Body Systems Powerpoint Slideshow
... Body (skeletal muscles) - Biceps – “the beach is THAT way” - Triceps – back of upper arm - Deltoids – shoulder muscle - Gluteus maximus – “Buns of steel” - Hamstrings – back of upper leg - Pectoralis – chest muscle - Abdominals – stomach/core muscles ...
... Body (skeletal muscles) - Biceps – “the beach is THAT way” - Triceps – back of upper arm - Deltoids – shoulder muscle - Gluteus maximus – “Buns of steel” - Hamstrings – back of upper leg - Pectoralis – chest muscle - Abdominals – stomach/core muscles ...
First ANATOMY Quiz
... a- It terminates as the basilica vein b- It begins opposite the outer border of the first rib c- It is lateral to the axillary artery d- It is anterior to pectoralis major muscle e- The cephalic vein is one of its tributaries 3- the largest body cavity is a- The abdominal b- The pelvic c- The diaphr ...
... a- It terminates as the basilica vein b- It begins opposite the outer border of the first rib c- It is lateral to the axillary artery d- It is anterior to pectoralis major muscle e- The cephalic vein is one of its tributaries 3- the largest body cavity is a- The abdominal b- The pelvic c- The diaphr ...
the neurovascular compression due to the third head of biceps
... muscle originated distally from the medial humeral shaft, adjacent to and in common with the brachialis muscle or a dual origin where the medial fibers originated from the short head of biceps brachii muscle and the lateral fibers from the deltoid fascia and the insertion area of this muscle. In ano ...
... muscle originated distally from the medial humeral shaft, adjacent to and in common with the brachialis muscle or a dual origin where the medial fibers originated from the short head of biceps brachii muscle and the lateral fibers from the deltoid fascia and the insertion area of this muscle. In ano ...
File - SCIENCE WITH MISS ALOLABI
... The digestive system: a) Digests food (break down large particulate food particles into molecules that can be absorbed), b) Produces enzymes that help in the digestion process, and c) Absorption: moves molecules from the alimentary canal to the bloodstream. 2. Is the digestive system a multi-organ s ...
... The digestive system: a) Digests food (break down large particulate food particles into molecules that can be absorbed), b) Produces enzymes that help in the digestion process, and c) Absorption: moves molecules from the alimentary canal to the bloodstream. 2. Is the digestive system a multi-organ s ...
Bodyworks Test Review Things to know: Functions of body systems
... ___ 5. This moves food from the mouth into the stomach. ___ 6. This system helps our body absorb nutrients ___ 7. Air passes through these just before it reaches the lungs ___ 8. This system gives the body structure and protects organs ___ 9. This stretchy muscular sac holds food ___ 10. Urine is el ...
... ___ 5. This moves food from the mouth into the stomach. ___ 6. This system helps our body absorb nutrients ___ 7. Air passes through these just before it reaches the lungs ___ 8. This system gives the body structure and protects organs ___ 9. This stretchy muscular sac holds food ___ 10. Urine is el ...
Joint - HCC Learning Web
... Knee, elbow, ankle, interphalangeal joints Movements produced flexion = decreasing the joint angle extension = increasing the angle hyperextension = opening the joint beyond the anatomical position ...
... Knee, elbow, ankle, interphalangeal joints Movements produced flexion = decreasing the joint angle extension = increasing the angle hyperextension = opening the joint beyond the anatomical position ...
ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 1 LECTURE NOTES
... Body Cavities: coelom = a cavity between the outer body wall and the gut, maybe fluid filled. 1) Acoelomate – have no body cavity; flatworms and ribbon worms 2) Psuedocoelomate – false cavity lacking peritoneum; nematodes 3) Eucoelomate – a true coelom lined with peritoneum; humans Metamerism (segm ...
... Body Cavities: coelom = a cavity between the outer body wall and the gut, maybe fluid filled. 1) Acoelomate – have no body cavity; flatworms and ribbon worms 2) Psuedocoelomate – false cavity lacking peritoneum; nematodes 3) Eucoelomate – a true coelom lined with peritoneum; humans Metamerism (segm ...
ANATOMY Part 1 The female pelvis
... symphysis to the sacrum at the back level with S3-4. The pelvic diaphragm attaches to this rim. 3. The inferior opening = from coccyx at back to lower edge of pubic symphysis at front, side to side to the lower edges of the ischia or sit bones. The baby’s journey out is also affected by the shape of ...
... symphysis to the sacrum at the back level with S3-4. The pelvic diaphragm attaches to this rim. 3. The inferior opening = from coccyx at back to lower edge of pubic symphysis at front, side to side to the lower edges of the ischia or sit bones. The baby’s journey out is also affected by the shape of ...
Instructor`s Guide The Human Body: How It Works THE SKELETAL
... The four segments of the appendicular skeleton are reviewed in this section. Clearly labeled animations depict the bones of the pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, and upper and lower limbs. Also covered: flat feet, or “fallen arches.” Chapter 5: Joints and Soft Tissues This section spells out the diffe ...
... The four segments of the appendicular skeleton are reviewed in this section. Clearly labeled animations depict the bones of the pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, and upper and lower limbs. Also covered: flat feet, or “fallen arches.” Chapter 5: Joints and Soft Tissues This section spells out the diffe ...
Human Body Systems
... muscular system (MUS-kyuh-lur SIStuhm) the organ system that allows the body to move; includes the muscles and tendons (16) nerve (NURV) a bundle of nerve cells that carries signals, such as information from the senses, to and from the brain and spinal cord (19) nervous system (NUR-vuhs SIStuhm) the ...
... muscular system (MUS-kyuh-lur SIStuhm) the organ system that allows the body to move; includes the muscles and tendons (16) nerve (NURV) a bundle of nerve cells that carries signals, such as information from the senses, to and from the brain and spinal cord (19) nervous system (NUR-vuhs SIStuhm) the ...
Invertebrates Animal Kingdom Characteristics Body Plans
... Mollusks have 3 parts to body: Visceral mass – contains organs Mantle – tissue around visceral mass (secretes a shell) Foot - locomotion ...
... Mollusks have 3 parts to body: Visceral mass – contains organs Mantle – tissue around visceral mass (secretes a shell) Foot - locomotion ...
Inverterates - Grafton School District
... Mollusks have 3 parts to body: Visceral mass – contains organs Mantle – tissue around visceral mass (secretes a shell) Foot - locomotion ...
... Mollusks have 3 parts to body: Visceral mass – contains organs Mantle – tissue around visceral mass (secretes a shell) Foot - locomotion ...
Study Guide for Lab Practicals in Biol 241
... * types of tarsals - calcaneus, talus, cuboid, navicular, first, second, and third (lateral, intermediate and medial) cuneiform * metatarsals –base (proximal), shaft, head (distal), and know the numbering types and parts of the phalanges - proximal, middle, distal, hallus (hallux) ...
... * types of tarsals - calcaneus, talus, cuboid, navicular, first, second, and third (lateral, intermediate and medial) cuneiform * metatarsals –base (proximal), shaft, head (distal), and know the numbering types and parts of the phalanges - proximal, middle, distal, hallus (hallux) ...
MUSCLES AND TOPOGRAPHY OF THE UPPER AND LOWER LIMBS
... • The canal has three openings — superior, inferior, and anterior. The superior opening of the canal is bounded by the popliteus in the front and by the tendineous arch of the soleus in the back. • The inferior opening resides between the tibialis posterior and soleus, where the latter becomes the A ...
... • The canal has three openings — superior, inferior, and anterior. The superior opening of the canal is bounded by the popliteus in the front and by the tendineous arch of the soleus in the back. • The inferior opening resides between the tibialis posterior and soleus, where the latter becomes the A ...
1 - Hillsborough Community College
... – Divides body vertically into right and left parts – Produces a sagittal section if cut along this plane – Midsagittal (median) plane • Cut was made perfectly on midline ...
... – Divides body vertically into right and left parts – Produces a sagittal section if cut along this plane – Midsagittal (median) plane • Cut was made perfectly on midline ...
Human Anatomy Worksheet II Due
... d. thoroughfare channels, capillaries b. arterioles, venules e. thoroughfare channels, venules c. venules, arterioles 11. The tunica (intima/media/externa) of a blood vessel contains more elastic tissue than the other layers and is thickest in (arteries/veins/capillaries). 12. a. Order the following ...
... d. thoroughfare channels, capillaries b. arterioles, venules e. thoroughfare channels, venules c. venules, arterioles 11. The tunica (intima/media/externa) of a blood vessel contains more elastic tissue than the other layers and is thickest in (arteries/veins/capillaries). 12. a. Order the following ...
Organization of Life Study Guide Skeletal System pg.444
... Mary wrote a science fiction story about another rectum. planet. The animals who lived there were similar to they are passed from the body is the Which organ mixes food with a mild acid and breaks it into a pastelike substance? stomach ...
... Mary wrote a science fiction story about another rectum. planet. The animals who lived there were similar to they are passed from the body is the Which organ mixes food with a mild acid and breaks it into a pastelike substance? stomach ...
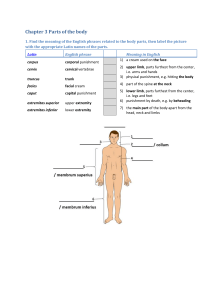
Chapter 3 Parts of the body
... Both in English and in Latin words may change their forms to indicate some change in sense or use, as, who, whose; farmer, farmer’s; woman, women. This is called inflection. The inflection of a noun, adjective, or pronoun is called its declension, that of a verb its conjugation. Nominative or subjec ...
... Both in English and in Latin words may change their forms to indicate some change in sense or use, as, who, whose; farmer, farmer’s; woman, women. This is called inflection. The inflection of a noun, adjective, or pronoun is called its declension, that of a verb its conjugation. Nominative or subjec ...
FACTS
... extension (plantarflexion.) Subtalar joint (ankle joint) -bones: Talus & Calcaneus -triplanar-movement around the oblique axis. -most stable when in dorsiflexion ...
... extension (plantarflexion.) Subtalar joint (ankle joint) -bones: Talus & Calcaneus -triplanar-movement around the oblique axis. -most stable when in dorsiflexion ...
Rotator Cuff
... Two sets of muscles are important for the stabilization of this joint in the proper joint formation. [ help stabilize the clavicle and the scapula] 1) the trapezius: The upper trapezius muscle fibers connects the lower base of the skull to the clavicle. The middle and lower trapezius muscle fibers c ...
... Two sets of muscles are important for the stabilization of this joint in the proper joint formation. [ help stabilize the clavicle and the scapula] 1) the trapezius: The upper trapezius muscle fibers connects the lower base of the skull to the clavicle. The middle and lower trapezius muscle fibers c ...
Anatomy of the Spine and Repro - Part 1 - UQMBBS-2013
... • Permit rotation, some lateral flexion • Spinous processes angle inferiorly and overlap ...
... • Permit rotation, some lateral flexion • Spinous processes angle inferiorly and overlap ...
Chapter 8 - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... Loads on the Hip • During swing phase of walking: – Compression on hip approx. same as body weight (due to muscle tension) • Increases with hard-soled shoes • Increases with gait increases (both support and swing phase) • Body weight, impact forces translated upward thru skeleton from feet and musc ...
... Loads on the Hip • During swing phase of walking: – Compression on hip approx. same as body weight (due to muscle tension) • Increases with hard-soled shoes • Increases with gait increases (both support and swing phase) • Body weight, impact forces translated upward thru skeleton from feet and musc ...
Bony Thorax
... ulna (radius on thumb side) • Carpus or wrist contains 8 small bones arranged in two rows • Manual region or hand contains 19 bones in 2 groups – 5 metacarpals in the palm – 14 phalanges in the fingers ...
... ulna (radius on thumb side) • Carpus or wrist contains 8 small bones arranged in two rows • Manual region or hand contains 19 bones in 2 groups – 5 metacarpals in the palm – 14 phalanges in the fingers ...
Orientation to the Human Body
... face & eyes facing forward Feet flat on floor, slightly apart Arms at sides Palms face forward (forearms in supine position) ...
... face & eyes facing forward Feet flat on floor, slightly apart Arms at sides Palms face forward (forearms in supine position) ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.