Fetal Pig Dissection
... 12. Lying on either side of the spine are two bean shaped organs: the kidneys. The kidneys are responsible for removing harmful substances from the blood, these substances are excreted as urine. (more on this later) ...
... 12. Lying on either side of the spine are two bean shaped organs: the kidneys. The kidneys are responsible for removing harmful substances from the blood, these substances are excreted as urine. (more on this later) ...
Human Body Systems
... Skin, hair, nails, sweat and oil glands Function: Serves as a barrier against infection and injury; helps to regulate body temperature; provides protection against ultraviolet radiation from the ...
... Skin, hair, nails, sweat and oil glands Function: Serves as a barrier against infection and injury; helps to regulate body temperature; provides protection against ultraviolet radiation from the ...
EMBRYOLOGY GENERAL EMBRYOLOGY SECOND WEEK
... baby).The pregnancy extends for 40 wks from the date of the last menstrual period(L.M.P) which is equivalent to 280 days. Or 38 wks from the date of fertilization( 266 days). The length of the fetus can be estimated as Crown-Rump length(CRL)i.e sitting position early in the fetal period ,or Crown-He ...
... baby).The pregnancy extends for 40 wks from the date of the last menstrual period(L.M.P) which is equivalent to 280 days. Or 38 wks from the date of fertilization( 266 days). The length of the fetus can be estimated as Crown-Rump length(CRL)i.e sitting position early in the fetal period ,or Crown-He ...
Muscular System - walker2015
... Skeletal muscles – attach to the body’s skeleton Cardiac – heart Smooth – walls of hollow organs such as the stomach, urinary bladder, intestines, and respiratory tract ...
... Skeletal muscles – attach to the body’s skeleton Cardiac – heart Smooth – walls of hollow organs such as the stomach, urinary bladder, intestines, and respiratory tract ...
EXERCISE #2: Respiratory division anatomy
... Identify all of the lobes, surfaces and fissures of both lungs which you identified on the preserved specimens above. ...
... Identify all of the lobes, surfaces and fissures of both lungs which you identified on the preserved specimens above. ...
Fetal Pig Dissection with Photos
... provide friction for food handling and contain taste buds. Like all young mammals, fetal pigs have milk teeth (baby teeth) that are later replaced by permanent teeth. There are 3 pairs of salivary glands (Fig. 2). Of these, we will view only the mandibular (the parotid is rather diffuse and the subl ...
... provide friction for food handling and contain taste buds. Like all young mammals, fetal pigs have milk teeth (baby teeth) that are later replaced by permanent teeth. There are 3 pairs of salivary glands (Fig. 2). Of these, we will view only the mandibular (the parotid is rather diffuse and the subl ...
educator guide grades 4-8
... to once again become aware of the naturalness of their bodies and to recognize the individuality and anatomical beauty inside of them. The authenticity of the specimens on display is essential for such insight. Every human being is unique. Humans reveal their individuality not only through the visib ...
... to once again become aware of the naturalness of their bodies and to recognize the individuality and anatomical beauty inside of them. The authenticity of the specimens on display is essential for such insight. Every human being is unique. Humans reveal their individuality not only through the visib ...
Fetal_Pig_Dissection_Directions_100501.1
... in a diagram. If the purpose of this exercise were simply to have you memorize diagrams (or computer screens), we would do only that and bypass the expense, time, and controversy of dissecting! Dissection is a powerful teaching method, especially for concrete thinkers and visual learners. Only by di ...
... in a diagram. If the purpose of this exercise were simply to have you memorize diagrams (or computer screens), we would do only that and bypass the expense, time, and controversy of dissecting! Dissection is a powerful teaching method, especially for concrete thinkers and visual learners. Only by di ...
urinary bladder - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... uterine cavity, where the uterine tubes enter. The wall of the body of the uterus consists of three coats, or ...
... uterine cavity, where the uterine tubes enter. The wall of the body of the uterus consists of three coats, or ...
7-3.3 - S2TEM Centers SC
... Understand Conceptual Knowledge (2.4-B ) Previous/Future Knowledge: This is the first time in science that students have been introduced to the concept of the relationships between the major body systems. Students will not develop this concept further in high school Biology as the primary focus in t ...
... Understand Conceptual Knowledge (2.4-B ) Previous/Future Knowledge: This is the first time in science that students have been introduced to the concept of the relationships between the major body systems. Students will not develop this concept further in high school Biology as the primary focus in t ...
cnidaria - Sakshieducation.com
... a.ventral central nervous system—leech b. no pharyngeal gill slits in the embryo-Chaemeleon c.ventral heart- scorpion d.post anal tail—Octopus ...
... a.ventral central nervous system—leech b. no pharyngeal gill slits in the embryo-Chaemeleon c.ventral heart- scorpion d.post anal tail—Octopus ...
Lab 1 External Characteristics of Vertebrates
... Aves is a diverse group that includes more than 9,700 species. Most species are specialized for flight, and even those that have abandoned flight for strictly aquatic or terrestrial lifestyles retain those characters that readily distinguish a bird from other vertebrates. Birds are the only vert ...
... Aves is a diverse group that includes more than 9,700 species. Most species are specialized for flight, and even those that have abandoned flight for strictly aquatic or terrestrial lifestyles retain those characters that readily distinguish a bird from other vertebrates. Birds are the only vert ...
Biology 320 Invertebrate Zoology Fall 2005
... Lateral outgrowths of body wall Supported by chitinous rod Each segment bears one pair Posses a chaetal sac which secretes a bundle of chaetae ...
... Lateral outgrowths of body wall Supported by chitinous rod Each segment bears one pair Posses a chaetal sac which secretes a bundle of chaetae ...
Introduction - Harris Training Institute, Inc.
... Basic unit of all living tissues or organisms All living organisms made of cells Cellular function is essential process of living things Cells have several functioning structures called organelle, that carry on work of cell Structure and Function – Cells Are building blocks of the human bo ...
... Basic unit of all living tissues or organisms All living organisms made of cells Cellular function is essential process of living things Cells have several functioning structures called organelle, that carry on work of cell Structure and Function – Cells Are building blocks of the human bo ...
Heart Anatomy
... marginal artery: lateral wall of the right side of the heart Cardiac Veins follow arteries and join at the Coronary Sinus which empties blood into the right ...
... marginal artery: lateral wall of the right side of the heart Cardiac Veins follow arteries and join at the Coronary Sinus which empties blood into the right ...
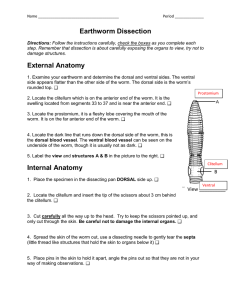
Earthworm Dissection External Anatomy Internal Anatomy
... 5. Place pins in the skin to hold it apart, angle the pins out so that they are not in your way of making observations. ...
... 5. Place pins in the skin to hold it apart, angle the pins out so that they are not in your way of making observations. ...
Untitled - SCUSOMA
... of this book, a system is defined as an organ group that works to perform a function for the body. This book looks at 11 systems, with each chapter dedicated to exploring a specific system. The first chapter of the book provides an overview of the human body, including a look at its cellular foundation ...
... of this book, a system is defined as an organ group that works to perform a function for the body. This book looks at 11 systems, with each chapter dedicated to exploring a specific system. The first chapter of the book provides an overview of the human body, including a look at its cellular foundation ...
Chapter 26 Sponges and Cnidarians Chapter Vocabulary Review
... Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition that matches each term. a. animal that has no backbone b. characterized by body parts that repeat around the center of a body c. the concentration of nerve cells and sense organs at the anterior end of the body d. animal with a backb ...
... Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition that matches each term. a. animal that has no backbone b. characterized by body parts that repeat around the center of a body c. the concentration of nerve cells and sense organs at the anterior end of the body d. animal with a backb ...
human body systems final project
... gluteus maximus, quadriceps, tibialis, masseter, rectus abdominis, and triceps Describe how muscles work in pairs to make parts of the body move using the biceps and triceps as an example. Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. You will need at least 2 examples. Fin ...
... gluteus maximus, quadriceps, tibialis, masseter, rectus abdominis, and triceps Describe how muscles work in pairs to make parts of the body move using the biceps and triceps as an example. Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. You will need at least 2 examples. Fin ...
Frog Dissection
... As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in water. On the outside of the frog’s head are two external nares, or nostrils; two tympani, or eardrums; and two eyes, each of which has thre ...
... As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in water. On the outside of the frog’s head are two external nares, or nostrils; two tympani, or eardrums; and two eyes, each of which has thre ...
Handout 6
... Air flows from lungs through larynx, between the vocal folds, through resonating cavities and out of mouth and nose. Airflow is essential to speech. Framework for Respiration and Lungs and Muscles and other soft tissues responsible for respiratory functions attach to bony framework consisting of: ...
... Air flows from lungs through larynx, between the vocal folds, through resonating cavities and out of mouth and nose. Airflow is essential to speech. Framework for Respiration and Lungs and Muscles and other soft tissues responsible for respiratory functions attach to bony framework consisting of: ...
Reproduction
... Spermatogonia: reproduce by mitosis to produce primary spermatocytes. Sustentacular (Sertoli) cells: form blood testis barrier (BTB), supplies nutrients to developing sperm, protect. (Also called nurse cells) Primary spermatocytes divide by meiosis to form secondary spermatocytes which are loc ...
... Spermatogonia: reproduce by mitosis to produce primary spermatocytes. Sustentacular (Sertoli) cells: form blood testis barrier (BTB), supplies nutrients to developing sperm, protect. (Also called nurse cells) Primary spermatocytes divide by meiosis to form secondary spermatocytes which are loc ...
MS Diagnostic Coding
... Diaphragm (G: partition, barrier) • Dome-shaped structure that separates thoracic and abdominal cavities • Major muscle of respiration • Innervated by the Phrenic nerve ...
... Diaphragm (G: partition, barrier) • Dome-shaped structure that separates thoracic and abdominal cavities • Major muscle of respiration • Innervated by the Phrenic nerve ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... 3. All peripheral nerves are classified as Cranial or Spinal A) Cranial nerves – *refer to Cranial Nerves Table on the Lecture Material webpage* B) Spinal nerves – 1) Terminology a) ...
... 3. All peripheral nerves are classified as Cranial or Spinal A) Cranial nerves – *refer to Cranial Nerves Table on the Lecture Material webpage* B) Spinal nerves – 1) Terminology a) ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.