fish. They lack cilia on their body covering (tegument). Trematodes have a fascinating and complex life cycle. Two or more hosts are involved. The final or primary host is a vertebrate and intermediate host ...
Evolution of Reptiles
... • Includes crocodiles, alligators, caimans, & gavials • Direct descendants of Archosaurs • Carnivorous (wait for prey to come near & then ...
... • Includes crocodiles, alligators, caimans, & gavials • Direct descendants of Archosaurs • Carnivorous (wait for prey to come near & then ...
MODULE 1 FROM CELL TO ORGANISM
... living things and what they are made up of. Organ systems work together to help organisms meet their basic needs and to survive. The digestive system helps organisms get energy from the food they eat. The circulatory system moves the nutrients that come from digested food, along with blood, to the d ...
... living things and what they are made up of. Organ systems work together to help organisms meet their basic needs and to survive. The digestive system helps organisms get energy from the food they eat. The circulatory system moves the nutrients that come from digested food, along with blood, to the d ...
Arthropods - Norman Public Schools
... metabolism for fast movements • 3 types of respiratory structures – gills (aquatic arthropods) – tracheal tubes (terrestrial arthropods) – book lungs (terrestrial arthropods) ...
... metabolism for fast movements • 3 types of respiratory structures – gills (aquatic arthropods) – tracheal tubes (terrestrial arthropods) – book lungs (terrestrial arthropods) ...
Rat LAB
... Mammals show CEPHALIZATION (the concentration of their sense organs in the anterior end). Locate the forward facing eyes (for depth perception). Notice there is NO NICTITATING MEMBRANE over the eye as in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Another characteristic of mammals is SPECIALIZED TEETH. All ani ...
... Mammals show CEPHALIZATION (the concentration of their sense organs in the anterior end). Locate the forward facing eyes (for depth perception). Notice there is NO NICTITATING MEMBRANE over the eye as in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Another characteristic of mammals is SPECIALIZED TEETH. All ani ...
BIODIVERSITY OF ANIMALS: INVERTEBRATES 06
... Tissue Layers At a certain stage of embryonic development the cells start to move into different layers and start to differentiate. In most of the organisms, but not all, all three layers start to appear ...
... Tissue Layers At a certain stage of embryonic development the cells start to move into different layers and start to differentiate. In most of the organisms, but not all, all three layers start to appear ...
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline A. gustation
... A. gustation - gustatory receptor cells are located in organs called taste buds 1. taste buds located in mucosa of mouth and pharynx most are on the sides of fungiform and circumvallate papillae ...
... A. gustation - gustatory receptor cells are located in organs called taste buds 1. taste buds located in mucosa of mouth and pharynx most are on the sides of fungiform and circumvallate papillae ...
1 - BrainMass
... with fluid, it allows fluid circulation, even in primitive animals that lack circulatory systems. ...
... with fluid, it allows fluid circulation, even in primitive animals that lack circulatory systems. ...
Nervous system
... Autonomic nervous system, has a chain of two motor neurons The first neuron (in brain or spinal cord),it’s axon (preganglionic axon) leave the CNS to synapse with the second motor neuron in a ganglion outside the CNS. The axon of this neuron, (the postganglionic axon), that extends to the organ it s ...
... Autonomic nervous system, has a chain of two motor neurons The first neuron (in brain or spinal cord),it’s axon (preganglionic axon) leave the CNS to synapse with the second motor neuron in a ganglion outside the CNS. The axon of this neuron, (the postganglionic axon), that extends to the organ it s ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepepharmanatomy.wordpress.com Y
... The ovoid kidneys remove excess water, salts, and wastes of protein metabolism from the blood while returning nutrients and chemicals to the blood. They lie retroperitoneally on the posterior abdominal wall, one on each side of the vertebral column. At the concave medial margin of each kidney is a v ...
... The ovoid kidneys remove excess water, salts, and wastes of protein metabolism from the blood while returning nutrients and chemicals to the blood. They lie retroperitoneally on the posterior abdominal wall, one on each side of the vertebral column. At the concave medial margin of each kidney is a v ...
Amphibians - walker2013
... A salamander (order Caudata) has a long, slender body with a neck and tail Salamanders resemble lizards, but have smooth, moist skin and lack claws ...
... A salamander (order Caudata) has a long, slender body with a neck and tail Salamanders resemble lizards, but have smooth, moist skin and lack claws ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.