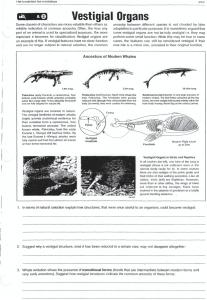
Vestigial Organs
... Some classes of characters are more valuable than others as reliable indicators of common ancestry. Often, the less any part of an animal is used for specialised purposes, the more important it becomes for classification. Vestigial organs are an example of this. If vestigial features have no clear f ...
... Some classes of characters are more valuable than others as reliable indicators of common ancestry. Often, the less any part of an animal is used for specialised purposes, the more important it becomes for classification. Vestigial organs are an example of this. If vestigial features have no clear f ...
Fetal Pig Dissection
... system, identifying the structure You need to be able to... -trace & name the circulatory system and studying the function of -identify the areas of the heart and the each aspect of the system with a focus on the heart and the associated major arteries and veins major arteries and veins -know the fu ...
... system, identifying the structure You need to be able to... -trace & name the circulatory system and studying the function of -identify the areas of the heart and the each aspect of the system with a focus on the heart and the associated major arteries and veins major arteries and veins -know the fu ...
Introduction to the Amphibian Body
... – Due to the mixing the efficiency of lungs is much less than that of gills – This is okay though because air contains 20x as much oxygen as sea water ...
... – Due to the mixing the efficiency of lungs is much less than that of gills – This is okay though because air contains 20x as much oxygen as sea water ...
Earthworm Anatomy
... The openings near the clitellum are the genital setae. Locate the dark line that runs down the dorsal side of the worm, this is the dorsal blood vessel. The ventral blood vessel can be seen on the underside of the worm, though it is usually not as dark. Locate the worm's mouth and anus. Note the swe ...
... The openings near the clitellum are the genital setae. Locate the dark line that runs down the dorsal side of the worm, this is the dorsal blood vessel. The ventral blood vessel can be seen on the underside of the worm, though it is usually not as dark. Locate the worm's mouth and anus. Note the swe ...
Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle General:
... ¨ Features of the diaphysis (shaft): ¤ Deltoid tuberosity: attachment for the deltoid(shoulder) muscle Radial groove-‐ marks the course ...
... ¨ Features of the diaphysis (shaft): ¤ Deltoid tuberosity: attachment for the deltoid(shoulder) muscle Radial groove-‐ marks the course ...
Introduction to Splanchnology
... Internal organs of human body Internal organs – viscera (splanchna): organs of the digestive, respiratory and urogenital systems located primarily in the thoracic and abdominal cavities functions – organs of vegetative state (vegetative organs) metabolism reproduction ...
... Internal organs of human body Internal organs – viscera (splanchna): organs of the digestive, respiratory and urogenital systems located primarily in the thoracic and abdominal cavities functions – organs of vegetative state (vegetative organs) metabolism reproduction ...
Body cavities and abdominal regions
... Body Cavities Are openings within the torso which contain organs, protect delicate organs from accidental shocks and bumps, and permit the expansion and contraction of organs without disrupting the activities of other organs. ...
... Body Cavities Are openings within the torso which contain organs, protect delicate organs from accidental shocks and bumps, and permit the expansion and contraction of organs without disrupting the activities of other organs. ...
Formation of body wall
... • With expansion of the lungs, mesoderm of the body wall splits into 2 components: (a) the definitive wall of the thorax and (b) the Pleuro-pericardial membranes, which are extensions of the pleuropericardial folds that contain the common cardinal veins and phrenic nerves . • Descent of the heart a ...
... • With expansion of the lungs, mesoderm of the body wall splits into 2 components: (a) the definitive wall of the thorax and (b) the Pleuro-pericardial membranes, which are extensions of the pleuropericardial folds that contain the common cardinal veins and phrenic nerves . • Descent of the heart a ...
Ch 28 Outline
... The exoskeleton will crack when the arthropod’s body becomes too large The arthropods have a special internal appendage that can break open the endoskeleton from the inside. The epidermal layer digests the inner exoskeleton layer to re-cycle the chitin The arthropod must find a sharp object to scrat ...
... The exoskeleton will crack when the arthropod’s body becomes too large The arthropods have a special internal appendage that can break open the endoskeleton from the inside. The epidermal layer digests the inner exoskeleton layer to re-cycle the chitin The arthropod must find a sharp object to scrat ...
Gi tract embryology 1
... • The posterior part, or root, of the tongue originates from the second, third, and part of the fourth pharyngeal arch. • The fact that sensory innervation to this part of the tongue is supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve indicates that tissue of the third arch overgrows that of the second. • Th ...
... • The posterior part, or root, of the tongue originates from the second, third, and part of the fourth pharyngeal arch. • The fact that sensory innervation to this part of the tongue is supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve indicates that tissue of the third arch overgrows that of the second. • Th ...
Mollusca - Net Start Class
... the body of the mollusk the space between the mantle and the actual body is called the mantle cavity This cavity in some mollusks acts as a lung In other mollusks, it contains gills that capture the oxygen from the water when the water passes through the cavity ...
... the body of the mollusk the space between the mantle and the actual body is called the mantle cavity This cavity in some mollusks acts as a lung In other mollusks, it contains gills that capture the oxygen from the water when the water passes through the cavity ...
tissues
... Epithelium a) Location: 2 types of epithelium: 1. covering the surfaces of the body, internal and external ...
... Epithelium a) Location: 2 types of epithelium: 1. covering the surfaces of the body, internal and external ...
Name: Date: Subject: Evidence for Evolution Objectives Objective 1
... Farmers and breeders have been using the idea of selection to cause major changes in the features of their plants and animals for centuries. Farmers and breeders allowed only the plants and animals with desirable traits to reproduce, causing the evolution of the animals and plants that they breed. T ...
... Farmers and breeders have been using the idea of selection to cause major changes in the features of their plants and animals for centuries. Farmers and breeders allowed only the plants and animals with desirable traits to reproduce, causing the evolution of the animals and plants that they breed. T ...
BIO 102: GENERAL BIOLOGY II UNIT: 4
... They have the polyp and medusa forms in their life cycle The polyp is the predominant stage while the medusa is the simple stage They reproduce by alternation of asexual and sexual phases of life cycles e.g Hydra, Obelia, Physalia (Portuguese man-of-war) ...
... They have the polyp and medusa forms in their life cycle The polyp is the predominant stage while the medusa is the simple stage They reproduce by alternation of asexual and sexual phases of life cycles e.g Hydra, Obelia, Physalia (Portuguese man-of-war) ...
Document
... • Amphioxus is especial1y interesting, for it has the four distinctive characteristics of chordates in simple form, and in other ways it may be considered a blueprint of the phylum. It has a 1ong, slender, laterally compressed body 2 to 3 inches long, with both ends pointed. There is a long dorsa ...
... • Amphioxus is especial1y interesting, for it has the four distinctive characteristics of chordates in simple form, and in other ways it may be considered a blueprint of the phylum. It has a 1ong, slender, laterally compressed body 2 to 3 inches long, with both ends pointed. There is a long dorsa ...
LECTURE 17 Arthropods I Phylum Arthropoda (arthros – jointed
... 6. As the arthropods evolved, the trend was for the fusion of segments, so that they became fewer in number, and the appendages became more specialized. 7. The basic anatomy of insects. Head, thorax, abdomen. a. The head is the condensation of antennae and an assortment of pairs of mouthparts. b. Ea ...
... 6. As the arthropods evolved, the trend was for the fusion of segments, so that they became fewer in number, and the appendages became more specialized. 7. The basic anatomy of insects. Head, thorax, abdomen. a. The head is the condensation of antennae and an assortment of pairs of mouthparts. b. Ea ...
Lesson 1: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
... thick endometrial lining which is the menstrual flow. This occurs for 3 to 5 days. (2) Days 6-14. This is known as the proliferative phase. A drop in progesterone and estrogen stimulates the release of FSH from the anterior pituitary. FSH stimulates the maturation of an ovum with graafian follicle. ...
... thick endometrial lining which is the menstrual flow. This occurs for 3 to 5 days. (2) Days 6-14. This is known as the proliferative phase. A drop in progesterone and estrogen stimulates the release of FSH from the anterior pituitary. FSH stimulates the maturation of an ovum with graafian follicle. ...
LESSON 5 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION The
... The pharynx is a common area for both air and food or drink. To prevent the passage of food or drink into the larynx and then into the lungs, a cartilage flap covers the opening (or glottis) into the larynx. This flap of cartilage is called the epiglottis. When swallowing food or drink, the epiglott ...
... The pharynx is a common area for both air and food or drink. To prevent the passage of food or drink into the larynx and then into the lungs, a cartilage flap covers the opening (or glottis) into the larynx. This flap of cartilage is called the epiglottis. When swallowing food or drink, the epiglott ...
The sphenoid.
... The sphenoid is one of the 8 bones of the neurocranium (the bones that protect the brain). It is the keystone* bone at the base of the skull. *In architecture, a keystone is the piece at the apex of an arch, locking all the other pieces together and bearing the weight of it all. ...
... The sphenoid is one of the 8 bones of the neurocranium (the bones that protect the brain). It is the keystone* bone at the base of the skull. *In architecture, a keystone is the piece at the apex of an arch, locking all the other pieces together and bearing the weight of it all. ...
The sphenoid.
... The sphenoid is one of the 8 bones of the neurocranium (the bones that protect the brain). It is the keystone* bone at the base of the skull. *In architecture, a keystone is the piece at the apex of an arch, locking all the other pieces together and bearing the weight of it all. ...
... The sphenoid is one of the 8 bones of the neurocranium (the bones that protect the brain). It is the keystone* bone at the base of the skull. *In architecture, a keystone is the piece at the apex of an arch, locking all the other pieces together and bearing the weight of it all. ...
Reptile Notes Parts 1 and 2
... • When a lizard is grasped by the tail, these vertebrae can be broken, and a portion of the tail is lost. • Tail loss, or autotomy, is an adaptation that allows a lizard to escape from a predator’s grasp, or the disconnected piece of tail may distract a predator from the lizard. • The lizard will la ...
... • When a lizard is grasped by the tail, these vertebrae can be broken, and a portion of the tail is lost. • Tail loss, or autotomy, is an adaptation that allows a lizard to escape from a predator’s grasp, or the disconnected piece of tail may distract a predator from the lizard. • The lizard will la ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.























