Reading Guide CH 13
... 14. a. How does gas exchange occur in the respiratory membrane (i.e. what process)? ______________________ b. How much gas exchange surface has been estimated to be in a healthy man’s alveolar walls? _________________________ c. Which is how much greater than the surface area of his skin? __________ ...
... 14. a. How does gas exchange occur in the respiratory membrane (i.e. what process)? ______________________ b. How much gas exchange surface has been estimated to be in a healthy man’s alveolar walls? _________________________ c. Which is how much greater than the surface area of his skin? __________ ...
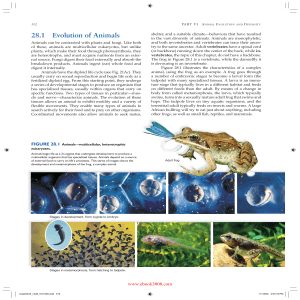
28.1 Evolution of Animals
... Echinoderms (sea stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, sea cucumbers): Radial symmetry as adults; unique water-vascular system and tube feet; endoskeleton of calcium plates. 7,000+ Chordates (tunicates, lancelets, vertebrates): All have notochord, dorsal tubular nerve cord, pharyngeal pouches, and posta ...
... Echinoderms (sea stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, sea cucumbers): Radial symmetry as adults; unique water-vascular system and tube feet; endoskeleton of calcium plates. 7,000+ Chordates (tunicates, lancelets, vertebrates): All have notochord, dorsal tubular nerve cord, pharyngeal pouches, and posta ...
What Is A Reptile
... scaly skin; are cold-blooded; are vertebrates; and lay eggs with a leathery shell. Background Information • All reptiles are vertebrates, breathe with lungs, and have dry, scaly skin. • Reptiles lay eggs that have a dry leathery shell. Unlike amphibians, which lay eggs with a jelly coat that must re ...
... scaly skin; are cold-blooded; are vertebrates; and lay eggs with a leathery shell. Background Information • All reptiles are vertebrates, breathe with lungs, and have dry, scaly skin. • Reptiles lay eggs that have a dry leathery shell. Unlike amphibians, which lay eggs with a jelly coat that must re ...
Cells Last modified January 9, 2017 at 5:21 am
... D) stratified squamous E) stratified columnar Question # 11 The type of epithelial cell found in the lining of the stomach, intestinal tract, and part of the respiratory tract is ...
... D) stratified squamous E) stratified columnar Question # 11 The type of epithelial cell found in the lining of the stomach, intestinal tract, and part of the respiratory tract is ...
Body Systems Project
... Objective: To gain an in depth understanding about one of the 8 body systems found in the human body. Procedure: Students will engage in an in-depth study of two of the seven body systems. They will be given five days of research/development time in class to complete the project. ALL PROJECTS ARE DU ...
... Objective: To gain an in depth understanding about one of the 8 body systems found in the human body. Procedure: Students will engage in an in-depth study of two of the seven body systems. They will be given five days of research/development time in class to complete the project. ALL PROJECTS ARE DU ...
BERTO2-for low res pdf.indd
... Position in which the subject is neither prone nor supine, but rotated somewhere between. In radiographic terminology, the subject is in a posterior oblique position if some part of the posterior surface of the body is closer to the film, and in an anterior oblique position if some part of the anter ...
... Position in which the subject is neither prone nor supine, but rotated somewhere between. In radiographic terminology, the subject is in a posterior oblique position if some part of the posterior surface of the body is closer to the film, and in an anterior oblique position if some part of the anter ...
Body diagrams during pregnancy
... the only one undergoing big changes. Try this interactive, which shows a pregnancy's impact on the mother's body as her . Explore the female reproductive system – interactive anatomy diagrams by sperm and supports the development of offspring during pregnancy and infancy. right sides of the pelvic b ...
... the only one undergoing big changes. Try this interactive, which shows a pregnancy's impact on the mother's body as her . Explore the female reproductive system – interactive anatomy diagrams by sperm and supports the development of offspring during pregnancy and infancy. right sides of the pelvic b ...
Gross Anatomy of the Brain and Cranial Nerves
... frontal lobe from parietal lobe Lateral sulcus –seperates temporal lobe from parietal lobe Parieto-occipital sulcus – diveds occipital lobe from parietal lobe Insula –buried deep within lateral sulcus ...
... frontal lobe from parietal lobe Lateral sulcus –seperates temporal lobe from parietal lobe Parieto-occipital sulcus – diveds occipital lobe from parietal lobe Insula –buried deep within lateral sulcus ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Exception to the dual innervation rule: Sweat glands and blood vessel smooth muscle are only innervated by symp and rely strictly on up-down control. Exception to the antagonism rule: Symp and parasymp work cooperatively to achieve male sexual function. Parasymp is responsible for erection while sy ...
... Exception to the dual innervation rule: Sweat glands and blood vessel smooth muscle are only innervated by symp and rely strictly on up-down control. Exception to the antagonism rule: Symp and parasymp work cooperatively to achieve male sexual function. Parasymp is responsible for erection while sy ...
Kingdom Animalia
... from the same opening • Complete digestive system: two openings; food enters the mouth and wastes exit the anus ...
... from the same opening • Complete digestive system: two openings; food enters the mouth and wastes exit the anus ...
Anatomy of the Reproductive System (Chapter 42) Lab Objectives
... Know the following terms for orientation: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral, proximal, distal, superficial, deep, parietal, visceral Know the common sections: sagittal, midsagittal, parasagittal, frontal, transverse Tissues: Know the functions ...
... Know the following terms for orientation: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral, proximal, distal, superficial, deep, parietal, visceral Know the common sections: sagittal, midsagittal, parasagittal, frontal, transverse Tissues: Know the functions ...
bee vocabulary
... Metapleura – thorax segment bearing the hind legs and hind wings Notaulices - a pair of lines on some bees that appear on either side of the scutum near the base of the wings Ocelli – the 3 simple eyes or lenses that sit at the top of the head of bees Ochraceous – pale yellow Papillae (Papilate) – v ...
... Metapleura – thorax segment bearing the hind legs and hind wings Notaulices - a pair of lines on some bees that appear on either side of the scutum near the base of the wings Ocelli – the 3 simple eyes or lenses that sit at the top of the head of bees Ochraceous – pale yellow Papillae (Papilate) – v ...
Slide 1
... tetrapods—ver tebrates with two pairs of limbs ◦ Amphibians Were the first tetrapods with limbs allowing movement on land ...
... tetrapods—ver tebrates with two pairs of limbs ◦ Amphibians Were the first tetrapods with limbs allowing movement on land ...
Introduction to Vertebrates
... • The swim bladder is a thin-walled sac in the abdominal cavity that contains a mixture of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen obtained from the bloodstream. • Swim bladders evolved from balloonlike lungs, which ancestral bony fishes may have used to supplement the oxygen absorbed by the gills. ...
... • The swim bladder is a thin-walled sac in the abdominal cavity that contains a mixture of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen obtained from the bloodstream. • Swim bladders evolved from balloonlike lungs, which ancestral bony fishes may have used to supplement the oxygen absorbed by the gills. ...
ANIMAL BIOLOGY LABORATORY Lab 4
... • Recognize the basic structure and organization of sponges. • Understand the pattern of water flow through sponges. • Recognize the three basic body types of sponges. • Recognize and distinguish between the three cnidarian classes. • Understand the differences between the polyp and medusa forms. ...
... • Recognize the basic structure and organization of sponges. • Understand the pattern of water flow through sponges. • Recognize the three basic body types of sponges. • Recognize and distinguish between the three cnidarian classes. • Understand the differences between the polyp and medusa forms. ...
God`s AMAZING Design
... My Body: God’s Amazing Design Review Game Copyright © 2017 by Michelle Hubbard www.hubbardscupboard.org and www.joyfulheartlearning.com Clipart from the following resources: Educlips , Kari Bolt , PaulaKimStudio , The Painted Crow ,The Cher Room , Hidesy’s Clipart ...
... My Body: God’s Amazing Design Review Game Copyright © 2017 by Michelle Hubbard www.hubbardscupboard.org and www.joyfulheartlearning.com Clipart from the following resources: Educlips , Kari Bolt , PaulaKimStudio , The Painted Crow ,The Cher Room , Hidesy’s Clipart ...
bones of the skull - Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
... connected to the five metacarpals that form the bones of the hand and connect to each of the fingers. Each finger has three bones known as phalanges, except for the thumb, which only has two phalanges. Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limb Formed by the left and right hip bones, the pelvic girdle connects t ...
... connected to the five metacarpals that form the bones of the hand and connect to each of the fingers. Each finger has three bones known as phalanges, except for the thumb, which only has two phalanges. Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limb Formed by the left and right hip bones, the pelvic girdle connects t ...
Kingdom Animalia
... strate. Both forms are found in the life cycle of many coelenterates. Some coelenterate colonies are com posed of both forms of individuals. Both forms are ...
... strate. Both forms are found in the life cycle of many coelenterates. Some coelenterate colonies are com posed of both forms of individuals. Both forms are ...
student - Union Station
... health and wellness. The exhibition includes whole-body plastinates, a large arrangement of individual organs, organ and arterial configurations, and translucent slices that give a complete picture of how the human body works. Vital tells the fascinating story of how best to fight life-threatening d ...
... health and wellness. The exhibition includes whole-body plastinates, a large arrangement of individual organs, organ and arterial configurations, and translucent slices that give a complete picture of how the human body works. Vital tells the fascinating story of how best to fight life-threatening d ...
Concepts of Biology - Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
... While we can easily identify dogs, lizards, fish, spiders, and worms as animals, other animals, such as corals and sponges, might be easily mistaken as plants or some other form of life. Yet scientists have recognized a set of common characteristics shared by all animals, including sponges, jellyfis ...
... While we can easily identify dogs, lizards, fish, spiders, and worms as animals, other animals, such as corals and sponges, might be easily mistaken as plants or some other form of life. Yet scientists have recognized a set of common characteristics shared by all animals, including sponges, jellyfis ...
The Muscular System
... stimulus- any agent, act, or influence that produces a change in the development or function of tissues tonus- slight, continuous contraction of muscle visceral- pertaining to any large interior organ in any one of the cavities of the body ...
... stimulus- any agent, act, or influence that produces a change in the development or function of tissues tonus- slight, continuous contraction of muscle visceral- pertaining to any large interior organ in any one of the cavities of the body ...
Document
... • Deep to SCM across posterior triangle over levator scapulae deep to trapezius • Clinical note: can be damaged – Difficulty turning head to side (with resistance) SCM – Shoulders droop/cannot raise and retract shoulder/cannot raise arm above horizontal Trapezius ...
... • Deep to SCM across posterior triangle over levator scapulae deep to trapezius • Clinical note: can be damaged – Difficulty turning head to side (with resistance) SCM – Shoulders droop/cannot raise and retract shoulder/cannot raise arm above horizontal Trapezius ...
y. - كلية طب الاسنان
... Occipitofrontalis consists of occipitalis and frontalis muscular parts with an intervening epicranial aponeurosis (galea aponeurotica) into which they are inserted at the back and front respectively. Occipitalis arises from the superior nuchal line and passes upwards into the aponeurosis which lies ...
... Occipitofrontalis consists of occipitalis and frontalis muscular parts with an intervening epicranial aponeurosis (galea aponeurotica) into which they are inserted at the back and front respectively. Occipitalis arises from the superior nuchal line and passes upwards into the aponeurosis which lies ...
Human Systems and Homeostasis
... in the organism have different functions. Take a moment to study the images of the blood cells and nerve cells, or neurons, in FIGURE 1.1. You will notice that the red blood cells are round with a concave center. This structure gives them more surface area to help deliver oxygen to all parts of the ...
... in the organism have different functions. Take a moment to study the images of the blood cells and nerve cells, or neurons, in FIGURE 1.1. You will notice that the red blood cells are round with a concave center. This structure gives them more surface area to help deliver oxygen to all parts of the ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.