AACE/ACE Principles of Endocrine Neck Sonography Course
... Term derived from Greek word, Thureos, an ancient oblong shield ...
... Term derived from Greek word, Thureos, an ancient oblong shield ...
Earthworm lab analysis
... 8. How can you tell the ventral from the dorsal side of the earthworm? ...
... 8. How can you tell the ventral from the dorsal side of the earthworm? ...
Zoology Vertebrate Project
... location of mouth (terminal? anterior? ventral? dorsal?) swim bladder? yes or no? - what does this mean for the animal? describe heart (# of chambers) reproductive patterns - monoecious or dioecious ? - fertilization type (internal? external?) - oviparous, ovoviviparous, or viviparous? [define all t ...
... location of mouth (terminal? anterior? ventral? dorsal?) swim bladder? yes or no? - what does this mean for the animal? describe heart (# of chambers) reproductive patterns - monoecious or dioecious ? - fertilization type (internal? external?) - oviparous, ovoviviparous, or viviparous? [define all t ...
LECTURE 11
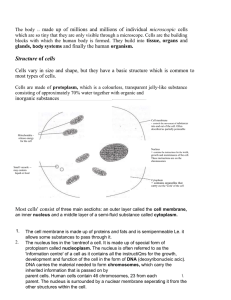
... o cells can remain small even in large organisms o materials can diffuse throughout whole cell more quickly 6. have tissue tissue – groups of structurally similar cells that function together tissues can functions together as organs to complete more complex tasks nervous – conducts impulses (e ...
... o cells can remain small even in large organisms o materials can diffuse throughout whole cell more quickly 6. have tissue tissue – groups of structurally similar cells that function together tissues can functions together as organs to complete more complex tasks nervous – conducts impulses (e ...
Overview of Invertebrates
... _____ 1. An earthworm is an example of a segmented invertebrate. _____ 2. Invertebrates with an incomplete digestive system starve, because their food cannot be completely digested. _____ 3. A psuedocoelom refers to concentration of nervous tissue at one end of the animal. _____ 4. Some invertebrate ...
... _____ 1. An earthworm is an example of a segmented invertebrate. _____ 2. Invertebrates with an incomplete digestive system starve, because their food cannot be completely digested. _____ 3. A psuedocoelom refers to concentration of nervous tissue at one end of the animal. _____ 4. Some invertebrate ...
Chap 35-1
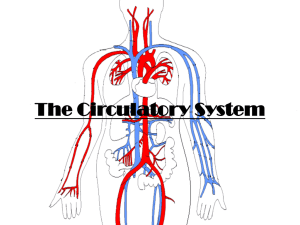
... A group of different types of tissues that work together to perform a single function is called an organ. A group of organs that perform closely related functions is an organ system. There are eleven organ systems in the body. ...
... A group of different types of tissues that work together to perform a single function is called an organ. A group of organs that perform closely related functions is an organ system. There are eleven organ systems in the body. ...
Vertebrate Zoology
... They tend to live on and in muddy sea floors in very dense groups (up to 15,000 in an area). Because females tend to produce large eggs in small numbers, their population sizes suggest a low death rate. ...
... They tend to live on and in muddy sea floors in very dense groups (up to 15,000 in an area). Because females tend to produce large eggs in small numbers, their population sizes suggest a low death rate. ...
Cervical Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz
... Transverse foramina C1 transverse process Spinous Processes ...
... Transverse foramina C1 transverse process Spinous Processes ...
35–1 Human Body Systems
... A group of different types of tissues that work together to perform a single function is called an organ. A group of organs that perform closely related functions is an organ system. There are eleven organ systems in the body. ...
... A group of different types of tissues that work together to perform a single function is called an organ. A group of organs that perform closely related functions is an organ system. There are eleven organ systems in the body. ...
Jaw movements and articulators - King George`s Medical University
... Immediate side shift 0.3mm Progressive side shift 6° ...
... Immediate side shift 0.3mm Progressive side shift 6° ...
NSC Chapter 3
... Abdominal – located in the trunk between the diaphragm and the pelvis. It contains the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, intestines, stomach, kidneys and spleen. Because most of the abdominal cavity is not protected by bones, the organs within it are especially vulnerable to injury Pelvic – located in ...
... Abdominal – located in the trunk between the diaphragm and the pelvis. It contains the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, intestines, stomach, kidneys and spleen. Because most of the abdominal cavity is not protected by bones, the organs within it are especially vulnerable to injury Pelvic – located in ...
OCR Document
... There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: 1. Skeletal or voluntary muscle tissue which is primarily attached to bone 2. Cardiac muscle tissue which is found in the walls of the heart 3. Smooth or involuntary muscle tissue which is found inside the digestive and urinary tracts, as well as ...
... There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: 1. Skeletal or voluntary muscle tissue which is primarily attached to bone 2. Cardiac muscle tissue which is found in the walls of the heart 3. Smooth or involuntary muscle tissue which is found inside the digestive and urinary tracts, as well as ...
35–1 Human Body Systems
... Organs and Organ Systems A group of different types of tissues that work together to perform a single function is called an organ. A group of organs that perform closely related functions is an organ system. There are eleven organ systems in the body. ...
... Organs and Organ Systems A group of different types of tissues that work together to perform a single function is called an organ. A group of organs that perform closely related functions is an organ system. There are eleven organ systems in the body. ...
OMT in the Hospitalized Patient - American Academy of Osteopathy
... – Skeletal muscle contractions affect the deep circulation, but not the superficial lymph just below the dermis – Active or passive limb motion – Peristaltic contractions of smooth muscles (viscera & adjacent arteries) – External compression ...
... – Skeletal muscle contractions affect the deep circulation, but not the superficial lymph just below the dermis – Active or passive limb motion – Peristaltic contractions of smooth muscles (viscera & adjacent arteries) – External compression ...
Head and Neck Embryology and Anatomy
... the frontal bone is hollowed out and expanded to form the frontal sinuses. The orbital part of the frontal bone forms most part of the roof of the orbits. The orbital cavity is a vital anatomical part of the facial skeleton; it contains the eye and important neural and vascular elements and connecti ...
... the frontal bone is hollowed out and expanded to form the frontal sinuses. The orbital part of the frontal bone forms most part of the roof of the orbits. The orbital cavity is a vital anatomical part of the facial skeleton; it contains the eye and important neural and vascular elements and connecti ...
Introduction to Human Anatomy
... Somatic cells are diverse cells which make up somatic structure of body. ...
... Somatic cells are diverse cells which make up somatic structure of body. ...
the anatomy of the orbita wall and the preseptal
... bral ligament (14). Lateral palpebral raphe is a weak structure which is formed by the blending of muscle ...
... bral ligament (14). Lateral palpebral raphe is a weak structure which is formed by the blending of muscle ...
What is an animal?
... What is an animal? • No cell walls • Cells supported by structural proteins: collagen – Extracellular matrix, supports >ssues, gives cells structure from outside – Triple‐helix structural protein ...
... What is an animal? • No cell walls • Cells supported by structural proteins: collagen – Extracellular matrix, supports >ssues, gives cells structure from outside – Triple‐helix structural protein ...
What is an animal?
... Mesoderm - gives rise to musculature and organ systems Ectoderm – gives rise to outer layer and ...
... Mesoderm - gives rise to musculature and organ systems Ectoderm – gives rise to outer layer and ...
Features Used to Classify Animals
... Each of the three germ layers is programmed to give rise to particular body tissues and organs. The endoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive tract (including the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas), as well as to the lining of the trachea, bronchi, and lungs of the respiratory tract, ...
... Each of the three germ layers is programmed to give rise to particular body tissues and organs. The endoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive tract (including the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas), as well as to the lining of the trachea, bronchi, and lungs of the respiratory tract, ...
03-31-06 - life.illinois.edu.
... animals. Smaller animals have higher metabolic rate both in endotherms and ectotherms. In the case of endotherms a greater surface to volume ration might explain this relationship, but it is also present in ectotherms that assume the temperature of the ...
... animals. Smaller animals have higher metabolic rate both in endotherms and ectotherms. In the case of endotherms a greater surface to volume ration might explain this relationship, but it is also present in ectotherms that assume the temperature of the ...
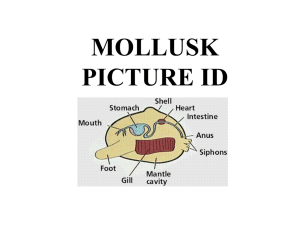
Mollusks PICTURE ID REVIEW
... http://www.discoveryvillage.net/img/oyster.jpg Scallops image : http://www.lib.noaa.gov/japan/aquaculture/exchange/2000tripimages/scallops.jpg ...
... http://www.discoveryvillage.net/img/oyster.jpg Scallops image : http://www.lib.noaa.gov/japan/aquaculture/exchange/2000tripimages/scallops.jpg ...
Applied Anatomy and Physiology for EMS Course Outcome
... development with assessment and communication strategies for patients of all ages. a. Apply concepts to scenario based testing. b. Compare assessment differences in various age groups. Discuss the relevance of understanding human body system function and structure to conditions commonly found in the ...
... development with assessment and communication strategies for patients of all ages. a. Apply concepts to scenario based testing. b. Compare assessment differences in various age groups. Discuss the relevance of understanding human body system function and structure to conditions commonly found in the ...
Animal s Animal, any member of the kingdom Animalia, which
... were proposed, in which the definitions of Plantae and Animalia became more restricted. What constitutes an animal, therefore, depends on the scheme followed. In the five-kingdom system used in this encyclopedia , animals are limited to organisms with differentiated tissues, and the protozoan groups ...
... were proposed, in which the definitions of Plantae and Animalia became more restricted. What constitutes an animal, therefore, depends on the scheme followed. In the five-kingdom system used in this encyclopedia , animals are limited to organisms with differentiated tissues, and the protozoan groups ...
Anterior - Mr. Morrison's Biology Class
... a fist. Even so, it works just like any other muscle in the body by contracting and expanding. The heart unlike the skeletal muscles works on an All-or-Nothing Law; this means that each time the heart contracts it uses its full force. ...
... a fist. Even so, it works just like any other muscle in the body by contracting and expanding. The heart unlike the skeletal muscles works on an All-or-Nothing Law; this means that each time the heart contracts it uses its full force. ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.