reptile notes - Warren County Schools
... • Some reptiles have a median eye that develops from the roof of the forebrain. • In the tuatara, it is an eye with a lens, a nerve, and a retina. • In other reptiles, the parietal eye is less developed. • They are covered by skin and probably can not form images. • They can tell the dif ...
... • Some reptiles have a median eye that develops from the roof of the forebrain. • In the tuatara, it is an eye with a lens, a nerve, and a retina. • In other reptiles, the parietal eye is less developed. • They are covered by skin and probably can not form images. • They can tell the dif ...
Reptile Notes Parts 1 and 2
... • When a lizard is grasped by the tail, these vertebrae can be broken, and a portion of the tail is lost. • Tail loss, or autotomy, is an adaptation that allows a lizard to escape from a predator’s grasp, or the disconnected piece of tail may distract a predator from the lizard. • The lizard will la ...
... • When a lizard is grasped by the tail, these vertebrae can be broken, and a portion of the tail is lost. • Tail loss, or autotomy, is an adaptation that allows a lizard to escape from a predator’s grasp, or the disconnected piece of tail may distract a predator from the lizard. • The lizard will la ...
COOL FACt Learn with BODY WORLDS
... Although it may seem easy to do something like throw a ball, it’s actually complicated when looked at inside the body. To make the motion of throwing, many muscle groups in the shoulders, arms, chest, abdomen and even legs must be used! Each of these groups must work together with nerves in order fo ...
... Although it may seem easy to do something like throw a ball, it’s actually complicated when looked at inside the body. To make the motion of throwing, many muscle groups in the shoulders, arms, chest, abdomen and even legs must be used! Each of these groups must work together with nerves in order fo ...
Hemorrhoidal Products
... vascularized and does not contain sensory fibers. Like anal canal, however, it does contain pressure receptors Substances absorbed through the rectal mucous membranes may enter systemic circulation without passing through the liver The rectal pH ranges from neutral to basic, determining the extent t ...
... vascularized and does not contain sensory fibers. Like anal canal, however, it does contain pressure receptors Substances absorbed through the rectal mucous membranes may enter systemic circulation without passing through the liver The rectal pH ranges from neutral to basic, determining the extent t ...
Appendicular Skeleton
... Appendicular Skeleton • The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the limbs and their girdles • Shoulder girdles attach the upper limbs to the body trunk ...
... Appendicular Skeleton • The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the limbs and their girdles • Shoulder girdles attach the upper limbs to the body trunk ...
ANIMAL EVOLUTION AND DIVERSITY
... body plan Molluscs (phylum Mollusca) have – a muscular foot that functions in locomotion, – a visceral (內臟) mass containing most of the internal organs, – a mantle, which may secrete a shell that encloses the visceral mass, and – a true coelom and a circulatory system that pumps blood throughout t ...
... body plan Molluscs (phylum Mollusca) have – a muscular foot that functions in locomotion, – a visceral (內臟) mass containing most of the internal organs, – a mantle, which may secrete a shell that encloses the visceral mass, and – a true coelom and a circulatory system that pumps blood throughout t ...
Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy
... bone located at the point where the femur and tibia articulate with each other. The foot subdivides into smaller bones of the ankle, instep, and toes. The table below lists the location and function of the major bones of the appendicular skeleton: ...
... bone located at the point where the femur and tibia articulate with each other. The foot subdivides into smaller bones of the ankle, instep, and toes. The table below lists the location and function of the major bones of the appendicular skeleton: ...
CHAPTER 48: VERTEBRATES
... downward in the water as they swim forward. Their skin is covered by small denticles from which teeth are derived. Bony fish possess a denser, less buoyant skeleton and have evolved a gas-filled swim bladder to help position themselves in the water. Their scales are composed of thin, bony plates and ...
... downward in the water as they swim forward. Their skin is covered by small denticles from which teeth are derived. Bony fish possess a denser, less buoyant skeleton and have evolved a gas-filled swim bladder to help position themselves in the water. Their scales are composed of thin, bony plates and ...
Full Text PDF
... suggests that the motor branch of the long head of triceps may arise from the axillary nerve [7]. DEVELOPMENTAL BASIS The origin of anomalous muscles may be explained on the basis of embryogenesis of muscles of the arm. The intrinsic muscles of the upper limb differentiate in situ from the limb bud ...
... suggests that the motor branch of the long head of triceps may arise from the axillary nerve [7]. DEVELOPMENTAL BASIS The origin of anomalous muscles may be explained on the basis of embryogenesis of muscles of the arm. The intrinsic muscles of the upper limb differentiate in situ from the limb bud ...
Directional Terms
... • Divides body into equal right and left halves • Sagittal • Separate right and left parts • Frontal • Divides anterior and posterior parts • Horizontal/ Transverse • Divides superior and inferior ...
... • Divides body into equal right and left halves • Sagittal • Separate right and left parts • Frontal • Divides anterior and posterior parts • Horizontal/ Transverse • Divides superior and inferior ...
Body Planes and Anatomical References
... • The ventral cavity is divided into three sections: ▫ The thoracic cavity contains the trachea, esophagus, bronchi, lungs, heart, and major blood vessels. It is also known as the chest cavity. ▫ The abdominal cavity contains the stomach, small intestine, most of the large intestine, liver, gallblad ...
... • The ventral cavity is divided into three sections: ▫ The thoracic cavity contains the trachea, esophagus, bronchi, lungs, heart, and major blood vessels. It is also known as the chest cavity. ▫ The abdominal cavity contains the stomach, small intestine, most of the large intestine, liver, gallblad ...
Name: Anatomical Terms
... Circle the correct answer. Assume the individual is in anatomical position. a. The big toe is on the lateral/medial side of the foot. b. The shoulder blade is on the anterior/posterior side of the body. c. The hand is distal/proximal to the elbow. d. The hips are superior/inferior to the shoulders. ...
... Circle the correct answer. Assume the individual is in anatomical position. a. The big toe is on the lateral/medial side of the foot. b. The shoulder blade is on the anterior/posterior side of the body. c. The hand is distal/proximal to the elbow. d. The hips are superior/inferior to the shoulders. ...
Respiration
... • Two common terrestrial respiratory structures – Tracheae (insects) – Lungs (most terrestrial vertebrates) ...
... • Two common terrestrial respiratory structures – Tracheae (insects) – Lungs (most terrestrial vertebrates) ...
E1. - De Anza
... formation of a multicellular stage called a blastula. The blastula of many animals is a hollow ball of cells. ...
... formation of a multicellular stage called a blastula. The blastula of many animals is a hollow ball of cells. ...
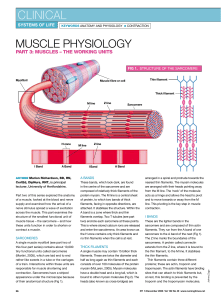
061205Muscle physiology
... quickly use up their stores of it as well as manufacturing it while they are working. When oxygen is present in the muscle, the mitochondria absorb substances, particularly fatty acids, from the cytoplasm and break them down. This is an efficient process that releases large amounts of energy, which ...
... quickly use up their stores of it as well as manufacturing it while they are working. When oxygen is present in the muscle, the mitochondria absorb substances, particularly fatty acids, from the cytoplasm and break them down. This is an efficient process that releases large amounts of energy, which ...
Features Used to Classify Animals
... a few other structures. The mesoderm is the third germ layer; it forms between the endoderm and ectoderm in triploblasts. This germ layer gives rise to all muscle tissues (including the cardiac tissues and muscles of the intestines), connective tissues such as the skeleton and blood cells, and most ...
... a few other structures. The mesoderm is the third germ layer; it forms between the endoderm and ectoderm in triploblasts. This germ layer gives rise to all muscle tissues (including the cardiac tissues and muscles of the intestines), connective tissues such as the skeleton and blood cells, and most ...
Platyhelminthes
... Digestive juices are sprayed onto pray, and small pieces are sucked into pharynx, where digestion continues Undigested wastes are egested through the mouth ...
... Digestive juices are sprayed onto pray, and small pieces are sucked into pharynx, where digestion continues Undigested wastes are egested through the mouth ...
Slides
... • A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve formed by the junction of nerves from the – Dorsal root (sensory) – Ventral root (motor) • Somatic • Autonomic ...
... • A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve formed by the junction of nerves from the – Dorsal root (sensory) – Ventral root (motor) • Somatic • Autonomic ...
I. Integument as exoskeleton II. Structure A. Major Components B
... Epidermis – cellular and biologically active part of integument ...
... Epidermis – cellular and biologically active part of integument ...
Medial Lateral Anatomy - American Orthopaedic Society for Sports
... o Knee flexed to 90° and a 3 cm vertical incision placed 1/3 above and 2/3 below the medial joint line o Incision posterior to superficial MCL in‐line with longitudinal axis of knee *Caution: Infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve and saphenous vein posterior and inferior to incision ...
... o Knee flexed to 90° and a 3 cm vertical incision placed 1/3 above and 2/3 below the medial joint line o Incision posterior to superficial MCL in‐line with longitudinal axis of knee *Caution: Infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve and saphenous vein posterior and inferior to incision ...
Cranial Nerves
... 3. soft palate 4. upper 2/3 of esophagus (for speech/swallowing) Parasympathetic 1. Preganglionic fiber to thoracic and abdominal smooth muscle, viscera, glands Branches: Embryo: ...
... 3. soft palate 4. upper 2/3 of esophagus (for speech/swallowing) Parasympathetic 1. Preganglionic fiber to thoracic and abdominal smooth muscle, viscera, glands Branches: Embryo: ...
Peripheral Nervous System Structures
... nervous system (PNS). Nerves are bundles of many axons supported by several layers of connective tissue (analogous to the arrangement of muscle fascicles in muscles) and will appear as long tough fibrous strands. Each axon in a nerve may be either sensory, carrying information to the CNS (brain and ...
... nervous system (PNS). Nerves are bundles of many axons supported by several layers of connective tissue (analogous to the arrangement of muscle fascicles in muscles) and will appear as long tough fibrous strands. Each axon in a nerve may be either sensory, carrying information to the CNS (brain and ...
Human Body
... 2a. Students know many multicellular organisms have specialized structures to support the transport of materials. 2b. Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, ...
... 2a. Students know many multicellular organisms have specialized structures to support the transport of materials. 2b. Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.