BIOL_218_MTX3_QA_101110.53
... A) hold the pharynx open during speech. B) produce surfactant. C) close off the nasal cavity during swallowing. D) close off the larynx during swallowing. E) vibrate to produce sound as air passes over it. ...
... A) hold the pharynx open during speech. B) produce surfactant. C) close off the nasal cavity during swallowing. D) close off the larynx during swallowing. E) vibrate to produce sound as air passes over it. ...
eye-layers 1
... • Series of delicate fibrils attached to ciliary processes and through the furrows between them, further back on ciliary body • Most fibres attach themselves to the lens- mostly in front and a few behind the circumference ...
... • Series of delicate fibrils attached to ciliary processes and through the furrows between them, further back on ciliary body • Most fibres attach themselves to the lens- mostly in front and a few behind the circumference ...
osteology - Yeditepe University Pharma Anatomy
... to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern scientists. It has been characterized, over time, by a continually developing understanding of the functions of organs and structures in the body. The field of Human Anatomy has a prestigious history, and is considered to be the most prom ...
... to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern scientists. It has been characterized, over time, by a continually developing understanding of the functions of organs and structures in the body. The field of Human Anatomy has a prestigious history, and is considered to be the most prom ...
The cardiac cycle - Websupport1
... Blood flow through the heart • Right atria –receives blood from superior and inferior vena cava and pumps it to the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve • Right ventricle –receives blood from right atrium and pumps it toto the pulmonary artery through the pulmonary semilunar valve • Pulmonar ...
... Blood flow through the heart • Right atria –receives blood from superior and inferior vena cava and pumps it to the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve • Right ventricle –receives blood from right atrium and pumps it toto the pulmonary artery through the pulmonary semilunar valve • Pulmonar ...
ORTHOPAEDIC SCREWS
... Figure 2 and the three types of planes are always at right angles to each other. The sagittal plane, which passes through the middle of the body, is known as the median plane. Other terms in common use are midsagittal instead of median; and not so frequently, parasagittal instead of sagittal. The me ...
... Figure 2 and the three types of planes are always at right angles to each other. The sagittal plane, which passes through the middle of the body, is known as the median plane. Other terms in common use are midsagittal instead of median; and not so frequently, parasagittal instead of sagittal. The me ...
Lecture 12
... –Uterine arteries from internal iliac and arcuate branches =uterus –Ovarian arteries from abdominal aorta and ovarian branches of uterine arteries = ovaries ...
... –Uterine arteries from internal iliac and arcuate branches =uterus –Ovarian arteries from abdominal aorta and ovarian branches of uterine arteries = ovaries ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR THE ASANAS
... The body weight is balanced on the abdominal muscles and they are given pressure so that the intra-abdominal organs, i.e. stomach, liver, spleen pancreas and intestines, are massaged by the change in pressure. It also improves the secretions of these organ. It improves the peristalsis of the intesti ...
... The body weight is balanced on the abdominal muscles and they are given pressure so that the intra-abdominal organs, i.e. stomach, liver, spleen pancreas and intestines, are massaged by the change in pressure. It also improves the secretions of these organ. It improves the peristalsis of the intesti ...
Animal Quiz
... c. paralyzing small crustaceans with stinging cells d. absorbing nutrients from the guts of their hosts ...
... c. paralyzing small crustaceans with stinging cells d. absorbing nutrients from the guts of their hosts ...
NECK MUSCLES, THEIR INNERVATION, OSTEOFASCIAL
... Balance of head and vertebrae suboccipital triangle (vertebral a.) m. rectus capitis posterior major (5) m. rectus capitis posterior minor (3) m. obliquus capitis superior (2) m. obliquus capitis inferior (4) ...
... Balance of head and vertebrae suboccipital triangle (vertebral a.) m. rectus capitis posterior major (5) m. rectus capitis posterior minor (3) m. obliquus capitis superior (2) m. obliquus capitis inferior (4) ...
PHYLUMS OF INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS
... • Have a complete digestive system • Most are free-living, with few parasitic species ...
... • Have a complete digestive system • Most are free-living, with few parasitic species ...
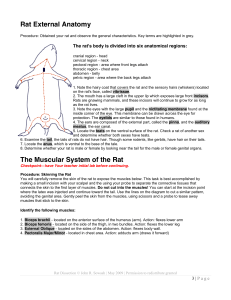
Rat External Anatomy The Muscular System of the Rat
... The rat's body is divided into six anatomical regions: cranial region - head cervical region - neck pectoral region - area where front legs attach thoracic region - chest area abdomen - belly pelvic region - area where the back legs attach 1. Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory h ...
... The rat's body is divided into six anatomical regions: cranial region - head cervical region - neck pectoral region - area where front legs attach thoracic region - chest area abdomen - belly pelvic region - area where the back legs attach 1. Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory h ...
Variant Musculo-tendinous Slip between Teres major
... Extended insertion of teres minor into the postero-superior and lateral portions of capsule of the shoulder joint and surgical neck of humerus has been reported by Jain et al.(4) In the present case, teres minor muscle took origin from a narrow area at the root of the spine of scapula. Developmental ...
... Extended insertion of teres minor into the postero-superior and lateral portions of capsule of the shoulder joint and surgical neck of humerus has been reported by Jain et al.(4) In the present case, teres minor muscle took origin from a narrow area at the root of the spine of scapula. Developmental ...
Annelida By: Omar Abdulkader, Marcus Bray
... • Metanephridium: excretory tubes with ciliated funnels called nephrostomes • Remove waste from the blood and coelomic fluid through exterior pores. • Each segment of the worm has a pair of metanephridium. ...
... • Metanephridium: excretory tubes with ciliated funnels called nephrostomes • Remove waste from the blood and coelomic fluid through exterior pores. • Each segment of the worm has a pair of metanephridium. ...
Heart Chambers - Cloudfront.net
... amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, use lungs • However, some animals “break the rules”: – For example, several fishes, such as lungfishes, have both gills and lungs ...
... amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, use lungs • However, some animals “break the rules”: – For example, several fishes, such as lungfishes, have both gills and lungs ...
Knee Anatomy and Evaluation
... These two articulation are not independent of each other but have a biomechanical relationship ...
... These two articulation are not independent of each other but have a biomechanical relationship ...
Biol 241 Spring 13 Syllabus
... Four lab practicals will be administered in the class that will test your knowledge of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected PowerPoint slides, models, and fresh tissues. You will have time in lab to le ...
... Four lab practicals will be administered in the class that will test your knowledge of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected PowerPoint slides, models, and fresh tissues. You will have time in lab to le ...
anatomy 6: formation of body cavities and diaphragm
... folding causes cardiogenic region and septum transversum to be caudal to oropharyngeal membrane and located in the chest region septum transversum- most cranial; furthest from primitive streak diaphragm; connects cardiac field to amnion *think of envelop example* Day 27: formed primitive he ...
... folding causes cardiogenic region and septum transversum to be caudal to oropharyngeal membrane and located in the chest region septum transversum- most cranial; furthest from primitive streak diaphragm; connects cardiac field to amnion *think of envelop example* Day 27: formed primitive he ...
Animal Diversity – I (Invertebrate Phyla)
... This class includes sea cucumbers. Body elongated in the oral – aboral axis. Arms, spines and pedicellariae are absent. Skin is soft and leathery (Coriaceous). Dermis contains microscopic, isolated ossicles. Madreporite is internal, suspended in the perivisceral coelom. Tube feet are provided with s ...
... This class includes sea cucumbers. Body elongated in the oral – aboral axis. Arms, spines and pedicellariae are absent. Skin is soft and leathery (Coriaceous). Dermis contains microscopic, isolated ossicles. Madreporite is internal, suspended in the perivisceral coelom. Tube feet are provided with s ...
Sperm - My Anatomy Mentor
... Complex interplay between hormones and organs: at level of brain, ovaries and uterus ...
... Complex interplay between hormones and organs: at level of brain, ovaries and uterus ...
Chapter 3 - Morgan Community College
... • The lumbar plexus supplies the anterolateral abdominal wall, external genitals, and part of the lower extremities (Figure 13.9a and b, Exhibit 13.3). – The largest nerve arising from the lumbar plexus is the femoral nerve. – Injury to the femoral nerve is indicated by an inability to extend the le ...
... • The lumbar plexus supplies the anterolateral abdominal wall, external genitals, and part of the lower extremities (Figure 13.9a and b, Exhibit 13.3). – The largest nerve arising from the lumbar plexus is the femoral nerve. – Injury to the femoral nerve is indicated by an inability to extend the le ...
Medical Gross Anatomy Movements of the Upper Limb
... anteriorly along the chest wall. Muscles: serratus anterior is the prime mover. Pectoralis minor and major, the latter acting through the humerus, may assist (act as synergists). ...
... anteriorly along the chest wall. Muscles: serratus anterior is the prime mover. Pectoralis minor and major, the latter acting through the humerus, may assist (act as synergists). ...
Unit 5B - Workforce Solutions
... Skeletal divisions General bone features Bone development Classification of bones ...
... Skeletal divisions General bone features Bone development Classification of bones ...
B6A-8 - De Anza
... • Typical mammalian body is composed of ~50,000,000,000,000 cells • Typical vertebrate body is composed of >100 specialized types of cells (tissue types) ...
... • Typical mammalian body is composed of ~50,000,000,000,000 cells • Typical vertebrate body is composed of >100 specialized types of cells (tissue types) ...
Diversity and Life History of Caecilians (Gymnophiona)
... Life History of Caecilians Reproduction • Unlike most amphibians all caecilians reproduce via internal fertilization. • Males have a copulatory organ called a phallodeum. • Eggs are similar to those of fish and other amphibians in gelatinous ; they are not especially adapted for dry land. ...
... Life History of Caecilians Reproduction • Unlike most amphibians all caecilians reproduce via internal fertilization. • Males have a copulatory organ called a phallodeum. • Eggs are similar to those of fish and other amphibians in gelatinous ; they are not especially adapted for dry land. ...
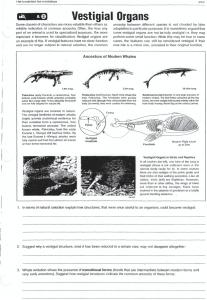
Vestigial Organs
... Some classes of characters are more valuable than others as reliable indicators of common ancestry. Often, the less any part of an animal is used for specialised purposes, the more important it becomes for classification. Vestigial organs are an example of this. If vestigial features have no clear f ...
... Some classes of characters are more valuable than others as reliable indicators of common ancestry. Often, the less any part of an animal is used for specialised purposes, the more important it becomes for classification. Vestigial organs are an example of this. If vestigial features have no clear f ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.